Systems Neuroscience - College of William and Mary
... and continues without lapse for the entire lifespan of the animal, which in humans can last up to, or exceed, 100 years. Diseases that affect the neural control of breathing can strike at any age, but newborns and premature babies are particularly susceptible to various forms of apnea and SIDS. We a ...
... and continues without lapse for the entire lifespan of the animal, which in humans can last up to, or exceed, 100 years. Diseases that affect the neural control of breathing can strike at any age, but newborns and premature babies are particularly susceptible to various forms of apnea and SIDS. We a ...
Rat LIFR Protein (His Tag)
... CNTF (ciliary neurotrophic factor) and CLC (cardiotrophin like cytokine). Evidence showed that in the retina, LIFR activating LIF, CT-1 and cardiotrophin like cytokine (CLC) are strongly upregulated in response to preconditioning with bright cyclic light leading to robust activation of signal transd ...
... CNTF (ciliary neurotrophic factor) and CLC (cardiotrophin like cytokine). Evidence showed that in the retina, LIFR activating LIF, CT-1 and cardiotrophin like cytokine (CLC) are strongly upregulated in response to preconditioning with bright cyclic light leading to robust activation of signal transd ...
The Nervous System
... ▫ Cerebral cortex: outer layer of gray matter; short and long term memory Convolutions: elevated ridges/folds that increases gray area of brain ...
... ▫ Cerebral cortex: outer layer of gray matter; short and long term memory Convolutions: elevated ridges/folds that increases gray area of brain ...
Figure 8.12
... ◦ Allows for light to pass through ◦ Repairs itself easily ◦ The only human tissue that can be transplanted without fear of rejection ...
... ◦ Allows for light to pass through ◦ Repairs itself easily ◦ The only human tissue that can be transplanted without fear of rejection ...
Structure of the Nervous System
... •Neurons link together to form neural circuits which perform special tasks. Many of these are reflexes. •Signaling within these circuits gives rise to higher cognitive functions, such as thinking. •Since circuits are needed for even the most basic function, it has been suggested that the functional ...
... •Neurons link together to form neural circuits which perform special tasks. Many of these are reflexes. •Signaling within these circuits gives rise to higher cognitive functions, such as thinking. •Since circuits are needed for even the most basic function, it has been suggested that the functional ...
The Nervous System allows communication
... o A. Parkinson’s disease – muscles function is impaired as a result of destruction fo nerve cells in the brain o B. multiple sclerosis – is an autoimmune disease in which the body attacks tits own tissues, destroying the myelin sheath o C. Alzheimers disease – gradual mental deterioration when neuro ...
... o A. Parkinson’s disease – muscles function is impaired as a result of destruction fo nerve cells in the brain o B. multiple sclerosis – is an autoimmune disease in which the body attacks tits own tissues, destroying the myelin sheath o C. Alzheimers disease – gradual mental deterioration when neuro ...
(5 points).
... b) Give the name of a cortical brain region or tract to the following properties and motor functions. (8 points) a) The most important executive motor pathway: b) A so-called homunculus can be derived from its receptive field: c) It is responsible for the integration of emotion induced motions: d) M ...
... b) Give the name of a cortical brain region or tract to the following properties and motor functions. (8 points) a) The most important executive motor pathway: b) A so-called homunculus can be derived from its receptive field: c) It is responsible for the integration of emotion induced motions: d) M ...
The Nervous System
... A response in determined by interneurons. 4. Motor neurons transmit a response message to the shoulder muscles. 5. The shoulder muscles are activated, causing the head to turn. ...
... A response in determined by interneurons. 4. Motor neurons transmit a response message to the shoulder muscles. 5. The shoulder muscles are activated, causing the head to turn. ...
Theramine™ for the Management of Pain Syndromes
... empty stomach at least 30 minutes before or after eating Take two (2) capsules every four hours or as needed under medical supervision Theramine™ can be taken with prescription medications under medical supervision ...
... empty stomach at least 30 minutes before or after eating Take two (2) capsules every four hours or as needed under medical supervision Theramine™ can be taken with prescription medications under medical supervision ...
The Nervous System
... A response in determined by interneurons. 4. Motor neurons transmit a response message to the shoulder muscles. 5. The shoulder muscles are activated, causing the head to turn. ...
... A response in determined by interneurons. 4. Motor neurons transmit a response message to the shoulder muscles. 5. The shoulder muscles are activated, causing the head to turn. ...
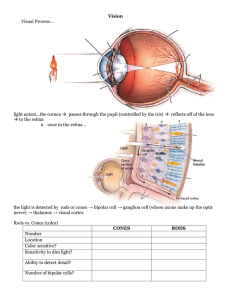
Vision Lecture Notes
... ● Frequency theory: the basilar membrane vibrates at the same rate as incoming sound waves, triggering neural impulses at the same rate ● explains low-pitched sounds ● Place theory: different frequencies cause vibrations at different locations (hair cells) along the basilar membrane, triggering the ...
... ● Frequency theory: the basilar membrane vibrates at the same rate as incoming sound waves, triggering neural impulses at the same rate ● explains low-pitched sounds ● Place theory: different frequencies cause vibrations at different locations (hair cells) along the basilar membrane, triggering the ...
Mader/Biology, 11/e – Chapter Outline
... d. The neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across the synaptic cleft to the postsynaptic membrane where they bind with specific receptors. e. The type of neurotransmitter and/or receptor determines if the response is excitation or inhibition. f. Excitatory neurotransmitters use gated ion channels and ...
