31.1 The Neuron Functions of the Nervous System and external
... temperature. It helps coordinate the nervous and endocrine systems. The cerebellum is the second largest region of the brain. It receives infor information mation about muscle and joint position and coordinates the actions of these muscles. The brain stem connects the brain and spinal cord. It regu ...
... temperature. It helps coordinate the nervous and endocrine systems. The cerebellum is the second largest region of the brain. It receives infor information mation about muscle and joint position and coordinates the actions of these muscles. The brain stem connects the brain and spinal cord. It regu ...
Biopsychology Revision
... An action potential occurs when a neuron sends information down an axon, away from the cell body. The action potential is an explosion of electrical activity - this means that some event (a stimulus) causes the resting potential to move forward ...
... An action potential occurs when a neuron sends information down an axon, away from the cell body. The action potential is an explosion of electrical activity - this means that some event (a stimulus) causes the resting potential to move forward ...
Nervous System Test Review
... Cerebrum Controls It regulates all your thoughts and actions. There are many sections of the cerebrum that control what you hear, smell, how you move, how you think, write, talk and express emotions. ...
... Cerebrum Controls It regulates all your thoughts and actions. There are many sections of the cerebrum that control what you hear, smell, how you move, how you think, write, talk and express emotions. ...
MAPPINGS BETWEEN BRAINS - Wichita State University
... specific areas of the retina. • Once the lateral geniculate neurons are triggered, in returning to the visual cortex; if they are hypercomplex cells what ...
... specific areas of the retina. • Once the lateral geniculate neurons are triggered, in returning to the visual cortex; if they are hypercomplex cells what ...
Nervous System
... alpha waves (8-13 cycles per second) are produced when a person is a wake but resting, with eyes closed. beta waves (13 cps ) are produced when a person is actively engaged in mental activity. Theta waves (4-7 cps ) are normally produced by children; in adults, these may be related to early st ...
... alpha waves (8-13 cycles per second) are produced when a person is a wake but resting, with eyes closed. beta waves (13 cps ) are produced when a person is actively engaged in mental activity. Theta waves (4-7 cps ) are normally produced by children; in adults, these may be related to early st ...
Neurons
... • Nerves Collections of neurons that are joined together by connective tissue. • Responsible for transferring impulses from receptors to CNS and back to effectors. ...
... • Nerves Collections of neurons that are joined together by connective tissue. • Responsible for transferring impulses from receptors to CNS and back to effectors. ...
C48 Nervous System
... Myelin sheath – insulating layer of many axons Synaptic terminals – specialized endings of the axons which relay signals to other cells by releasing neurotransmitters (chemical messengers). Synapse – junction between neurons or to a muscle or gland cell. Membrane potential – voltage measured a ...
... Myelin sheath – insulating layer of many axons Synaptic terminals – specialized endings of the axons which relay signals to other cells by releasing neurotransmitters (chemical messengers). Synapse – junction between neurons or to a muscle or gland cell. Membrane potential – voltage measured a ...
The role of the nervous system in detecting and
... The role of the nervous system in detecting and responding to stimuli Detecting and responding in animals A complex animal may need to respond immediately to a stimulus. In many situations, it is important that a change is detected instantly and appropriate signals sent quickly to relevant parts of ...
... The role of the nervous system in detecting and responding to stimuli Detecting and responding in animals A complex animal may need to respond immediately to a stimulus. In many situations, it is important that a change is detected instantly and appropriate signals sent quickly to relevant parts of ...
Shape of Thought
... the brute power and fragile equilibrium of potassium, sodium, magnesium, and other salts essential to the brain's electricity. Without water, they cant dissolve, and it doesnt take much to disturb them a water loss of only zbout 2 percent will do. Brain cells communicate by sort of shaking hands at ...
... the brute power and fragile equilibrium of potassium, sodium, magnesium, and other salts essential to the brain's electricity. Without water, they cant dissolve, and it doesnt take much to disturb them a water loss of only zbout 2 percent will do. Brain cells communicate by sort of shaking hands at ...
The Nervous System - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... • Reflexes are automatic, involuntary responses to changes occurring inside or outside the body. Can involve the brain (e.g. blinking) or not involve brain (e.g. withdraw hand from hot stove). • The Reflex arc is the main functional unit of the nervous system. It allows us to react to internal and ...
... • Reflexes are automatic, involuntary responses to changes occurring inside or outside the body. Can involve the brain (e.g. blinking) or not involve brain (e.g. withdraw hand from hot stove). • The Reflex arc is the main functional unit of the nervous system. It allows us to react to internal and ...
Chapter 2
... neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron – tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap or cleft • Neurotransmitters – chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons – Excite or inhibit – Lock and key – Reuptake ...
... neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron – tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap or cleft • Neurotransmitters – chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons – Excite or inhibit – Lock and key – Reuptake ...
File
... • Myelinated cat fiber = carry impulses up to 100 m/s • Unmyelinated cat fiber = carry impulses only 5 m/s ...
