Market Equilibrium and Applications
... C. the difference between the dollar amounts people would willingly pay for specific quantities of goods and the amounts they pay at market prices. D. less for goods that are luxuries than for necessities. E. all of the above. 8. According to the law of diminishing marginal utility: A. marginal util ...
... C. the difference between the dollar amounts people would willingly pay for specific quantities of goods and the amounts they pay at market prices. D. less for goods that are luxuries than for necessities. E. all of the above. 8. According to the law of diminishing marginal utility: A. marginal util ...
Lecture 13
... To return to equality the consumer must adjust his/her consumption. (Have in mind that the consumer cannot change prices, and he/she has an income constraint.) What are the consumer’s options? ...
... To return to equality the consumer must adjust his/her consumption. (Have in mind that the consumer cannot change prices, and he/she has an income constraint.) What are the consumer’s options? ...
uwcmaastricht-econ
... As I had already mentioned in class, except for the last question, your answers should be in essay form, which means that a simple list of points is not enough. Abbreviations such as P or Q are only accepted in the diagram: your answers should include full words, so supply (not S!), demand (not ...
... As I had already mentioned in class, except for the last question, your answers should be in essay form, which means that a simple list of points is not enough. Abbreviations such as P or Q are only accepted in the diagram: your answers should include full words, so supply (not S!), demand (not ...
Chapter 9: Monopoly
... sell all four diamonds for $6,750 each, sacrificing $250 on each of the first three diamonds that could have been sold for $7,000 each The loss in revenue from the first three units is $750 The net change in total revenue from selling the 4th diamond is ...
... sell all four diamonds for $6,750 each, sacrificing $250 on each of the first three diamonds that could have been sold for $7,000 each The loss in revenue from the first three units is $750 The net change in total revenue from selling the 4th diamond is ...
Chapter 2 An Introduction to Modeling, Efficiency and Equity
... 2. Each consumer is non satiable 3. Each consumer has strictly convex preferences or stated informally, prefer diversity in consumption bundles 4. Each consumer makes resource allocation choices in accordance with his/her ordering We will explain those assumptions in the next slide ...
... 2. Each consumer is non satiable 3. Each consumer has strictly convex preferences or stated informally, prefer diversity in consumption bundles 4. Each consumer makes resource allocation choices in accordance with his/her ordering We will explain those assumptions in the next slide ...
CHAPTER 10 MARKET POWER: MONOPOLY AND MONOPSONY
... Chapter 10: Market Power: Monopoly and Monopsony Suppose initially that the consumers must pay the tax to the government. Since the total price (including the tax) consumers would be willing to pay remains unchanged, we know that the demand function is P* + T = 100 - 0.01Q, or P* = 100 - 0.01Q - T, ...
... Chapter 10: Market Power: Monopoly and Monopsony Suppose initially that the consumers must pay the tax to the government. Since the total price (including the tax) consumers would be willing to pay remains unchanged, we know that the demand function is P* + T = 100 - 0.01Q, or P* = 100 - 0.01Q - T, ...
sol_10
... Chapter 10: Market Power: Monopoly and Monopsony Suppose initially that the consumers must pay the tax to the government. Since the total price (including the tax) consumers would be willing to pay remains unchanged, we know that the demand function is P* + T = 100 - 0.01Q, or P* = 100 - 0.01Q - T, ...
... Chapter 10: Market Power: Monopoly and Monopsony Suppose initially that the consumers must pay the tax to the government. Since the total price (including the tax) consumers would be willing to pay remains unchanged, we know that the demand function is P* + T = 100 - 0.01Q, or P* = 100 - 0.01Q - T, ...
Demand
... How much does the person really want to go to China or how big a hassle is it to come back. Number of Individuals going to Chinese Consulate for visa. ...
... How much does the person really want to go to China or how big a hassle is it to come back. Number of Individuals going to Chinese Consulate for visa. ...
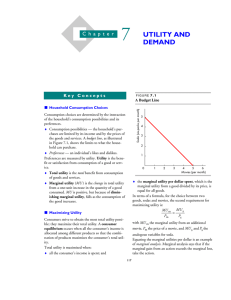
Chapter 7: Utility and Demand
... curve for soda. The demand curve for movies, a substitute for soda, shifts rightward. ♦ Movies and soda are normal goods, so an increase in income increases the consumption of both products and thereby increases the demand for both products. The individual demand is the relationship between the pric ...
... curve for soda. The demand curve for movies, a substitute for soda, shifts rightward. ♦ Movies and soda are normal goods, so an increase in income increases the consumption of both products and thereby increases the demand for both products. The individual demand is the relationship between the pric ...
Chapter 2
... Production Possibilities and Opportunity Cost The production possibilities frontier (PPF) is the boundary between those combinations of goods and services that can be produced and those that cannot. To illustrate the PPF, we focus on two goods at a time and hold the quantities of all other goods an ...
... Production Possibilities and Opportunity Cost The production possibilities frontier (PPF) is the boundary between those combinations of goods and services that can be produced and those that cannot. To illustrate the PPF, we focus on two goods at a time and hold the quantities of all other goods an ...
ANSWERS PS#2 - Economics 352
... 1. Critically evaluate the following statements and explain in what way they are true, false, or uncertain. a) Monopolists are never ever allocatively efficient. ANS: True, unless their demand curve is completely elastic (unlikely), or they successfully practice 1st degree price discriminate, or the ...
... 1. Critically evaluate the following statements and explain in what way they are true, false, or uncertain. a) Monopolists are never ever allocatively efficient. ANS: True, unless their demand curve is completely elastic (unlikely), or they successfully practice 1st degree price discriminate, or the ...
11 PERFECT COMPETITION
... infinite. More realistically, Lin would probably sell the quantity that maximizes his profit but that profit will be less than if he sells at the going market price of $10 a box. The elasticity of demand for Lin’s cookies is infinite. The elasticity of demand in the market for cookies is not infinit ...
... infinite. More realistically, Lin would probably sell the quantity that maximizes his profit but that profit will be less than if he sells at the going market price of $10 a box. The elasticity of demand for Lin’s cookies is infinite. The elasticity of demand in the market for cookies is not infinit ...
ap microeconomics - Northview High School
... Unit 1: Key Concepts and Skills 1. Define the science of economics; distinguish between macroeconomics and microeconomics. 2. Distinguish between opportunity cost, scarcity, and tradeoffs. 3. Use a production possibilities curve (PPC) to illustrate opportunity cost and growth. 4. Describe the impact ...
... Unit 1: Key Concepts and Skills 1. Define the science of economics; distinguish between macroeconomics and microeconomics. 2. Distinguish between opportunity cost, scarcity, and tradeoffs. 3. Use a production possibilities curve (PPC) to illustrate opportunity cost and growth. 4. Describe the impact ...
expectimax search - inst.eecs.berkeley.edu
... So limiting depth is less damaging But pruning is less possible… ...
... So limiting depth is less damaging But pruning is less possible… ...
Document
... total fixed costs of $25,000, average variable costs for 1,000 units of the product of $45, and marginal revenue of $75. What is his total economic profit? ...
... total fixed costs of $25,000, average variable costs for 1,000 units of the product of $45, and marginal revenue of $75. What is his total economic profit? ...