The Markets for the Factors of Production
... The supply of labor arises from individuals’ trade-off between work and leisure. An upward-sloping labor-supply curve means that people respond to an increase in the wage by enjoying less leisure and working more hours. Although labor supply need not be upward sloping in all cases, for now we will a ...
... The supply of labor arises from individuals’ trade-off between work and leisure. An upward-sloping labor-supply curve means that people respond to an increase in the wage by enjoying less leisure and working more hours. Although labor supply need not be upward sloping in all cases, for now we will a ...
International Trade Chapter 9
... – A country that is isolated from the rest of the world and produces tomatoes. – The market for tomatoes consists of the buyers and sellers of the country. – Domestic Price adjusts to balance Demand and Supply. – The sum of consumer and producer surplus measures the total benefits. Principles of Mic ...
... – A country that is isolated from the rest of the world and produces tomatoes. – The market for tomatoes consists of the buyers and sellers of the country. – Domestic Price adjusts to balance Demand and Supply. – The sum of consumer and producer surplus measures the total benefits. Principles of Mic ...
ECON211 Midterm I_an..
... c. section (a) of the demand curve in diagram 1 d. over section (b) of the demand curve in diagram 1 19. Demand is perfectly inelastic a. over the entire demand curve in diagram 3 b. over the entire demand curve in diagram 2 c. over the entire demand curve in diagram 1 d. section (a) of the demand c ...
... c. section (a) of the demand curve in diagram 1 d. over section (b) of the demand curve in diagram 1 19. Demand is perfectly inelastic a. over the entire demand curve in diagram 3 b. over the entire demand curve in diagram 2 c. over the entire demand curve in diagram 1 d. section (a) of the demand c ...
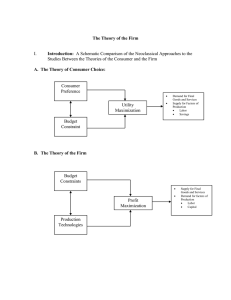
influence of isocost and isoquant on firm out subject to
... and consider the special cases where the commodities can only be produced with least cost factor combination. ...
... and consider the special cases where the commodities can only be produced with least cost factor combination. ...
B. The Theory of the Firm
... isoquant implies that, as a general rule, the marginal rate of technical substitution of labor for capital tends to decrease as an increasing amount of labor is substituted for capital. This is known as the law of diminishing marginal rate of technical substitution. This law can be easily verified ...
... isoquant implies that, as a general rule, the marginal rate of technical substitution of labor for capital tends to decrease as an increasing amount of labor is substituted for capital. This is known as the law of diminishing marginal rate of technical substitution. This law can be easily verified ...
File
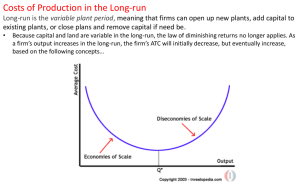
... Explain the relationship in the short run between the marginal costs of a firm and its average total costs. (10 marks) The short-run refers to the "fixed-plant period" when capital and land are fixed and labor is the only variable resource. As output increases in the SR, marginal product of labor in ...
... Explain the relationship in the short run between the marginal costs of a firm and its average total costs. (10 marks) The short-run refers to the "fixed-plant period" when capital and land are fixed and labor is the only variable resource. As output increases in the SR, marginal product of labor in ...
Labor Demand
... equals the value of marginal product of labor (left panel). This corresponds to the marginal cost of production being equal to the output price (right panel). For example, if the wage is $22, the rm hires eight workers. However, if the wage is $38, the value of average product of labor would be les ...
... equals the value of marginal product of labor (left panel). This corresponds to the marginal cost of production being equal to the output price (right panel). For example, if the wage is $22, the rm hires eight workers. However, if the wage is $38, the value of average product of labor would be les ...
332 selected chapter +
... productivity and will cause an increase or rightward shift in the demand for unskilled labor. To the extent that the benefits of an increase in the quality of education are recognized by students, more will stay in school and a secondary effect of a decrease or leftward shift in the supply of unskil ...
