Types of neurons
... Neurons communicate by means of an electrical signal called the Action Potential Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to ...
... Neurons communicate by means of an electrical signal called the Action Potential Action Potentials are based on movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell When an Action Potential occurs a molecular message is sent to ...
Nerve Signals
... allowing current to flow via gap junctions between the cells Unbroken transmission Rapid transmission and synchronous activity ...
... allowing current to flow via gap junctions between the cells Unbroken transmission Rapid transmission and synchronous activity ...
NEUROCHEMISTRY & NEUROTRANSMITTERS
... THEIR RECEPTORS. AFTER BINDING TO THEIR RECEPTORS, NTs MAY BE ENZYMATICALLY BROKEN DOWN (e.g. ACETYLCHOLINE BY THE ACTION OF ACETYLCHOLINESTERASE) OR TAKEN BACK UP AGAIN BY THE PRESYNAPSE (e.g. NOREPINEPHRINE IS TAKEN BACK UP BY A TRANSPORT PROTEIN). ...
... THEIR RECEPTORS. AFTER BINDING TO THEIR RECEPTORS, NTs MAY BE ENZYMATICALLY BROKEN DOWN (e.g. ACETYLCHOLINE BY THE ACTION OF ACETYLCHOLINESTERASE) OR TAKEN BACK UP AGAIN BY THE PRESYNAPSE (e.g. NOREPINEPHRINE IS TAKEN BACK UP BY A TRANSPORT PROTEIN). ...
Application Six - Sheila Tooker Impey
... left side of his face, because of the neural damage to the right precentral gyrus which is the location of the primary motor cortex that controls voluntary movement. Most normal functioning neurons receive chemical signals from the axon termini of other neurons (Freeman, 2000). There is then an acti ...
... left side of his face, because of the neural damage to the right precentral gyrus which is the location of the primary motor cortex that controls voluntary movement. Most normal functioning neurons receive chemical signals from the axon termini of other neurons (Freeman, 2000). There is then an acti ...
Slide ()
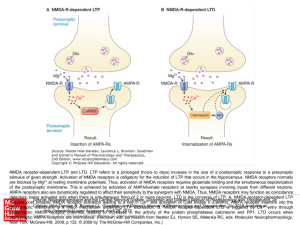
... NMDA receptor-dependent LTP and LTD. LTP refers to a prolonged (hours to days) increase in the size of a postsynaptic response to a presynaptic stimulus of given strength. Activation of NMDA receptors is obligatory for the induction of LTP that occurs in the hippocampus. NMDA receptors normally are ...
... NMDA receptor-dependent LTP and LTD. LTP refers to a prolonged (hours to days) increase in the size of a postsynaptic response to a presynaptic stimulus of given strength. Activation of NMDA receptors is obligatory for the induction of LTP that occurs in the hippocampus. NMDA receptors normally are ...
Chapter 2 Lecture Notes Module 4 – Neural and Hormonal Systems
... Synapse/synaptic gap - microscopic fluid-filled space between the rounded areas on the end of the axon terminals of one cell and the dendrites or surface of the next cell. ...
... Synapse/synaptic gap - microscopic fluid-filled space between the rounded areas on the end of the axon terminals of one cell and the dendrites or surface of the next cell. ...
The Nervous System
... or electrical signal. Electrical synapses cross gap junctions, such as in cardiac and smooth muscle. Neurotransmitters are used in nervous system synapses. They are released from the axon. Bouton / knobs / presynaptic terminal Neuromodulators – can influence an action potential ...
... or electrical signal. Electrical synapses cross gap junctions, such as in cardiac and smooth muscle. Neurotransmitters are used in nervous system synapses. They are released from the axon. Bouton / knobs / presynaptic terminal Neuromodulators – can influence an action potential ...
Nervous System
... Membrane is more permeable to K+ than Na+ so diffusion more likely. Na+ channels often closed. ...
... Membrane is more permeable to K+ than Na+ so diffusion more likely. Na+ channels often closed. ...
The Nervous System
... -Original stimulation must be above threshold level in order for an impulse to be started (all or nothing) Transmission of impulses between neurons -Communication between cells occurs at synapses (gap between axon and neighboring dendrite) -Pre-synaptic cells contain synaptic vesicles which contain ...
... -Original stimulation must be above threshold level in order for an impulse to be started (all or nothing) Transmission of impulses between neurons -Communication between cells occurs at synapses (gap between axon and neighboring dendrite) -Pre-synaptic cells contain synaptic vesicles which contain ...
Chapter - Heartland Community College
... A. The resting potential of a typical neuron is -70 mV within the neuron. B. There is a difference in electrical potential between the sides of the cell membrane. C. There is a voltage difference between the inside and the outside of the cell membrane. D. The resting potential is the difference in e ...
... A. The resting potential of a typical neuron is -70 mV within the neuron. B. There is a difference in electrical potential between the sides of the cell membrane. C. There is a voltage difference between the inside and the outside of the cell membrane. D. The resting potential is the difference in e ...
Neuronal Function
... changes in ion concentration and is the site at which an action potential is initiated. An action potential is a self-propagating depolarization of the axonal membrane that initiates at the hillock and runs to the axon terminus without diminishing in strength. All action potentials are the same “siz ...
... changes in ion concentration and is the site at which an action potential is initiated. An action potential is a self-propagating depolarization of the axonal membrane that initiates at the hillock and runs to the axon terminus without diminishing in strength. All action potentials are the same “siz ...
