Spike-timing dependent plasticity and the cognitive map
... a rate of ∼0.1 Hz (this being realistic of CA3) is generated in the network by the constant application of excitatory current drawn from a uniform random distribution in the range (0:Inoise) where Inoise = 0.8 in all simulations (Frerking et al., 2005). The interplay between afferent inhibitory and ...
... a rate of ∼0.1 Hz (this being realistic of CA3) is generated in the network by the constant application of excitatory current drawn from a uniform random distribution in the range (0:Inoise) where Inoise = 0.8 in all simulations (Frerking et al., 2005). The interplay between afferent inhibitory and ...
Bipolar neurons in rat visual cortex: A combined
... endoplasmic reticulum in all of the gold-toned bipolar cells examined with the electron microscope. In cell b the cytoplasm at the poles of the cell body contains very well organized and extensive cisternae of rough endoplasmic reticulum with many free ribosomes between the cisternae (Fig. 3). The b ...
... endoplasmic reticulum in all of the gold-toned bipolar cells examined with the electron microscope. In cell b the cytoplasm at the poles of the cell body contains very well organized and extensive cisternae of rough endoplasmic reticulum with many free ribosomes between the cisternae (Fig. 3). The b ...
Nervous System PPT notes
... 5. Describe the differences of neural communication between the ANS & SNS neuron systems (monosynaptic? polysynaptic?) 6. Discuss the accuracy of your smell sense. Which sense is more accurate without the assistance of sight…smell or taste? Scientifically ...
... 5. Describe the differences of neural communication between the ANS & SNS neuron systems (monosynaptic? polysynaptic?) 6. Discuss the accuracy of your smell sense. Which sense is more accurate without the assistance of sight…smell or taste? Scientifically ...
1 - Test Bank
... her __________ will play an important role in helping her to perform the routines correctly and smoothly. a. medulla b. pons c. reticular formation d. cerebellum ANS: d LO=2.7 18. Which sensory information does NOT have to be first sent to the thalamus before going to the cortex? a. auditory (hearin ...
... her __________ will play an important role in helping her to perform the routines correctly and smoothly. a. medulla b. pons c. reticular formation d. cerebellum ANS: d LO=2.7 18. Which sensory information does NOT have to be first sent to the thalamus before going to the cortex? a. auditory (hearin ...
chapter 24 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... A. ___________________ Respond to Physical __________________ or Movement (Figure 24-15) B. The Perception of _____________ Is a Specialized Type of Mechanoreception 1. The ear converts ___________ __________ to ____________ signals (Figure 24-16) 2. Sound is converted into electrical signals in the ...
... A. ___________________ Respond to Physical __________________ or Movement (Figure 24-15) B. The Perception of _____________ Is a Specialized Type of Mechanoreception 1. The ear converts ___________ __________ to ____________ signals (Figure 24-16) 2. Sound is converted into electrical signals in the ...
relating nerve cells to behavior
... crayfish tail flip response synapses behavior Drosophila escape response restricted circuits behavior ...
... crayfish tail flip response synapses behavior Drosophila escape response restricted circuits behavior ...
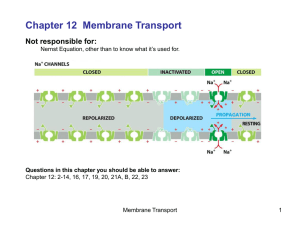
What is “membrane potential”
... Why do the Na+ and K+ channels open and close at different times? -- Membrane potential alters their state voltage-gated Na+ channels ...
... Why do the Na+ and K+ channels open and close at different times? -- Membrane potential alters their state voltage-gated Na+ channels ...
network - Ohio University
... Equilibrium for potential Q for which currents don't flow is established by the level of inhibitory conductance. ...
... Equilibrium for potential Q for which currents don't flow is established by the level of inhibitory conductance. ...
Stable propagation of synchronous spiking in cortical neural networks
... made using the group size w 100. To determine how many simultaneously ®ring neurons are needed to guarantee that synchronous activity survives in the network, we examined how the structure of the state space depends on the groups size (Fig. 4). For increasing numbers of neurons per group, the two ...
... made using the group size w 100. To determine how many simultaneously ®ring neurons are needed to guarantee that synchronous activity survives in the network, we examined how the structure of the state space depends on the groups size (Fig. 4). For increasing numbers of neurons per group, the two ...
