Slide ()
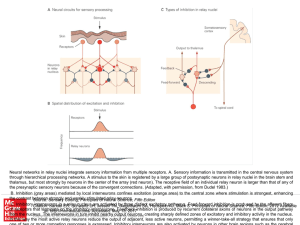
... interneurons in a relay nucleus are activated three distinct Feed-forward is produced the afferent fibers Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM,by Siegelbaum SA,excitatory Hudspethpathways. AJ, Mack S. Principles ofinhibition Neural Science, Fifth by Editon; 2012 Available of receptors that terminate o ...
... interneurons in a relay nucleus are activated three distinct Feed-forward is produced the afferent fibers Kandel ER, Schwartz JH, Jessell TM,by Siegelbaum SA,excitatory Hudspethpathways. AJ, Mack S. Principles ofinhibition Neural Science, Fifth by Editon; 2012 Available of receptors that terminate o ...
In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by
... In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by way of glutamate and most inhibitory communication occurs by way of gamma-aminobutyric acid. In general terms, describe what the other neurotransmitters do. ...
... In the brain, most excitatory communication in synapses occurs by way of glutamate and most inhibitory communication occurs by way of gamma-aminobutyric acid. In general terms, describe what the other neurotransmitters do. ...
More Introductory Stuff
... Cells in cortex that respond to different line orientation Truly cool, maybe they network together to recognize objects? ...
... Cells in cortex that respond to different line orientation Truly cool, maybe they network together to recognize objects? ...
Neurons - WordPress.com
... • found to be intimately involved in emotion and mood. • Too little serotonin has been shown to lead to depression, problems with anger control, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and suicide. • Too little also leads to an increased appetite for carbohydrates (starchy foods) and trouble sleeping, which ...
... • found to be intimately involved in emotion and mood. • Too little serotonin has been shown to lead to depression, problems with anger control, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and suicide. • Too little also leads to an increased appetite for carbohydrates (starchy foods) and trouble sleeping, which ...
The Dynamics of Learning and Memory: Lessons from Neuroscience
... As we have seen, the changes which occur in synaptic efficacy as the result of Hebbian pairing of pre- and postsynaptic activity can substantially alter the dynamic characteristics of the synaptic connection. In addition it has been observed that the induction of long-term changes in synaptic effica ...
... As we have seen, the changes which occur in synaptic efficacy as the result of Hebbian pairing of pre- and postsynaptic activity can substantially alter the dynamic characteristics of the synaptic connection. In addition it has been observed that the induction of long-term changes in synaptic effica ...
What is the structure of the neuron? (continued)
... than neurons. • Surround and support neurons, control the supply of nutrients to neurons, assist in the exchange of chemicals between neurons, destroy and remove damaged neurons. ...
... than neurons. • Surround and support neurons, control the supply of nutrients to neurons, assist in the exchange of chemicals between neurons, destroy and remove damaged neurons. ...
The Nervous System WS-11A Review Quest
... Step 2 The impulse opens channel proteins on the membrane of the synapse that allows calcium (Ca2+) to enter ...
... Step 2 The impulse opens channel proteins on the membrane of the synapse that allows calcium (Ca2+) to enter ...
Lecture 9
... 5. Outflow K, hyperpolarizing cell, bringing it back to resting potential Hodgkin-Huxley Model ...
... 5. Outflow K, hyperpolarizing cell, bringing it back to resting potential Hodgkin-Huxley Model ...
Action Potential Webquest
... Part 2 - Resting Potential and Action Potential Videos (short) Go to http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/content/electricalsignaling.html Watch this animation. It shows how membrane potential (resting potential) develops in the neuron cell. 1. What causes the inside of the cell to be mor ...
... Part 2 - Resting Potential and Action Potential Videos (short) Go to http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/content/electricalsignaling.html Watch this animation. It shows how membrane potential (resting potential) develops in the neuron cell. 1. What causes the inside of the cell to be mor ...
Neural Conduction - U
... • thus, any time that there is an accumulation of a particular class of ions in one area, the probability is increased that random motion will move ions out of this area (because there are more ions available to leave) and the probability is decreased that random motion will move more ions into the ...
... • thus, any time that there is an accumulation of a particular class of ions in one area, the probability is increased that random motion will move ions out of this area (because there are more ions available to leave) and the probability is decreased that random motion will move more ions into the ...
Peripheral nervous system
... transmission Synapse Intercellular junction between dendrites and soma • electrical synapse - uses direct cytoplasmic connections ...
