Rexed`s Lamina
... second order neuron occurs in spinal cord Third order neurons arise in thalamus and continue to cerebral cortex ...
... second order neuron occurs in spinal cord Third order neurons arise in thalamus and continue to cerebral cortex ...
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS
... A: Receptive fields. Size and locations of the receptive fields of 15 sensory units, determined by recording from the median nerve. All of these sensory units were rapidly adapting and were most likely conducting from Meissner-corpuscles. Within each receptive fields there are many Meissner corpuscl ...
... A: Receptive fields. Size and locations of the receptive fields of 15 sensory units, determined by recording from the median nerve. All of these sensory units were rapidly adapting and were most likely conducting from Meissner-corpuscles. Within each receptive fields there are many Meissner corpuscl ...
Nervous Systems II PPT
... allows the giant squid to have near simultaneous contraction of its mantel, ...
... allows the giant squid to have near simultaneous contraction of its mantel, ...
NEURAL CONTROL AND COORDINATION
... Neurons or the nerve cell is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. The nervous system of human is made up of innumerable neurons. The total no. of estimated neurons in the human brain is more than 100 billion. These are linked together in a highly intricate manner. It is through ...
... Neurons or the nerve cell is the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. The nervous system of human is made up of innumerable neurons. The total no. of estimated neurons in the human brain is more than 100 billion. These are linked together in a highly intricate manner. It is through ...
Nervous Tissue
... bundles of unmyelinated axons and neuroglia (gray color) – In the spinal cord = gray matter forms an H-shaped inner core surrounded by white matter – In the brain = a thin outer shell of gray matter covers the surface & is found in clusters called nuclei inside the CNS ...
... bundles of unmyelinated axons and neuroglia (gray color) – In the spinal cord = gray matter forms an H-shaped inner core surrounded by white matter – In the brain = a thin outer shell of gray matter covers the surface & is found in clusters called nuclei inside the CNS ...
Motor Units and Motor Neuron Disease
... As mentioned in the pathophysiology section, there are a wide variety of triggers implicated in the motor neurone degeneration seen in ALS. The main two implicated currently implicated in ALS are: Oxidative damage – as a result of a mutant SOD1, superoxide radicals accumulate hence cause damage. Thi ...
... As mentioned in the pathophysiology section, there are a wide variety of triggers implicated in the motor neurone degeneration seen in ALS. The main two implicated currently implicated in ALS are: Oxidative damage – as a result of a mutant SOD1, superoxide radicals accumulate hence cause damage. Thi ...
Biology and Behavior
... Communication between Neurons (chemical) • Axon terminals release neurotransmitter • Neurotransmitter enters synaptic gap • Neurotransmitter binds to receptor site that it fits • Reuptake: surplus neurotransmitter reabsorbed by sending neuron ...
... Communication between Neurons (chemical) • Axon terminals release neurotransmitter • Neurotransmitter enters synaptic gap • Neurotransmitter binds to receptor site that it fits • Reuptake: surplus neurotransmitter reabsorbed by sending neuron ...
Chapters 11: Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous
... 1. AP in presynaptic neuron triggers ________ion channels in axon terminal to open 2. ____________ of calcium ions causes synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft 3. Neurotransmitters bind to ____________ on postsynaptic neuron 4. Ion channels open, leading to a local potent ...
... 1. AP in presynaptic neuron triggers ________ion channels in axon terminal to open 2. ____________ of calcium ions causes synaptic vesicles to release neurotransmitter into synaptic cleft 3. Neurotransmitters bind to ____________ on postsynaptic neuron 4. Ion channels open, leading to a local potent ...
Module 2.1 Neurons: The Body`s Wiring Lecture Outline
... Neurons don’t actually touch; they are separated by a synapse The neural impulse reaches the axon’s terminal buttons and triggers the release of chemicals that either increase or decrease the likelihood that neighboring cells will fire (Figure 2.3) Neurotransmitters are either excitatory, making an ...
... Neurons don’t actually touch; they are separated by a synapse The neural impulse reaches the axon’s terminal buttons and triggers the release of chemicals that either increase or decrease the likelihood that neighboring cells will fire (Figure 2.3) Neurotransmitters are either excitatory, making an ...
Note 11.1 - The Nervous System
... The projections from the cell’s body are responsible for conducting electrochemical signals. Ions and concentration gradients are responsible for producing the electrochemical signals. A dendrite is highly branched projections from the cell’s body that receives the signals and transmits them to the ...
... The projections from the cell’s body are responsible for conducting electrochemical signals. Ions and concentration gradients are responsible for producing the electrochemical signals. A dendrite is highly branched projections from the cell’s body that receives the signals and transmits them to the ...
Managing people in sport organisations: A strategic
... Hypothalamic thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) stimulates pituitary thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) secretion. TSH binds to TSH receptors (TSHR) in the thyroid gland (target organ) to trigger thyroid hormone (T3 and T4) secretion. Thyroid hormones are released into bloodstream and elicit their p ...
... Hypothalamic thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) stimulates pituitary thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) secretion. TSH binds to TSH receptors (TSHR) in the thyroid gland (target organ) to trigger thyroid hormone (T3 and T4) secretion. Thyroid hormones are released into bloodstream and elicit their p ...