Neural Activity and the Development of Brain Circuits
... how the neurons in its nervous system are connected with one another and the motor output. During early human development over 100 billion neurons each establish from dozens to thousands of connections with one another and with muscle fibres. At all levels of the nervous system, precise connections e ...
... how the neurons in its nervous system are connected with one another and the motor output. During early human development over 100 billion neurons each establish from dozens to thousands of connections with one another and with muscle fibres. At all levels of the nervous system, precise connections e ...
BIOGRAPHICAL SKETCH David A. Prince PRINCE
... Jin, X., Huguenard, J.R., and Prince, D.A. Reorganization of inhibitory synaptic circuits in rodent chronically injured epileptogenic neocortex, Cereb Cortex, Sep 20. 21(5):1094-1104, 2011. ...
... Jin, X., Huguenard, J.R., and Prince, D.A. Reorganization of inhibitory synaptic circuits in rodent chronically injured epileptogenic neocortex, Cereb Cortex, Sep 20. 21(5):1094-1104, 2011. ...
PowerPoint Slide Set Westen Psychology 2e
... Neurotransmitters (NTs) are chemicals NTs are stored within vesicles of the presynaptic cell NTs are released in response to the action potential sweeping along the presynaptic membrane Transmitter molecules diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to postsynaptic receptors Receptor bindin ...
... Neurotransmitters (NTs) are chemicals NTs are stored within vesicles of the presynaptic cell NTs are released in response to the action potential sweeping along the presynaptic membrane Transmitter molecules diffuse across the synaptic cleft and bind to postsynaptic receptors Receptor bindin ...
COMMUNICATION IN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM UNIT THREE
... The neural pathway involved in the reaction time experiment involves a series of neural processes. Catching the ruler begins with the eye watching the ruler in anticipation of it falling. After the ruler is dropped, the eye sends a message to the visual cortex, which perceives that the ruler has fal ...
... The neural pathway involved in the reaction time experiment involves a series of neural processes. Catching the ruler begins with the eye watching the ruler in anticipation of it falling. After the ruler is dropped, the eye sends a message to the visual cortex, which perceives that the ruler has fal ...
Identification of Mechanoafferent Neurons in Terrestrial Snail
... were located on the ventrolateral side of each pleural ganglion. Intracellular injection of neurobiotin revealed that all PlVL neurons sent their axons into the skin nerves. The PlVL neurons had no spontaneous spike activity or fast synaptic potentials. In the reduced “CNSfoot” preparations, mechani ...
... were located on the ventrolateral side of each pleural ganglion. Intracellular injection of neurobiotin revealed that all PlVL neurons sent their axons into the skin nerves. The PlVL neurons had no spontaneous spike activity or fast synaptic potentials. In the reduced “CNSfoot” preparations, mechani ...
Locally evoked potentials in slices of the rat nucleus - UvA-DARE
... A c b 46. T h e occurrence of N M D A receptor activity in this brain area is of special interest since this receptor mediates induction of long-term potentiation in the h i p p o c a m p u s 7"23'4°. As yet it is u n k n o w n whether it is involved in synaptic plasticity in the A c b as well. In t ...
... A c b 46. T h e occurrence of N M D A receptor activity in this brain area is of special interest since this receptor mediates induction of long-term potentiation in the h i p p o c a m p u s 7"23'4°. As yet it is u n k n o w n whether it is involved in synaptic plasticity in the A c b as well. In t ...
Realistic synaptic inputs for model neural networks
... set e q d to the excitatory ne.The two -yes intersect at rates corresponding to a d e n t state, E = 0, an unstable intermediate state and a stable self-sustainedfiring state for whidt the firing rate is essentially the maximum srnglenevron rate. The firing rate for this state is unrealistically hig ...
... set e q d to the excitatory ne.The two -yes intersect at rates corresponding to a d e n t state, E = 0, an unstable intermediate state and a stable self-sustainedfiring state for whidt the firing rate is essentially the maximum srnglenevron rate. The firing rate for this state is unrealistically hig ...
Chapter 3
... • Series of rapidly occurring events that change and then restore the membrane potential of a cell to its resting state • Ion channels open, Na+ rushes in (depolarization), K+ rushes out (repolarization) • All-or-none principal = with stimulation, either happens one specific way or not at all (lasts ...