... transmission Synapse Intercellular junction between dendrites and soma • electrical synapse - uses direct cytoplasmic connections ...
20141013134817
... C. Motor Output – Sending out of impulses from the brain or spinal cord to glands or muscles to “create” a response. 1. The response is carried out by Effector Cells. a. Effectors are Muscles or Glands. These structures can have an effect on your body. D. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 1. This incl ...
... C. Motor Output – Sending out of impulses from the brain or spinal cord to glands or muscles to “create” a response. 1. The response is carried out by Effector Cells. a. Effectors are Muscles or Glands. These structures can have an effect on your body. D. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) 1. This incl ...
File
... neurotransmitters (chemicals stored in the synaptic vesicles in axon terminals) • When an action potential arrives at an axon terminal: • Gated channels for Ca2+ open, and Ca2+ enters the terminal • Ca2+ interacts with contractile proteins, which contract and pull the synaptic vesicles to the presyn ...
... neurotransmitters (chemicals stored in the synaptic vesicles in axon terminals) • When an action potential arrives at an axon terminal: • Gated channels for Ca2+ open, and Ca2+ enters the terminal • Ca2+ interacts with contractile proteins, which contract and pull the synaptic vesicles to the presyn ...
Mind, Brain & Behavior
... neuron, receiving input from other neurons. Dendrites are covered with synapses. Each synapse has many receptors for neurotransmitters of various kinds. Dendritic spines – specialized dendrites that isolate reactions at some synapses. ...
... neuron, receiving input from other neurons. Dendrites are covered with synapses. Each synapse has many receptors for neurotransmitters of various kinds. Dendritic spines – specialized dendrites that isolate reactions at some synapses. ...
Neurotransmitters
... 3 Criteria for Neurotransmitter • 1: the substance must be in presynaptic neuron • 2: Substance released by presynaptic depolarization that is calcium depenedent • 3: Specific receptors must be present on post-synaptic membrane ...
... 3 Criteria for Neurotransmitter • 1: the substance must be in presynaptic neuron • 2: Substance released by presynaptic depolarization that is calcium depenedent • 3: Specific receptors must be present on post-synaptic membrane ...
neurons
... of its membrane and allowing positive ions to rush in. • The neuron then quickly pushes the positively charged ions back out again and closes that section of its membrane. • The neuron then opens the next section of its membrane and allows the positively charged ions to rush in, and quickly pushes t ...
... of its membrane and allowing positive ions to rush in. • The neuron then quickly pushes the positively charged ions back out again and closes that section of its membrane. • The neuron then opens the next section of its membrane and allows the positively charged ions to rush in, and quickly pushes t ...
Nerve Cell Impulses
... • Na+ (sodium) ions have restricted access • Action potential increases permeability of Na+ • There is selectivity in opening/closing Na+ and K+ gates • Remember: Plasma membrane is semi-permeable to K+ – Physico-chemical ion selectivity channels – (i.e., K+ weaker fields Æ Na+, larger ion size, gat ...
... • Na+ (sodium) ions have restricted access • Action potential increases permeability of Na+ • There is selectivity in opening/closing Na+ and K+ gates • Remember: Plasma membrane is semi-permeable to K+ – Physico-chemical ion selectivity channels – (i.e., K+ weaker fields Æ Na+, larger ion size, gat ...
Chemical synapse

Chemical synapses are specialized junctions through which neurons signal to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body.At a chemical synapse, one neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules into a small space (the synaptic cleft) that is adjacent to another neuron. The neurotransmitters are kept within small sacs called vesicles, and are released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. These molecules then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell's side of the synaptic cleft. Finally, the neurotransmitters must be cleared from the synapse through one of several potential mechanisms including enzymatic degradation or re-uptake by specific transporters either on the presynaptic cell or possibly by neuroglia to terminate the action of the transmitter.The adult human brain is estimated to contain from 1014 to 5 × 1014 (100–500 trillion) synapses. Every cubic millimeter of cerebral cortex contains roughly a billion (short scale, i.e. 109) of them.The word ""synapse"" comes from ""synaptein"", which Sir Charles Scott Sherrington and colleagues coined from the Greek ""syn-"" (""together"") and ""haptein"" (""to clasp""). Chemical synapses are not the only type of biological synapse: electrical and immunological synapses also exist. Without a qualifier, however, ""synapse"" commonly means chemical synapse.























