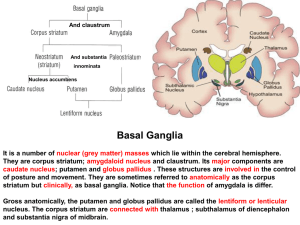
21. Basal ganglion
... This leads to disinhibition of the lateral pallidal neurons and inhibition of subthalamic nucleus. Medial pallidal neurons , therefore ,become abnormally underactive and unwanted; involuntary movements.The following signs is present: 1- Choreiform movements first appear as involuntary movements of t ...
... This leads to disinhibition of the lateral pallidal neurons and inhibition of subthalamic nucleus. Medial pallidal neurons , therefore ,become abnormally underactive and unwanted; involuntary movements.The following signs is present: 1- Choreiform movements first appear as involuntary movements of t ...
Ch 8 (Student MCQs etc)
... and blue–yellow opponent channels. d) There is also a group of large retinal cells alongside the smaller colouropponent cells that respond to the difference between the luminances in their centre and surrounding regions. The rods and cones in the retina function in dim and bright light, respectively ...
... and blue–yellow opponent channels. d) There is also a group of large retinal cells alongside the smaller colouropponent cells that respond to the difference between the luminances in their centre and surrounding regions. The rods and cones in the retina function in dim and bright light, respectively ...
The Brain and Behavior:
... System (CNS) • Composed of the brain and spinal cord. • Spinal cord is the primary means for transmitting messages between the brain and the rest of the body. © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. ...
... System (CNS) • Composed of the brain and spinal cord. • Spinal cord is the primary means for transmitting messages between the brain and the rest of the body. © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. ...
a few sensory concepts, 100416
... Generator potentials are produced by dendrites of free nerve endings, encapsulated nerve endings, and olfactory receptors (that is, first-order neurons). ...
... Generator potentials are produced by dendrites of free nerve endings, encapsulated nerve endings, and olfactory receptors (that is, first-order neurons). ...
ii. neuro-embryology
... Making Neuronal Connections: o Sometimes a neuron will reel out its axon as it grows. o At other times, a neuron will use physical or chemical (chemotaxis) cues to grow toward a target. Synaptic Plasticity: Modifications to neuronal connections made after development is complete. o They can be m ...
... Making Neuronal Connections: o Sometimes a neuron will reel out its axon as it grows. o At other times, a neuron will use physical or chemical (chemotaxis) cues to grow toward a target. Synaptic Plasticity: Modifications to neuronal connections made after development is complete. o They can be m ...
Character Recognition using Spiking Neural Networks
... spikes. Spiking neural networks belong to the third generation of neural networks and like their biological counterparts use spikes to represent information flow. They can use spatiotemporal information in communication and computation similar to biological neurons. As they use pulse coding for info ...
... spikes. Spiking neural networks belong to the third generation of neural networks and like their biological counterparts use spikes to represent information flow. They can use spatiotemporal information in communication and computation similar to biological neurons. As they use pulse coding for info ...
Introduction to Psychology - Shoreline School District
... Autonomic Nervous System the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart) ...
... Autonomic Nervous System the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart) ...
Seeds of Dementia
... contagious like mad cow or, for that matter, the flu. Rather the significance of these recent findings is that they provide scientists with a prime suspect for a slew of devastating brain disorders—a signpost that points toward a pathway for eventual treatments. Drugs developed for Alzheimer’s might ...
... contagious like mad cow or, for that matter, the flu. Rather the significance of these recent findings is that they provide scientists with a prime suspect for a slew of devastating brain disorders—a signpost that points toward a pathway for eventual treatments. Drugs developed for Alzheimer’s might ...
Brain and Nervous System Overview
... ~300 vesicles per action potential containing chemical transmitter (excitatory or inhibitory) (i.e. ACH acetylcholine or GABA) Each vesicle contains ~10,000 ACH and are passed to postsynaptic site through exocytosis in < 100 microsec. Transmitter causes change in post-synaptic membrane permeability ...
... ~300 vesicles per action potential containing chemical transmitter (excitatory or inhibitory) (i.e. ACH acetylcholine or GABA) Each vesicle contains ~10,000 ACH and are passed to postsynaptic site through exocytosis in < 100 microsec. Transmitter causes change in post-synaptic membrane permeability ...
Nervous System Intro Part 1
... Continuation of the Nerve Impulse between Neurons Impulses are able to cross the synapse to another nerve Neurotransmitter is released from a nerve’s axon terminal The dendrite of the next neuron has receptors that are stimulated by the neurotransmitter An action potential is started in the ...
... Continuation of the Nerve Impulse between Neurons Impulses are able to cross the synapse to another nerve Neurotransmitter is released from a nerve’s axon terminal The dendrite of the next neuron has receptors that are stimulated by the neurotransmitter An action potential is started in the ...
Datasheet - Sigma
... 50 kDa protein in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. Human, mouse, and bovine type IB activin receptors share greater than 98 % homology. ...
... 50 kDa protein in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. Human, mouse, and bovine type IB activin receptors share greater than 98 % homology. ...
Neural Networks (NN)
... If the step activation function is used (i.e., the neuron's output is 0 if the input is less than zero, and 1 if the input is greater than or equal to 0) then the neuron acts just like the biological neuron described earlier (subtracting the threshold from the weighted sum and comparing with zero is ...