... • Series of rapidly occurring events that change and then restore the membrane potential of a cell to its resting state • Ion channels open, Na+ rushes in (depolarization), K+ rushes out (repolarization) • All-or-none principal = with stimulation, either happens one specific way or not at all (lasts ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals which transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse.[1] Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind t ...
... Neurotransmitters are endogenous chemicals which transmit signals from a neuron to a target cell across a synapse.[1] Neurotransmitters are packaged into synaptic vesicles clustered beneath the membrane on the presynaptic side of a synapse, and are released into the synaptic cleft, where they bind t ...
Synaptic Distinction of Laminar-specific Prefrontal-temporal Pathways in Primates
... For single section analysis 1--4 pieces of tissue were cut from layer I from each case (total = 8 in 5 cases), and 1--3 pieces from the middle layers (total = 8 in 5 cases), representative of the labeling in area Ts1 (cases AY, BG, BC, BA), or in area Ts3 (case BF). The sites sampled from architecto ...
... For single section analysis 1--4 pieces of tissue were cut from layer I from each case (total = 8 in 5 cases), and 1--3 pieces from the middle layers (total = 8 in 5 cases), representative of the labeling in area Ts1 (cases AY, BG, BC, BA), or in area Ts3 (case BF). The sites sampled from architecto ...
Sensory Adaptation and Short Term Plasticity as Bayesian
... concentration [3] and circadian rhythms [4]. Such fluctuations are widely observed in experimental recordings where spike trains are collected over many trials in response to the same repeated stimulus [c.f. 5]. If a neuron encodes features of stimuli in the external world, such as the orientation o ...
... concentration [3] and circadian rhythms [4]. Such fluctuations are widely observed in experimental recordings where spike trains are collected over many trials in response to the same repeated stimulus [c.f. 5]. If a neuron encodes features of stimuli in the external world, such as the orientation o ...
Lecture 6: Single neuron models
... They describe the rate of change of some variable, say u, as a function u and other variables ...
... They describe the rate of change of some variable, say u, as a function u and other variables ...
Excitatory and Inhibitory Vestibular Pathways to the Extraocular
... negative than resting potentials. The inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) reversed with large amplitudes after the injection of chloride ions suggesting a proximal soma-dendritic location of terminals exhibiting high efficacy inhibitory synaptic conductances. In antidromically identified abdu ...
... negative than resting potentials. The inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) reversed with large amplitudes after the injection of chloride ions suggesting a proximal soma-dendritic location of terminals exhibiting high efficacy inhibitory synaptic conductances. In antidromically identified abdu ...
Spectro-Temporal Receptive Fields of Subthreshold Responses in
... where spikes were blocked (only in the neuron being recorded from) with the intracellular sodium channel blocker QX-314 (see Methods), is shown in Fig. 1(c). The responses feature robust stimulus-locked fluctuations of membrane potential, as well as some spontaneous activity. Both the spontaneous an ...
... where spikes were blocked (only in the neuron being recorded from) with the intracellular sodium channel blocker QX-314 (see Methods), is shown in Fig. 1(c). The responses feature robust stimulus-locked fluctuations of membrane potential, as well as some spontaneous activity. Both the spontaneous an ...
Chemical synapse

Chemical synapses are specialized junctions through which neurons signal to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body.At a chemical synapse, one neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules into a small space (the synaptic cleft) that is adjacent to another neuron. The neurotransmitters are kept within small sacs called vesicles, and are released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. These molecules then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell's side of the synaptic cleft. Finally, the neurotransmitters must be cleared from the synapse through one of several potential mechanisms including enzymatic degradation or re-uptake by specific transporters either on the presynaptic cell or possibly by neuroglia to terminate the action of the transmitter.The adult human brain is estimated to contain from 1014 to 5 × 1014 (100–500 trillion) synapses. Every cubic millimeter of cerebral cortex contains roughly a billion (short scale, i.e. 109) of them.The word ""synapse"" comes from ""synaptein"", which Sir Charles Scott Sherrington and colleagues coined from the Greek ""syn-"" (""together"") and ""haptein"" (""to clasp""). Chemical synapses are not the only type of biological synapse: electrical and immunological synapses also exist. Without a qualifier, however, ""synapse"" commonly means chemical synapse.