... d. The neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across the synaptic cleft to the postsynaptic membrane where they bind with specific receptors. e. The type of neurotransmitter and/or receptor determines if the response is excitation or inhibition. f. Excitatory neurotransmitters use gated ion channels and ...
Neuromuscular Transmission - Dr. Logothetis
... induce rapid changes, within a few milliseconds, in the permeability and potential of the postsynaptic membrane. In contrast, the postsynaptic responses triggered by activation of G protein-coupled receptors occur much more slowly, over seconds or minutes, because these receptors regulate opening an ...
... induce rapid changes, within a few milliseconds, in the permeability and potential of the postsynaptic membrane. In contrast, the postsynaptic responses triggered by activation of G protein-coupled receptors occur much more slowly, over seconds or minutes, because these receptors regulate opening an ...
Bi150 Problem Set 4 Due: Tuesday, November 18th 2014 at 4:30
... shown below, three simple cells (of different receptive fields) form synapses onto a complex cell at different locations on one long dendrite. This complex cell is more sensitive to a light bar moving from the receptive field of simple cell 123 but not a light bar moving in the opposite direction. ...
... shown below, three simple cells (of different receptive fields) form synapses onto a complex cell at different locations on one long dendrite. This complex cell is more sensitive to a light bar moving from the receptive field of simple cell 123 but not a light bar moving in the opposite direction. ...
NeuroReview3
... biochemical and structural changes of varying duration each of which may contribute to neuronal death or repair and regeneration • One therapeutic approach involves administering compounds to protect neural tissue from cytotoxic and excitotoxic effects of the injury cascade ...
... biochemical and structural changes of varying duration each of which may contribute to neuronal death or repair and regeneration • One therapeutic approach involves administering compounds to protect neural tissue from cytotoxic and excitotoxic effects of the injury cascade ...
Nervous System - cloudfront.net
... Part of the Autonomic system that is responsible for “Fight or Flight” Works by increasing heart rate and blood pressure, and slows down unnecessary systems Often animals will soil themselves when fighting or ...
... Part of the Autonomic system that is responsible for “Fight or Flight” Works by increasing heart rate and blood pressure, and slows down unnecessary systems Often animals will soil themselves when fighting or ...
document
... I) NERVOUS SYSTEM = Master control and communication system of the body. This system works with the ENDOCRINE system to maintain and regulate body HOMEOSTASIS (balance). NERVOUS SYSTEM – Fast action, uses electrical impulses. Changes by this system tend to be fast but temporary. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM – ...
... I) NERVOUS SYSTEM = Master control and communication system of the body. This system works with the ENDOCRINE system to maintain and regulate body HOMEOSTASIS (balance). NERVOUS SYSTEM – Fast action, uses electrical impulses. Changes by this system tend to be fast but temporary. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM – ...
Nervous System
... What is Parkinson disease? Parkinson disease is a brain disorder. It occurs when certain nerve cells (neurons) in a part of the brain called the substantia nigra die or become impaired. Normally, these cells produce a vital chemical known as dopamine. Dopamine allows smooth, coordinated function of ...
... What is Parkinson disease? Parkinson disease is a brain disorder. It occurs when certain nerve cells (neurons) in a part of the brain called the substantia nigra die or become impaired. Normally, these cells produce a vital chemical known as dopamine. Dopamine allows smooth, coordinated function of ...
Ch 2 Physiology - Texas A&M University
... schematically shown as a1 a2 a3 a4 The firing rate of neuron B is determined by the activation sent by neurons a1-a4. B ...
... schematically shown as a1 a2 a3 a4 The firing rate of neuron B is determined by the activation sent by neurons a1-a4. B ...
Chapter 15 - Marion ISD
... Sensations Sensory adaptation - receptor potential decreases over time in response to a continuous stimulus ...
... Sensations Sensory adaptation - receptor potential decreases over time in response to a continuous stimulus ...
Aim of Research
... membrane to release neurotransmitters as well as endocytosis and recycling of the vesicles. Whereas the essential proteins governing the SV cycle have been identified in the last decades, we still have only little knowledge about their exact operation and sequence in which they interact to carry ou ...
... membrane to release neurotransmitters as well as endocytosis and recycling of the vesicles. Whereas the essential proteins governing the SV cycle have been identified in the last decades, we still have only little knowledge about their exact operation and sequence in which they interact to carry ou ...
Cell Communication
... distances to target cells of another type – Endocrine signals (hormones) are produced by endocrine cells that release signaling molecules, which are specific and can travel long distances through the blood to reach all parts of the body – Examples: ...
... distances to target cells of another type – Endocrine signals (hormones) are produced by endocrine cells that release signaling molecules, which are specific and can travel long distances through the blood to reach all parts of the body – Examples: ...
Immune System Barriers Skin Outer surface is dry and oily, most
... Recognition: diversity of antibodies arises from gene shuffling and mutation of antibody genes during immune cell development, each antibody has specific sites that bind one or a few types of antigen, normally on foreign antigens are recognized by immune cells Attack: B cells divide rapidly, produci ...
... Recognition: diversity of antibodies arises from gene shuffling and mutation of antibody genes during immune cell development, each antibody has specific sites that bind one or a few types of antigen, normally on foreign antigens are recognized by immune cells Attack: B cells divide rapidly, produci ...
Active transport - CHS Science Department Mrs. Davis
... – Exocytosis is a process of releasing large amounts of materials from the cell. ...
... – Exocytosis is a process of releasing large amounts of materials from the cell. ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.