The Effect of International Competition on Firm Productivity and Market Power
... The effect of international integration is not always clear-cut. Tariff reductions will only affect a firm if its product competes with the products that benefit. The relevant market definition, both in terms of product characteristics and geographical distance, is not always known. It is not even n ...
... The effect of international integration is not always clear-cut. Tariff reductions will only affect a firm if its product competes with the products that benefit. The relevant market definition, both in terms of product characteristics and geographical distance, is not always known. It is not even n ...
Assignment Two, Micro
... ____ 49. If two goods have the same price, then a. the consumer will purchase the same amount of the two in order to maximize utility. b. the consumer will spend the same amount on each good or service. c. the consumer will buy enough of these goods or services so that the marginal utilities are the ...
... ____ 49. If two goods have the same price, then a. the consumer will purchase the same amount of the two in order to maximize utility. b. the consumer will spend the same amount on each good or service. c. the consumer will buy enough of these goods or services so that the marginal utilities are the ...
L = q 25 - Amazon S3
... the extra cost of producing one more unit of output. If this cost is diminishing, then it must be taking fewer units of labor to produce the extra unit of output. If fewer units of labor are required to produce a unit of output, then the marginal product (extra output produced by an extra unit ...
... the extra cost of producing one more unit of output. If this cost is diminishing, then it must be taking fewer units of labor to produce the extra unit of output. If fewer units of labor are required to produce a unit of output, then the marginal product (extra output produced by an extra unit ...
Marginal cost
... A Firm’s Labor Decisions • Business owners have to consider how the number of workers they hire will affect their total production. • The marginal product of labor is the change in output from hiring one additional unit of labor, or worker. ...
... A Firm’s Labor Decisions • Business owners have to consider how the number of workers they hire will affect their total production. • The marginal product of labor is the change in output from hiring one additional unit of labor, or worker. ...
Chapter 5
... 3) Note that profits do not rise or fall in that range. 4) Students may ask why the last unit should be produced given that profit doesn’t rise. Answer that this is an artifact of grouping units in 100’s and that if units were infinitely divisible then there would be one unique profit maximizing lev ...
... 3) Note that profits do not rise or fall in that range. 4) Students may ask why the last unit should be produced given that profit doesn’t rise. Answer that this is an artifact of grouping units in 100’s and that if units were infinitely divisible then there would be one unique profit maximizing lev ...
lista 1 - gabarito
... 55. "As the price of personal computers continues to fall, demand increases." This headline is inaccurate because A. a change in the price of personal computers shifts the demand curve. B. a change in the price of personal computers shifts the supply curve. C. the statement is backwards: increased d ...
... 55. "As the price of personal computers continues to fall, demand increases." This headline is inaccurate because A. a change in the price of personal computers shifts the demand curve. B. a change in the price of personal computers shifts the supply curve. C. the statement is backwards: increased d ...
This file includes the answers to the problems at the end of Chapters
... whether seeing the play is worth spending $10. If it is, you should see it; otherwise not. Whichever your answer, it must be the same in both cases. 8. Since you have already bought your ticket, the $30 you spent on it is a sunk cost. It is money you cannot recover, whether or not you go to the game ...
... whether seeing the play is worth spending $10. If it is, you should see it; otherwise not. Whichever your answer, it must be the same in both cases. 8. Since you have already bought your ticket, the $30 you spent on it is a sunk cost. It is money you cannot recover, whether or not you go to the game ...
Downlaod File
... firms is actually paid out in money. The second kind is implicit cost and it is a cost that does not require and actual expenditure of money. From an economist point of view cost is calculated by adding both explicit cost and implicit cost. Implicit cost is also counted as the opportunity cost of th ...
... firms is actually paid out in money. The second kind is implicit cost and it is a cost that does not require and actual expenditure of money. From an economist point of view cost is calculated by adding both explicit cost and implicit cost. Implicit cost is also counted as the opportunity cost of th ...
research paper series Research Paper 2008/35
... The possible relationship between international trade and wage inequality in developed countries has been a very important and regularly debated topic for both academics and politicians the last decade. Unskilled workers in many developed countries and especially in US have seen a significant declin ...
