The comparative electrobiology of gelatinous
... The degree of coupling within this population is extremely strong. In adjacent or closely separated neurons, the pattern of activity, even the form and number of synaptic potentials, is identical, and even those at diametrically opposite positions in the margin, undergo very similar changes in resti ...
... The degree of coupling within this population is extremely strong. In adjacent or closely separated neurons, the pattern of activity, even the form and number of synaptic potentials, is identical, and even those at diametrically opposite positions in the margin, undergo very similar changes in resti ...
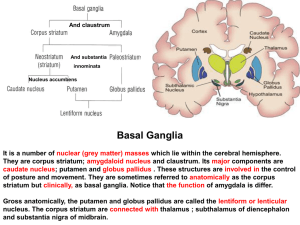
17-Basal ganglion
... This leads to disinhibition of the lateral pallidal neurons and inhibition of subthalamic nucleus. Medial pallidal neurons become abnormally underactive and unwanted; involuntary movements ensue. The following signs is present: 1- Choreiform movements first appear as involuntary movements of the ext ...
... This leads to disinhibition of the lateral pallidal neurons and inhibition of subthalamic nucleus. Medial pallidal neurons become abnormally underactive and unwanted; involuntary movements ensue. The following signs is present: 1- Choreiform movements first appear as involuntary movements of the ext ...
Chapter 02 - Neurons and Glia
... transport. In addition, describe axoplasmic transport and the concept of the molecular “legs” that drive it. (Refer to PowerPoint slide 21.) Teaching Suggestion: Using Figure 2.18, explain anterograde transport and retrograde transport and describe the roles of kinesin and dynein. Discussion Point: ...
... transport. In addition, describe axoplasmic transport and the concept of the molecular “legs” that drive it. (Refer to PowerPoint slide 21.) Teaching Suggestion: Using Figure 2.18, explain anterograde transport and retrograde transport and describe the roles of kinesin and dynein. Discussion Point: ...
Principles of neural ensemble physiology underlying the operation
... restoring mobility in severely paralysed patients. ...
... restoring mobility in severely paralysed patients. ...
600 Kb PDF
... The goal of the Animat project is to create a neurallycontrolled artificial animal with which we can study learning in-vitro. This preliminary work has shown that it is possible to construct a system that can respond to and provide feedback in real-time to a living neural network. We do not yet know ...
... The goal of the Animat project is to create a neurallycontrolled artificial animal with which we can study learning in-vitro. This preliminary work has shown that it is possible to construct a system that can respond to and provide feedback in real-time to a living neural network. We do not yet know ...
Arresting the Development of Addiction
... project to different brain regions (Lobo & Nestler, 2011). Indeed, activation of D1- versus D2containing MSNs causes differential changes in whole brain activity (Lee et al., 2016) and has opposite effects on reinforcement (Kravitz et al., 2012). βarr2 in D1-containing neurons was initially proposed ...
... project to different brain regions (Lobo & Nestler, 2011). Indeed, activation of D1- versus D2containing MSNs causes differential changes in whole brain activity (Lee et al., 2016) and has opposite effects on reinforcement (Kravitz et al., 2012). βarr2 in D1-containing neurons was initially proposed ...
L7- Physiology of Co..
... Peripheral chemoreceptors are stimulated by decreased or increased CO2, increased H+ ion concentration, and decreased pH and low O2. When peripheral chemoreceptors are stimulated, the impulses transmitted from these receptor sites to the dorsal inspiratory area causes the switch off of the inspirato ...
... Peripheral chemoreceptors are stimulated by decreased or increased CO2, increased H+ ion concentration, and decreased pH and low O2. When peripheral chemoreceptors are stimulated, the impulses transmitted from these receptor sites to the dorsal inspiratory area causes the switch off of the inspirato ...
Dean’s A L
... signals, are early response signals to injury or infection and key regulators of resolution and healing. Our research efforts are focused on elucidating function and regulation of these protective lipid circuits in the eye. We have discovered intrinsic lipid circuits in the cornea and retina that co ...
... signals, are early response signals to injury or infection and key regulators of resolution and healing. Our research efforts are focused on elucidating function and regulation of these protective lipid circuits in the eye. We have discovered intrinsic lipid circuits in the cornea and retina that co ...