... productivity and will cause an increase or rightward shift in the demand for unskilled labor. To the extent that the benefits of an increase in the quality of education are recognized by students, more will stay in school and a secondary effect of a decrease or leftward shift in the supply of unskil ...
Econ Survey
... 62. If price rises, what happens to supply for a product? a. It increases. b. It decreases. c. It does not change. d. Uncertain-economic theory has no answer to this question. 63. . If price rises, what happens to quantity supplied for a product? a. It increases. b. It decreases. c. It does not cha ...
... 62. If price rises, what happens to supply for a product? a. It increases. b. It decreases. c. It does not change. d. Uncertain-economic theory has no answer to this question. 63. . If price rises, what happens to quantity supplied for a product? a. It increases. b. It decreases. c. It does not cha ...
Perfect Competition File
... The industry in perfect competition will face normal demand and supply curves. We would expect producers to wish to supply more at higher prices and we would expect consumers to demand less as price rises. The industry price would be P and the quantity demanded Q. For individual firms they have to ...
... The industry in perfect competition will face normal demand and supply curves. We would expect producers to wish to supply more at higher prices and we would expect consumers to demand less as price rises. The industry price would be P and the quantity demanded Q. For individual firms they have to ...
short-run production function
... • Law of Diminishing Returns: As additional units of a variable input are combined with a fixed input, at some point the additional output (i.e., marginal product) starts to diminish. – Nothing says when diminishing returns will start to take effect, only that it will happen at some point. – All in ...
... • Law of Diminishing Returns: As additional units of a variable input are combined with a fixed input, at some point the additional output (i.e., marginal product) starts to diminish. – Nothing says when diminishing returns will start to take effect, only that it will happen at some point. – All in ...
Econ 281 Chapter09
... increases. If for the next unit, MR>MC, that unit should be produced, as it yields profit. If for the last unit, MC>MR, that unit should not have been produced, as it decreases profit. Therefore profit is maximized where ...
... increases. If for the next unit, MR>MC, that unit should be produced, as it yields profit. If for the last unit, MC>MR, that unit should not have been produced, as it decreases profit. Therefore profit is maximized where ...
Increasing Returns to Scale and Monopolistic Competition Prepared
... price PM. The monopoly equilibrium is at point A. ...
... price PM. The monopoly equilibrium is at point A. ...
SOLUTIONS TO TEXT PROBLEMS:
... Since average income in the United States has roughly doubled every 35 years, we are likely to have a better standard of living than our parents, and a much better standard of living than our grandparents. This is mainly the result of increased productivity, so that an hour of work produces more goo ...
... Since average income in the United States has roughly doubled every 35 years, we are likely to have a better standard of living than our parents, and a much better standard of living than our grandparents. This is mainly the result of increased productivity, so that an hour of work produces more goo ...
Chapter 3 Lecture
... Product and Labor Markets Are Competitive Labor Demand in Terms of Real Wages • Labor demand can be analyzed in terms of either real or money wages. • The negative slope of the labor demand curve indicates that each additional unit of labor employed produces a progressively smaller increment in outp ...
... Product and Labor Markets Are Competitive Labor Demand in Terms of Real Wages • Labor demand can be analyzed in terms of either real or money wages. • The negative slope of the labor demand curve indicates that each additional unit of labor employed produces a progressively smaller increment in outp ...
Recovering Markups from Production Data
... made way for the use of fixed effects estimators, and consequently first differencing of the data, which did not produce satisfactory results and relied on hard to maintain assumptions that productivity shocks are not time varying while increasing the role of measurement error in the estimation proced ...
... made way for the use of fixed effects estimators, and consequently first differencing of the data, which did not produce satisfactory results and relied on hard to maintain assumptions that productivity shocks are not time varying while increasing the role of measurement error in the estimation proced ...
CHAPTER TWELVE
... spent on each makes the same contribution to total output; the rule implies that firms will change inputs in response to technological change or changes in input prices. B. A recent real-world example of firms using the least cost combination of inputs is in the banking industry, in which ATMs are r ...