... • Myelinated cat fiber = carry impulses up to 100 m/s • Unmyelinated cat fiber = carry impulses only 5 m/s ...
Excitatory_Inhibitory_Neural_Network_1
... Excitatory-Inhibitory Neural Network 1 From: Theoretical Neuroscience, by Peter Dayan and Larry Abbott, MIT Press, 2005 pp. 266-269 The system studied here is one the simplest types of neural networks to exhibit oscillatory activity. It can be regarded as a simplified model of a fully-connected netw ...
... Excitatory-Inhibitory Neural Network 1 From: Theoretical Neuroscience, by Peter Dayan and Larry Abbott, MIT Press, 2005 pp. 266-269 The system studied here is one the simplest types of neural networks to exhibit oscillatory activity. It can be regarded as a simplified model of a fully-connected netw ...
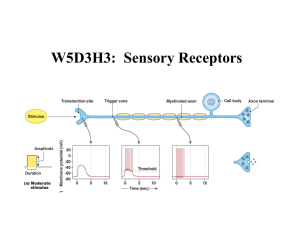
W5D3H3: Sensory Receptors
... • Understanding how external signals are detected and encoded by the nervous system is essential to a bigpicture understanding of how stimuli are detected and interpreted by the nervous system. Because defects in this process constrain the well-being and quality of life for many people and because c ...
... • Understanding how external signals are detected and encoded by the nervous system is essential to a bigpicture understanding of how stimuli are detected and interpreted by the nervous system. Because defects in this process constrain the well-being and quality of life for many people and because c ...
3.13
... along the axon. Increasing the intensity of the electrical shock further does not change the response. This impulse is thus an all-or-none response. A.L. Hodgkin and A.F. Huxley studied the giant axon of a squid experimentally, ...
... along the axon. Increasing the intensity of the electrical shock further does not change the response. This impulse is thus an all-or-none response. A.L. Hodgkin and A.F. Huxley studied the giant axon of a squid experimentally, ...
Time constants
... in what relative proportions. It turns out that each population of neurons has multiple types of receptor; in other words, most neurons have both NMDA and non-NMDA glutamate receptors, as well as GABAA and GABAB receptors. Quantitative estimates of receptor distribution are usually studied through t ...
... in what relative proportions. It turns out that each population of neurons has multiple types of receptor; in other words, most neurons have both NMDA and non-NMDA glutamate receptors, as well as GABAA and GABAB receptors. Quantitative estimates of receptor distribution are usually studied through t ...
Neurons Excitatory vs Inhibitory Neurons The Neuron and its Ions
... relationships between patterns of activity in a network • Cluster plots are constructed based on the distances between patterns of activity • Euclidean distance = sum (across all units) of the squared difference in activation ...
... relationships between patterns of activity in a network • Cluster plots are constructed based on the distances between patterns of activity • Euclidean distance = sum (across all units) of the squared difference in activation ...
Module_3vs9_Final - Doral Academy Preparatory
... – Skin has sensors that pick up mechanical pressure and transform it into electrical signals – Signals are sent by the neuron’s axon to various areas in the spinal cord and brain – Brain interprets electrical signals as “pain” • axon membrane has chemical gates that can open to allow electrically ch ...
... – Skin has sensors that pick up mechanical pressure and transform it into electrical signals – Signals are sent by the neuron’s axon to various areas in the spinal cord and brain – Brain interprets electrical signals as “pain” • axon membrane has chemical gates that can open to allow electrically ch ...
True or False Questions - Sinoe Medical Association
... b. Neurotransmitter is released from the synaptic terminal by exocytosis, when synaptic vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane of the terminal. c. An inhibitory neurotransmitter produces inhibition of a postsynaptic neuron by preventing excitatory neurotransmitters from binding to their receptors at ...
... b. Neurotransmitter is released from the synaptic terminal by exocytosis, when synaptic vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane of the terminal. c. An inhibitory neurotransmitter produces inhibition of a postsynaptic neuron by preventing excitatory neurotransmitters from binding to their receptors at ...
Laboratory Exercise 12: Sensory Physiology
... Receptors are not uniformly distributed on the body surface. Some areas of skin have a higher density of receptors than others and are more sensitive to a particular stimulus. For example, the fingers have a relatively high density of touch receptors and have great sensitivity, compared to the back. ...
... Receptors are not uniformly distributed on the body surface. Some areas of skin have a higher density of receptors than others and are more sensitive to a particular stimulus. For example, the fingers have a relatively high density of touch receptors and have great sensitivity, compared to the back. ...
File
... BellaSano Neurotransmitters are the chemicals which allow the transmission of signals from one neuron to the next across synapses. They and their close relatives are produced by glands such as the pituitary and the adrenal glands. ...
... BellaSano Neurotransmitters are the chemicals which allow the transmission of signals from one neuron to the next across synapses. They and their close relatives are produced by glands such as the pituitary and the adrenal glands. ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.