Connexionism and Computationalism
... the processing from the hidden nodes to the output nodes? Well we can view this as a decoding of the distributed symbolic information into the output values. But the encoding and decoding are not identical, since the input and output patterns are not the same. So we conclude that the ANN has learned ...
... the processing from the hidden nodes to the output nodes? Well we can view this as a decoding of the distributed symbolic information into the output values. But the encoding and decoding are not identical, since the input and output patterns are not the same. So we conclude that the ANN has learned ...
as PDF
... mild forgetfulness and difficulty in identifying familiar smells. The actual development of AD is marked by progressive decline in memory and language function, personality changes, and finally dementia. Death usually occurs as a result of minor respiratory complications in the middle of the night. ...
... mild forgetfulness and difficulty in identifying familiar smells. The actual development of AD is marked by progressive decline in memory and language function, personality changes, and finally dementia. Death usually occurs as a result of minor respiratory complications in the middle of the night. ...
Nervous system
... in large groups to the side of the main pathway of the fibers . In the PNS these aggregations are called ganglia . Within the CNS they are called nuclei ( but they are not be confused with cellular nuclei ) . Each nucleus in the brain consists of many cell bodies , each having its own cellular nucle ...
... in large groups to the side of the main pathway of the fibers . In the PNS these aggregations are called ganglia . Within the CNS they are called nuclei ( but they are not be confused with cellular nuclei ) . Each nucleus in the brain consists of many cell bodies , each having its own cellular nucle ...
Cation-Chloride Cotransporters and Neuronal Function
... GABAA and glycine receptors, CCCs also show close interactions with glutamatergic signaling. A crosstalk among CCCs and trophic factors is important in short-term and long-term modification of neuronal properties. CCCs appear to be multifunctional proteins that are also involved in shaping neuronal ...
... GABAA and glycine receptors, CCCs also show close interactions with glutamatergic signaling. A crosstalk among CCCs and trophic factors is important in short-term and long-term modification of neuronal properties. CCCs appear to be multifunctional proteins that are also involved in shaping neuronal ...
Regents Biology
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom more and gland ...
... bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious Research reason, controla Visit the single such as Glencoe spinal your heart Science nerve rate, can Web site at have breathing, tx.science. impulses digestion, glencoe.co going and to m forfrom more and gland ...
Lesson Plan
... ■■ Students will be able to describe how Na+ and K+ ions flow in and out of axons to create the action potential. ■■ Students will be able to explain how the action potential moves down the length of the axon. ■■ Students will be able to describe how Novocain works. Activities: This lesson begins wi ...
... ■■ Students will be able to describe how Na+ and K+ ions flow in and out of axons to create the action potential. ■■ Students will be able to explain how the action potential moves down the length of the axon. ■■ Students will be able to describe how Novocain works. Activities: This lesson begins wi ...
Pacifier Use May Decrease the Risk of SIDS Abstract Introduction
... When GABA reaches its target cells, they are inhibited because the membrane potential difference is highly negative following chloride entry. This inhibition prevents the release of neurotransmitters and the activity of critical proteins (e.g. dopamine transporter or monoamine oxidase). Therefore, a ...
... When GABA reaches its target cells, they are inhibited because the membrane potential difference is highly negative following chloride entry. This inhibition prevents the release of neurotransmitters and the activity of critical proteins (e.g. dopamine transporter or monoamine oxidase). Therefore, a ...
case study: squirrel - Bush Veterinary Neurology Service
... provide ongoing feedback and consultation. This allowed us to titrate treatment to the dissipation of epileptiform activity with 100 mg/kg of phenobarbital. Phenobarbital was selected because barbiturates are the most useful drugs in this situation in people as opposed to diazepam, propofol or levet ...
... provide ongoing feedback and consultation. This allowed us to titrate treatment to the dissipation of epileptiform activity with 100 mg/kg of phenobarbital. Phenobarbital was selected because barbiturates are the most useful drugs in this situation in people as opposed to diazepam, propofol or levet ...
Document
... To analyze the ‘what’, ‘how’, and ‘when’ of this system, we would have to (i) Model the muscle dynamics, spindle and anterior horn cell synapse (ii) Model the encoding and decoding of spike trains in neurons (iii) Recognize that the effects of other receptors and higher centers are neglected ...
... To analyze the ‘what’, ‘how’, and ‘when’ of this system, we would have to (i) Model the muscle dynamics, spindle and anterior horn cell synapse (ii) Model the encoding and decoding of spike trains in neurons (iii) Recognize that the effects of other receptors and higher centers are neglected ...