... spent on each makes the same contribution to total output; the rule implies that firms will change inputs in response to technological change or changes in input prices. B. A recent real-world example of firms using the least cost combination of inputs is in the banking industry, in which ATMs are r ...
Production & Cost in the Firm
... – Earn more than expected – Normal profit • The accounting profit earned when all resources earn their opportunity costs • What you expect to earn ...
... – Earn more than expected – Normal profit • The accounting profit earned when all resources earn their opportunity costs • What you expect to earn ...
Document
... 14. What will be the effect of the following on elasticity of demand for a commodity (a) Income level of buyers (b) Habit of the consumer 15. What will be the slope of demand curve under following situations. (a) Perfectly elastic demand (b) Perfectly inelastic demand (c) Unit elastic demand. 16. St ...
... 14. What will be the effect of the following on elasticity of demand for a commodity (a) Income level of buyers (b) Habit of the consumer 15. What will be the slope of demand curve under following situations. (a) Perfectly elastic demand (b) Perfectly inelastic demand (c) Unit elastic demand. 16. St ...
Practice Midterm #2
... a. set their own (firm) price at the point where it is equal to marginal cost b. produce where the firm’s marginal cost is equal to their own average cost c. set their own (firm) price at the point where it is equal to average cost d. produce where the market price is equal to marginal cost 19) Whic ...
... a. set their own (firm) price at the point where it is equal to marginal cost b. produce where the firm’s marginal cost is equal to their own average cost c. set their own (firm) price at the point where it is equal to average cost d. produce where the market price is equal to marginal cost 19) Whic ...
Supply
... primarily about the consumers (their choices about what to buy, when/how much to buy, etc.). When talking about supply, we are talking primarily about producers and firms. A very important distinction! ...
... primarily about the consumers (their choices about what to buy, when/how much to buy, etc.). When talking about supply, we are talking primarily about producers and firms. A very important distinction! ...
Pre-Test Chap 01 Handout Page
... Table 1.1 shows the production-possibilities frontier for the economy of “Relativity.” If this economy were to produce 2 (hundred) tractors and only 30 (tons) of corn, (a) it would be operating beyond its production-possibilities frontier. (b) it would be utilizing its resources with maximum efficie ...
... Table 1.1 shows the production-possibilities frontier for the economy of “Relativity.” If this economy were to produce 2 (hundred) tractors and only 30 (tons) of corn, (a) it would be operating beyond its production-possibilities frontier. (b) it would be utilizing its resources with maximum efficie ...
Microeconomics Released Exam no answers
... 17. A country can consume beyond its present production possibilities curve when it (A) trades with other countries, thus taking advantage of different opportunity costs (B) reduces unemployment, thus increasing output (C) experiences decreasing opportunity costs (D) faces an upward-sloping producti ...
... 17. A country can consume beyond its present production possibilities curve when it (A) trades with other countries, thus taking advantage of different opportunity costs (B) reduces unemployment, thus increasing output (C) experiences decreasing opportunity costs (D) faces an upward-sloping producti ...
Comparative advantage

The theory of comparative advantage is an economic theory about the work gains from trade for individuals, firms, or nations that arise from differences in their factor endowments or technological progress. In an economic model, an agent has a comparative advantage over another in producing a particular good if he can produce that good at a lower relative opportunity cost or autarky price, i.e. at a lower relative marginal cost prior to trade. One does not compare the monetary costs of production or even the resource costs (labor needed per unit of output) of production. Instead, one must compare the opportunity costs of producing goods across countries. The closely related law or principle of comparative advantage holds that under free trade, an agent will produce more of and consume less of a good for which he has a comparative advantage.David Ricardo developed the classical theory of comparative advantage in 1817 to explain why countries engage in international trade even when one country's workers are more efficient at producing every single good than workers in other countries. He demonstrated that if two countries capable of producing two commodities engage in the free market, then each country will increase its overall consumption by exporting the good for which it has a comparative advantage while importing the other good, provided that there exist differences in labor productivity between both countries. Widely regarded as one of the most powerful yet counter-intuitive insights in economics, Ricardo's theory implies that comparative advantage rather than absolute advantage is responsible for much of international trade.