Glossary
... A limited time span in the development of an organism when it is optimal for certain capacities to emerge because the organism is especially responsive to certain experiences. ...
... A limited time span in the development of an organism when it is optimal for certain capacities to emerge because the organism is especially responsive to certain experiences. ...
Nervous
... The depolarization of the action potential spreads to the neighboring region of the membrane, re-initiating the action potential there. To the left of this region, the membrane is repolarizing as K+ flows outward. ...
... The depolarization of the action potential spreads to the neighboring region of the membrane, re-initiating the action potential there. To the left of this region, the membrane is repolarizing as K+ flows outward. ...
Nervous_System_Neurons
... Endorphins are neurotransmitters produced in the brain that reduce pain They have also been known to induce euphoria. Drugs such as morphine, heroine and cocaine are classic endorphin-releasing entities Laughter, chocolate, acupuncture, exercise trigger an endorphin release “runner’s high” ...
... Endorphins are neurotransmitters produced in the brain that reduce pain They have also been known to induce euphoria. Drugs such as morphine, heroine and cocaine are classic endorphin-releasing entities Laughter, chocolate, acupuncture, exercise trigger an endorphin release “runner’s high” ...
29 - IWS2.collin.edu
... Neurotransmitter must be released, diffuse across the synapse, and bind to receptors Synaptic delay – time needed to do this Synaptic delay is the rate-limiting step of neural transmission ...
... Neurotransmitter must be released, diffuse across the synapse, and bind to receptors Synaptic delay – time needed to do this Synaptic delay is the rate-limiting step of neural transmission ...
Biology of Humans 2/e
... The signal passes across the synaptic cleft as a chemical called neurotransmitter which is released from vesicles by exocytosis. Neurotransmitter is a chemical that is secreted into a synaptic cleft by a neuron that affects another neuron or an effector by binding with receptors on it. The sending c ...
... The signal passes across the synaptic cleft as a chemical called neurotransmitter which is released from vesicles by exocytosis. Neurotransmitter is a chemical that is secreted into a synaptic cleft by a neuron that affects another neuron or an effector by binding with receptors on it. The sending c ...
D. Vertebrate Nervous Systems
... Contains nuclei involved in the regulation of visceral activities such as breathing. Relays information to and from higher brain centers. The Midbrain. Contains nuclei involved in the integration of sensory information. Superior colliculi are involved in the regulation of visual reflexes. ...
... Contains nuclei involved in the regulation of visceral activities such as breathing. Relays information to and from higher brain centers. The Midbrain. Contains nuclei involved in the integration of sensory information. Superior colliculi are involved in the regulation of visual reflexes. ...
Document
... http://www.its.caltech.edu/~lester/Bi-1-2006/Lecture-images/Lecture-4-2006(History).ppt ...
... http://www.its.caltech.edu/~lester/Bi-1-2006/Lecture-images/Lecture-4-2006(History).ppt ...
Option E: Neurobiology and behaviour
... E.4.2 Explain how decision-making in the CNS can result from the interaction between the activities of excitatory and inhibitory presynaptic neurons at synapses. E.4.3 Explain how psychoactive drugs affect the brain and personality by either increasing or decreasing postsynaptic transmission. E.4.4 ...
... E.4.2 Explain how decision-making in the CNS can result from the interaction between the activities of excitatory and inhibitory presynaptic neurons at synapses. E.4.3 Explain how psychoactive drugs affect the brain and personality by either increasing or decreasing postsynaptic transmission. E.4.4 ...
Anatomy, composition and physiology of neuron, dendrite, axon,and
... Brain has at least two types of neuronal map/ motor and sensory maps/ which are interconnected with each other by interneuron. The neurons that make up these map do not differ greatly in their electrical properties. Rather, They have different function because of the connections they make. deploymen ...
... Brain has at least two types of neuronal map/ motor and sensory maps/ which are interconnected with each other by interneuron. The neurons that make up these map do not differ greatly in their electrical properties. Rather, They have different function because of the connections they make. deploymen ...
Chemical synapse

Chemical synapses are specialized junctions through which neurons signal to each other and to non-neuronal cells such as those in muscles or glands. Chemical synapses allow neurons to form circuits within the central nervous system. They are crucial to the biological computations that underlie perception and thought. They allow the nervous system to connect to and control other systems of the body.At a chemical synapse, one neuron releases neurotransmitter molecules into a small space (the synaptic cleft) that is adjacent to another neuron. The neurotransmitters are kept within small sacs called vesicles, and are released into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis. These molecules then bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell's side of the synaptic cleft. Finally, the neurotransmitters must be cleared from the synapse through one of several potential mechanisms including enzymatic degradation or re-uptake by specific transporters either on the presynaptic cell or possibly by neuroglia to terminate the action of the transmitter.The adult human brain is estimated to contain from 1014 to 5 × 1014 (100–500 trillion) synapses. Every cubic millimeter of cerebral cortex contains roughly a billion (short scale, i.e. 109) of them.The word ""synapse"" comes from ""synaptein"", which Sir Charles Scott Sherrington and colleagues coined from the Greek ""syn-"" (""together"") and ""haptein"" (""to clasp""). Chemical synapses are not the only type of biological synapse: electrical and immunological synapses also exist. Without a qualifier, however, ""synapse"" commonly means chemical synapse.