UNIVERSITY OF MALTA
... oscillations (Crunelli et al., 2005). In particular, the transient opening of T-type Ca2+ channels gives rise to low threshold Ca2+ potentials and associated high frequency bursts of action potentials that are present during sleep spindles and delta wave. In addition, the window component of the T-t ...
... oscillations (Crunelli et al., 2005). In particular, the transient opening of T-type Ca2+ channels gives rise to low threshold Ca2+ potentials and associated high frequency bursts of action potentials that are present during sleep spindles and delta wave. In addition, the window component of the T-t ...
Introduction to neural computation
... Modularity and the brain • Different bits of the cortex do different things. – Local damage to the brain has specific effects – Specific tasks increase the blood flow to specific regions. • But cortex looks pretty much the same all over. – Early brain damage makes functions relocate • Cortex is mad ...
... Modularity and the brain • Different bits of the cortex do different things. – Local damage to the brain has specific effects – Specific tasks increase the blood flow to specific regions. • But cortex looks pretty much the same all over. – Early brain damage makes functions relocate • Cortex is mad ...
Do Now 03/03-04 - Ed White Anatomy and Physiology
... potentials further along the neuron creating a wave of action potentials from the dendrite to the axon (nerve impulse). 6. Na/K pump restores balance of ions. ...
... potentials further along the neuron creating a wave of action potentials from the dendrite to the axon (nerve impulse). 6. Na/K pump restores balance of ions. ...
primary motor Cortex
... of the stimulus, no new action potentials can be generated. The approximately 2-msec length of this period limits the number of action potentials that neurons can generate to up to 500 per second. The voltage-gated K+ channel has only one gate, which is typically closed at the resting membrane pote ...
... of the stimulus, no new action potentials can be generated. The approximately 2-msec length of this period limits the number of action potentials that neurons can generate to up to 500 per second. The voltage-gated K+ channel has only one gate, which is typically closed at the resting membrane pote ...
Nervous
... -The process by which organisms maintain, control, and coordinate their internal environment with a constantly changing external environment -It is all of the activities that help to maintain an organism’s ...
... -The process by which organisms maintain, control, and coordinate their internal environment with a constantly changing external environment -It is all of the activities that help to maintain an organism’s ...
Somatic sensations
... a. For any reason; it's not any different than other forms of identification. b. In place of or to enhance government identification, such as a driver's license or passport. c. For employment at any company that chooses to require it. d. It should never be required, it should only be used as a volun ...
... a. For any reason; it's not any different than other forms of identification. b. In place of or to enhance government identification, such as a driver's license or passport. c. For employment at any company that chooses to require it. d. It should never be required, it should only be used as a volun ...
Notes Chapter 50 Nervous and Sensory Systems
... electrical cord and speeds up transmission of action potentials through the axon. (2) In the peripheral nervous system, myelin is produced by cells called Schwann cells, which surround the axon. (3) Gaps in the myelin sheath along the length of the axon are known as the nodes of Ranvier. d) Neurons ...
... electrical cord and speeds up transmission of action potentials through the axon. (2) In the peripheral nervous system, myelin is produced by cells called Schwann cells, which surround the axon. (3) Gaps in the myelin sheath along the length of the axon are known as the nodes of Ranvier. d) Neurons ...
The Neuroscience of Psychiatry
... • Monoamine neurotransmitters comprise only a small percentage of neurons (vs. amino acid neurotransmitters), but: • Monoamines may regulate the balance of: – the excitatory actions of glutamate and the inhibitory actions of GABA ...
... • Monoamine neurotransmitters comprise only a small percentage of neurons (vs. amino acid neurotransmitters), but: • Monoamines may regulate the balance of: – the excitatory actions of glutamate and the inhibitory actions of GABA ...
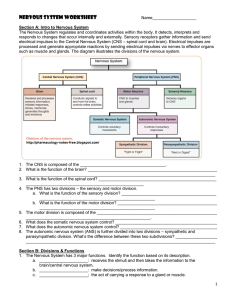
Nervous System Worksheet - Jackson County Faculty Sites!
... ‘high alert’. It’s important in forming memories. (Exercise increases the release of norepinephrine and stress decreases it.) Glutamate – an excitatory neurotransmitter which plays a role in memory. (Excessive amounts of glutamate due to a stroke or brain damage will kill neurons. ALS results from ...
... ‘high alert’. It’s important in forming memories. (Exercise increases the release of norepinephrine and stress decreases it.) Glutamate – an excitatory neurotransmitter which plays a role in memory. (Excessive amounts of glutamate due to a stroke or brain damage will kill neurons. ALS results from ...
Slide 1
... The axon of one neuron doesn't touch the dendrites of the next. Nerve signals have to jump across a tiny gap (synaptic cleft). To get across the gap they have to change from electrical signals into chemical signals (neurotransmitters) then back into electrical signals. ...
... The axon of one neuron doesn't touch the dendrites of the next. Nerve signals have to jump across a tiny gap (synaptic cleft). To get across the gap they have to change from electrical signals into chemical signals (neurotransmitters) then back into electrical signals. ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.