Artificial Intelligence CSC 361
... The synapses are the connections made by an axon to another neuron. They are tiny gaps between axons and dendrites (with chemical bridges) that transmit messages A synapse is called excitatory if it raises the local membrane potential of the post synaptic cell. Inhibitory if the potential is ...
... The synapses are the connections made by an axon to another neuron. They are tiny gaps between axons and dendrites (with chemical bridges) that transmit messages A synapse is called excitatory if it raises the local membrane potential of the post synaptic cell. Inhibitory if the potential is ...
Spinal nerves
... • The brain is the center for registering sensations, correlating them with one another and with stored information, making decisions, and taking action. • It is also the center for intellect, emotions, behavior, and memory. • It also directs our behavior towards others. • In this chapter we will co ...
... • The brain is the center for registering sensations, correlating them with one another and with stored information, making decisions, and taking action. • It is also the center for intellect, emotions, behavior, and memory. • It also directs our behavior towards others. • In this chapter we will co ...
BIOLOGICAL AND CULTURAL SHAPING OF MIND AND BEHAVIOUR
... (synaptic cleft) signals are transmitted from one neuron to another. The sending side of synapse is axon terminal where as the receiving side of synapses is the tips of the branching dendrites. The chemical substances that facilitate the transmission of the signals are called neurotransmitters. ...
... (synaptic cleft) signals are transmitted from one neuron to another. The sending side of synapse is axon terminal where as the receiving side of synapses is the tips of the branching dendrites. The chemical substances that facilitate the transmission of the signals are called neurotransmitters. ...
Hippocampus, hippocampal sclerosis and epilepsy
... bioelectrical activity of the principal neurons. The “latency” of these interneurons is due to the lack of their physiological stimulation by damaged hilar mossy cells [88]. In addition to neuronal degeneration and gliosis, the so called mossy fiber sprouting and the dentate gyrus granule cell dispe ...
... bioelectrical activity of the principal neurons. The “latency” of these interneurons is due to the lack of their physiological stimulation by damaged hilar mossy cells [88]. In addition to neuronal degeneration and gliosis, the so called mossy fiber sprouting and the dentate gyrus granule cell dispe ...
Spinal Cord Reflexes
... •Sherrington: Locomotion is automatic result of successive activation of reflexes. For example, alternating activation of Ia stretch reflex in flexors and extensors of limb, and FRA reflex with ...
... •Sherrington: Locomotion is automatic result of successive activation of reflexes. For example, alternating activation of Ia stretch reflex in flexors and extensors of limb, and FRA reflex with ...
Fast neural network simulations with population density methods Duane Q. Nykamp Daniel Tranchina
... excitatory and 18 inhibitory populations with preferred orientations between 0 and 180 deg [5]. The responses of two populations to a flashed bar oriented at zero deg are shown in figure 2. The population density simulation was over 100 times faster than the direct simulation (22 seconds versus 50 m ...
... excitatory and 18 inhibitory populations with preferred orientations between 0 and 180 deg [5]. The responses of two populations to a flashed bar oriented at zero deg are shown in figure 2. The population density simulation was over 100 times faster than the direct simulation (22 seconds versus 50 m ...
Sheet#6 Motor system
... * Action potential being through nerve then acetylcholine is released which effect postsynaptic on muscle and contraction is accomplished. *Motor neurons are present in the anterior gray horn of the spinal cord (where a neuron cell body is found), the axon of each neuron then travels to muscles for ...
... * Action potential being through nerve then acetylcholine is released which effect postsynaptic on muscle and contraction is accomplished. *Motor neurons are present in the anterior gray horn of the spinal cord (where a neuron cell body is found), the axon of each neuron then travels to muscles for ...
Overview of the Reticular Formation (RF)
... of the spinal cord. A “coordinating system” (like the Limbic system) with “connections” to sensory, somatic motor and visceral motor systems Organization can be subdivided into two neuronal cell “columns” (medial to lateral) as well as on the basis of their neurotransmitter release Neuronal columns ...
... of the spinal cord. A “coordinating system” (like the Limbic system) with “connections” to sensory, somatic motor and visceral motor systems Organization can be subdivided into two neuronal cell “columns” (medial to lateral) as well as on the basis of their neurotransmitter release Neuronal columns ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.