... The possible relationship between international trade and wage inequality in developed countries has been a very important and regularly debated topic for both academics and politicians the last decade. Unskilled workers in many developed countries and especially in US have seen a significant declin ...
Supply Powerpoint
... A subsidy is a government payment to an individual, business, or other group to encourage or protect a certain type of economic activity. The government pays suppliers to guarantee a consistent supply. The subsidy lowers production costs and allows for greater supply. ...
... A subsidy is a government payment to an individual, business, or other group to encourage or protect a certain type of economic activity. The government pays suppliers to guarantee a consistent supply. The subsidy lowers production costs and allows for greater supply. ...
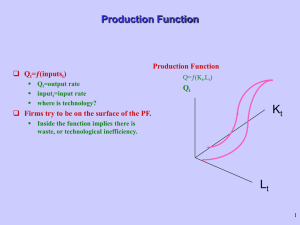
Production Function - National Bureau of Economic Research
... Different combinations of Kt and Lt which generate the same level of output, Qt. ...
... Different combinations of Kt and Lt which generate the same level of output, Qt. ...
Ch 5 notes
... An Introduction to Supply (cont.) • The quantity supplied is the amount producers bring to market at any given price. • A change in price leads to a change in quantity supplied. • Although the producer has the freedom to adjust production up or down, the interaction of supply and demand usually det ...
... An Introduction to Supply (cont.) • The quantity supplied is the amount producers bring to market at any given price. • A change in price leads to a change in quantity supplied. • Although the producer has the freedom to adjust production up or down, the interaction of supply and demand usually det ...
What is Supply? - Locust Fork High School
... If the cost of inputs increases, producers would not be willing to produce as many shirts at each and every. The supply curve would shift left. ...
... If the cost of inputs increases, producers would not be willing to produce as many shirts at each and every. The supply curve would shift left. ...
trade of quality differentiated goods and import elasticities.
... amount of all the characteristics, they are similar or horizontally differentiated. If one of them have a greater amount of all the characteristics, it is qualitatively better than the other, and will probably cost more. We refer to this situation talking of vertical differentiation. Every sector in ...
... amount of all the characteristics, they are similar or horizontally differentiated. If one of them have a greater amount of all the characteristics, it is qualitatively better than the other, and will probably cost more. We refer to this situation talking of vertical differentiation. Every sector in ...
PDF
... typically reported in bulk quantities and values at dockside. Consumers almost never purchase commodities in such quantities or at the port. Therefore, assuming that import decisions are made by a profit-maximizing firm is more consistent with how trade data is typically reported. Kohli (1991) notes ...
... typically reported in bulk quantities and values at dockside. Consumers almost never purchase commodities in such quantities or at the port. Therefore, assuming that import decisions are made by a profit-maximizing firm is more consistent with how trade data is typically reported. Kohli (1991) notes ...
Supply and Demand - Technology Learner
... are at the same level. In this case, the quantity of items available for sale is equal to customer demand for those items. In a situation of equilibrium, prices tend to remain stable. When a product is at equilibrium, business owners are happy because their stock is selling well and customers are ha ...
... are at the same level. In this case, the quantity of items available for sale is equal to customer demand for those items. In a situation of equilibrium, prices tend to remain stable. When a product is at equilibrium, business owners are happy because their stock is selling well and customers are ha ...
Taran Fæhn and Erling Holmøy Welfare Effects of Trade
... modelling rational intertemporal behaviour by both households and firms. Besides endogenous determination of the capital endowment, MSG-6 also determines how labour supply is endogenously affected by trade liberalisation. The role of scale economies and imperfect competition is addressed in several ...
... modelling rational intertemporal behaviour by both households and firms. Besides endogenous determination of the capital endowment, MSG-6 also determines how labour supply is endogenously affected by trade liberalisation. The role of scale economies and imperfect competition is addressed in several ...