... If the step activation function is used (i.e., the neuron's output is 0 if the input is less than zero, and 1 if the input is greater than or equal to 0) then the neuron acts just like the biological neuron described earlier (subtracting the threshold from the weighted sum and comparing with zero is ...
Multi-Scale Modeling of the Primary Visual Cortex
... Figure 4: (a) Preferred cortical state of the neuron in the middle of the plot. (b) Spike-triggered activity pattern of the same neuron. (c) Evolution of the similarity index over time and orientation preference. (d) Evolution of the similarity index over time for orientation preference −60 deg. (e ...
... Figure 4: (a) Preferred cortical state of the neuron in the middle of the plot. (b) Spike-triggered activity pattern of the same neuron. (c) Evolution of the similarity index over time and orientation preference. (d) Evolution of the similarity index over time for orientation preference −60 deg. (e ...
nervous system organization, 022817
... Much of the text material is from, “Principles of Anatomy and Physiology” by Gerald J. Tortora and Bryan Derrickson (2009, 2011, and 2014). I don’t claim authorship. Other sources are noted when they are used. The lecture slides are mapped to the three editions of the textbook based on the color-cod ...
... Much of the text material is from, “Principles of Anatomy and Physiology” by Gerald J. Tortora and Bryan Derrickson (2009, 2011, and 2014). I don’t claim authorship. Other sources are noted when they are used. The lecture slides are mapped to the three editions of the textbook based on the color-cod ...
Considerations on the structures involved in the
... the internal concentration of calcium ions through the opening of voltage-dependent calcium channels. These are located at the cell membrane ((Krumschnabel et.al., 2014). Calcium channels play an important role in smooth muscle, synaptic terminals, heart, adrenal chromaffin cells of, insulinsecretor ...
... the internal concentration of calcium ions through the opening of voltage-dependent calcium channels. These are located at the cell membrane ((Krumschnabel et.al., 2014). Calcium channels play an important role in smooth muscle, synaptic terminals, heart, adrenal chromaffin cells of, insulinsecretor ...
This is all we can do!
... • ACTION POTENTIALS – Unique to animal nerve and muscle tissue – Ability to rapidly carry an ion diffusion mediated change in voltage along the cell membrane – Only neurons and muscle cells can do it – Here’s how (more or less)…. ...
... • ACTION POTENTIALS – Unique to animal nerve and muscle tissue – Ability to rapidly carry an ion diffusion mediated change in voltage along the cell membrane – Only neurons and muscle cells can do it – Here’s how (more or less)…. ...
Chapter 48
... membrane. In this way, local currents of ions across the plasma membrane cause the action potential to be propagated along the length of the axon. ...
... membrane. In this way, local currents of ions across the plasma membrane cause the action potential to be propagated along the length of the axon. ...
9.01 Introduction to Neuroscience MIT OpenCourseWare Fall 2007
... • They are also called “stretch receptors,” ...
... • They are also called “stretch receptors,” ...
APOPTOSIS
... From the beginning of the 20th Century until the 1990s, it was stated that neurons DID NOT proliferate. The fact that they COULD NOT proliferate did not exclude the possibility of proliferation under “specific conditions.” In fact, the CNS has a considerable regenerative potential depending on ...
... From the beginning of the 20th Century until the 1990s, it was stated that neurons DID NOT proliferate. The fact that they COULD NOT proliferate did not exclude the possibility of proliferation under “specific conditions.” In fact, the CNS has a considerable regenerative potential depending on ...
text - Systems Neuroscience Course, MEDS 371, Univ. Conn. Health
... a. SNc axons synapse on or near the dendrites of the medium spiny neurons. Some of the medium spiny neurons in each matrix group have dopamine D1 receptors on their dendrites and project their axons into the ‘direct’ pathway to the GPi and SNr (Fig. 8, blue). Dopamine release and binding to D1 recep ...
... a. SNc axons synapse on or near the dendrites of the medium spiny neurons. Some of the medium spiny neurons in each matrix group have dopamine D1 receptors on their dendrites and project their axons into the ‘direct’ pathway to the GPi and SNr (Fig. 8, blue). Dopamine release and binding to D1 recep ...
PN - Neurobiologie, FU Berlin
... About equal numbers of FUAs increased and decreased rate responses (+/- stanfard deviation) More for CS+ than for CS- and Ctr. Out of 110 FUAs: 13 switched responses (mostly for CS+); 3 were recruited t o CS+, 2 did not respond to CS+ any more after conditioning. ...
... About equal numbers of FUAs increased and decreased rate responses (+/- stanfard deviation) More for CS+ than for CS- and Ctr. Out of 110 FUAs: 13 switched responses (mostly for CS+); 3 were recruited t o CS+, 2 did not respond to CS+ any more after conditioning. ...
New neurons retire early - The Gould Lab
... news and views projections of new neurons in hippocampal slices and confirmed that new granule cells gradually form mature projections onto neurons in the CA3 region of the hippocampus over the course of the first 4 weeks. Optical stimulation of 2-week-old granule neurons evoked excitatory postsynap ...
... news and views projections of new neurons in hippocampal slices and confirmed that new granule cells gradually form mature projections onto neurons in the CA3 region of the hippocampus over the course of the first 4 weeks. Optical stimulation of 2-week-old granule neurons evoked excitatory postsynap ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.