Lecture 2 - Illinois State University
... electricity. A study was done to determine the benefit to each city as follows: • Chicago – Marginal Benefit=10-0.5Q • Naperville – Marginal Benefit=5-0.5Q • Rockford – Marginal Benefit=10-1Q ...
... electricity. A study was done to determine the benefit to each city as follows: • Chicago – Marginal Benefit=10-0.5Q • Naperville – Marginal Benefit=5-0.5Q • Rockford – Marginal Benefit=10-1Q ...
3_Consumer_Theory
... preferences and tastes. It analyzes the individual behavior aimed at satisfying needs. ─ Economics gives an answer to the question: How should one act in the most rational manner? ─ Model of rational consumer describes the general patterns of consumer behavior. ─ The aim of the rational consumer is ...
... preferences and tastes. It analyzes the individual behavior aimed at satisfying needs. ─ Economics gives an answer to the question: How should one act in the most rational manner? ─ Model of rational consumer describes the general patterns of consumer behavior. ─ The aim of the rational consumer is ...
Ch5Sec2
... The marginal product of labor is the change in output from hiring one more worker. It measures the change in output at the margin, where the last worker has been hired or fired. Increasing Marginal Returns- Output increases with each additional worker. Diminishing Marginal Returns- Adding more worke ...
... The marginal product of labor is the change in output from hiring one more worker. It measures the change in output at the margin, where the last worker has been hired or fired. Increasing Marginal Returns- Output increases with each additional worker. Diminishing Marginal Returns- Adding more worke ...
Slides19.pdf
... If he tries perfect discrim., consumer can gain by pretending to be lower types. Let u(i, j) = utility of a consumer of Type i from offer intended for Type j. u(i, j) = Hi (Q∗j ) + [ Ii − Hj (Q∗j ) ] . So u(i, j) − u(i, i) = Hi (Q∗j ) − Hj (Q∗j ) ...
... If he tries perfect discrim., consumer can gain by pretending to be lower types. Let u(i, j) = utility of a consumer of Type i from offer intended for Type j. u(i, j) = Hi (Q∗j ) + [ Ii − Hj (Q∗j ) ] . So u(i, j) − u(i, i) = Hi (Q∗j ) − Hj (Q∗j ) ...
Principles of Microeconomics Sample Mid-Term Examination
... exchange. Several months later he is deciding whether to exchange the ticket for a ticket of the same price to Acapulco. The opportunity cost of go to Acapulco would equal the A. ticket price of $475 plus the $75 exchange fee, if he has no other trip that he will take within the year. B. ticket pric ...
... exchange. Several months later he is deciding whether to exchange the ticket for a ticket of the same price to Acapulco. The opportunity cost of go to Acapulco would equal the A. ticket price of $475 plus the $75 exchange fee, if he has no other trip that he will take within the year. B. ticket pric ...
Chapter 7
... Key Terms Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility Theory of Consumer Behavior Deriving the Demand Curve Applications and Extensions Last Word Appendix ...
... Key Terms Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility Theory of Consumer Behavior Deriving the Demand Curve Applications and Extensions Last Word Appendix ...
Review Session #2
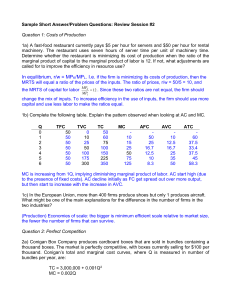
... 4c) Define a natural monopoly, explaining what the size of the market has to do with whether an industry is a natural monopoly. Suppose that a natural monopolist were required by law to charge its average cost. Draw a diagram, label the price charged, and the deadweight loss to society relative to m ...
... 4c) Define a natural monopoly, explaining what the size of the market has to do with whether an industry is a natural monopoly. Suppose that a natural monopolist were required by law to charge its average cost. Draw a diagram, label the price charged, and the deadweight loss to society relative to m ...
Rational Spending Rule
... • Suppose vanilla ice cream goes from $1 per pint to $2 – If Sarah spends all her income on vanilla, the amount she can buy goes down by half – At the original prices, she could buy 100 pints of vanilla and 150 pints of chocolate • At new price for vanilla, she buys 100 vanilla and only ...
... • Suppose vanilla ice cream goes from $1 per pint to $2 – If Sarah spends all her income on vanilla, the amount she can buy goes down by half – At the original prices, she could buy 100 pints of vanilla and 150 pints of chocolate • At new price for vanilla, she buys 100 vanilla and only ...
Name
... c. Explain the relationship between the marginal product curve and the marginal cost curve. In your response, explain why the marginal cost curve is “U” shaped using numerical examples. (____/5) 3. Below is information regarding Cory’s Surfboard Inc. Complete the table and do the following (____/5): ...
... c. Explain the relationship between the marginal product curve and the marginal cost curve. In your response, explain why the marginal cost curve is “U” shaped using numerical examples. (____/5) 3. Below is information regarding Cory’s Surfboard Inc. Complete the table and do the following (____/5): ...
ECON 501
... Meaning that consumer needs 2Y in order to be as happy as having 1X. MU is measured in “utils”, which is rather a subjective index, but it can be used because actual numbers are not important, order is important. ...
... Meaning that consumer needs 2Y in order to be as happy as having 1X. MU is measured in “utils”, which is rather a subjective index, but it can be used because actual numbers are not important, order is important. ...
Document
... ____ 9. Figure 4-4 depicts a market in which the government has imposed a price floor of $5.00 per unit. To maintain the price floor, the government should a. buy 200 units of the good b. sell 200 units of the good c. buy 700 units of the good d. sell 700 units of the good e. buy 500 units of the g ...
... ____ 9. Figure 4-4 depicts a market in which the government has imposed a price floor of $5.00 per unit. To maintain the price floor, the government should a. buy 200 units of the good b. sell 200 units of the good c. buy 700 units of the good d. sell 700 units of the good e. buy 500 units of the g ...