Efficiency and Adaptation: Production and Cost: Economic Cost: In
... enough that a firm can change all factors of production] decision. Production Costs in the Short-Run The key principle behind a firm's short-run cost curves is this: as one input increases while the other inputs are held fixed, output increases but at a decreasing rate (diminishing returns). The sho ...
... enough that a firm can change all factors of production] decision. Production Costs in the Short-Run The key principle behind a firm's short-run cost curves is this: as one input increases while the other inputs are held fixed, output increases but at a decreasing rate (diminishing returns). The sho ...
Price, income and cross price elasticities of demand Price elasticity
... A necessary good, such as bread or electricity, will have a relatively inelastic demand. In other words, even if the price increases significantly, consumers will still demand bread and electricity, because they need it. Luxury goods, such as holidays, are more elastic. If the price of flights incre ...
... A necessary good, such as bread or electricity, will have a relatively inelastic demand. In other words, even if the price increases significantly, consumers will still demand bread and electricity, because they need it. Luxury goods, such as holidays, are more elastic. If the price of flights incre ...
P w
... Supply, Demand, and Trade in a Single Industry • Suppose that there are two countries (Home and ...
... Supply, Demand, and Trade in a Single Industry • Suppose that there are two countries (Home and ...
Ch04 Labor and Financial Markets Multiple Choice Questions 1. The
... substitute for low-skill labor becomes cheaper, demand for low-skill labor will shift to the left, as shown by the shift from D0 to D1 in the market for low-skill labor. As the technology complement for high-skill labor becomes cheaper, demand for high-skill labor will shift to the right, as shown b ...
... substitute for low-skill labor becomes cheaper, demand for low-skill labor will shift to the left, as shown by the shift from D0 to D1 in the market for low-skill labor. As the technology complement for high-skill labor becomes cheaper, demand for high-skill labor will shift to the right, as shown b ...
Lecture 4
... 2500. How much does it pay? Now how much does the store pay if it is offered an incremental ...
... 2500. How much does it pay? Now how much does the store pay if it is offered an incremental ...
Chapter 3: Supply and Demand
... can be used to analyze market conditions in which management decisions about price and allocations must be made. • Use supply and demand diagrams to show how determinants of supply and demand interact to determine price in the short and long run 2006 Prentice Hall Business Publishing ...
... can be used to analyze market conditions in which management decisions about price and allocations must be made. • Use supply and demand diagrams to show how determinants of supply and demand interact to determine price in the short and long run 2006 Prentice Hall Business Publishing ...
Chapters 4&5 - Pearland ISD
... Taxpayers lose additional time and money documenting, computing, and avoiding taxes over and above the actual taxes they pay. The administrative burden of any tax system is part of the inefficiency it ...
... Taxpayers lose additional time and money documenting, computing, and avoiding taxes over and above the actual taxes they pay. The administrative burden of any tax system is part of the inefficiency it ...
Comparative advantage

The theory of comparative advantage is an economic theory about the work gains from trade for individuals, firms, or nations that arise from differences in their factor endowments or technological progress. In an economic model, an agent has a comparative advantage over another in producing a particular good if he can produce that good at a lower relative opportunity cost or autarky price, i.e. at a lower relative marginal cost prior to trade. One does not compare the monetary costs of production or even the resource costs (labor needed per unit of output) of production. Instead, one must compare the opportunity costs of producing goods across countries. The closely related law or principle of comparative advantage holds that under free trade, an agent will produce more of and consume less of a good for which he has a comparative advantage.David Ricardo developed the classical theory of comparative advantage in 1817 to explain why countries engage in international trade even when one country's workers are more efficient at producing every single good than workers in other countries. He demonstrated that if two countries capable of producing two commodities engage in the free market, then each country will increase its overall consumption by exporting the good for which it has a comparative advantage while importing the other good, provided that there exist differences in labor productivity between both countries. Widely regarded as one of the most powerful yet counter-intuitive insights in economics, Ricardo's theory implies that comparative advantage rather than absolute advantage is responsible for much of international trade.