Unit 1
... • Decisions require comparing costs and benefits of alternatives. – Whether to go to college or to work? – Whether to study or go out on a date? – Whether to go to class or sleep in? ...
... • Decisions require comparing costs and benefits of alternatives. – Whether to go to college or to work? – Whether to study or go out on a date? – Whether to go to class or sleep in? ...
WHAT IS ECONOMICS?
... scientifically, but individual human behavior is complicated, driven by many factors, and cannot be fully explained by simple precise mathematical relationships (e.g. E = mc^2 ) • We rely on simple theoretical models to understand consumer and producer behavior and price formation in markets of diff ...
... scientifically, but individual human behavior is complicated, driven by many factors, and cannot be fully explained by simple precise mathematical relationships (e.g. E = mc^2 ) • We rely on simple theoretical models to understand consumer and producer behavior and price formation in markets of diff ...
"economic decision making" unit powerpoint
... *hypothetical country that can use its resources to produce just two goods: cell phones or bananas. *Its workers can be trained to assemble phones, raise bananas, or both. Its capital goods consist of assembly-line equipment, farm machinery, or some of each. *This shape indicates that the tradeoffs ...
... *hypothetical country that can use its resources to produce just two goods: cell phones or bananas. *Its workers can be trained to assemble phones, raise bananas, or both. Its capital goods consist of assembly-line equipment, farm machinery, or some of each. *This shape indicates that the tradeoffs ...
Input Market
... unit of input brings in more, than it costs therefore, firms hire additional unit and extend the production, MRP < MFC – firm will hire less of given input and reduce the production. ...
... unit of input brings in more, than it costs therefore, firms hire additional unit and extend the production, MRP < MFC – firm will hire less of given input and reduce the production. ...
AP Microeconomics Syllabus
... 1.) Introduction to Economics. In this unit students will be introduced to the economic concepts of scarcity, opportunity cost, and marginal analysis; learn and use the production possibility frontier and circular flow models; and participate in a simulation of the circular flow model and use the pr ...
... 1.) Introduction to Economics. In this unit students will be introduced to the economic concepts of scarcity, opportunity cost, and marginal analysis; learn and use the production possibility frontier and circular flow models; and participate in a simulation of the circular flow model and use the pr ...
John Stuart Mill, Principles of Political Economy, 1848
... David Ricardo, Principles of Political Economy & Taxation, 1817 Nassau Senior, Outline of the Science of Political Economy, 1836 John Stuart Mill, Principles of Political Economy, 1848 Alfred Marshall, Principles of Economics, 1898 Paul Samuelson, Economics, 1948 ...
... David Ricardo, Principles of Political Economy & Taxation, 1817 Nassau Senior, Outline of the Science of Political Economy, 1836 John Stuart Mill, Principles of Political Economy, 1848 Alfred Marshall, Principles of Economics, 1898 Paul Samuelson, Economics, 1948 ...
Microeconomic Analysis
... 2. Identify and calculate producer and consumer surplus. 3. Analyze the effects of a demand/supply shock, per-unit tax, free trade, and trade restrictions on equilibrium price and quantity. 4. Describe the technical and legal barriers to entry that allow existence of a monopoly market structure. 5. ...
... 2. Identify and calculate producer and consumer surplus. 3. Analyze the effects of a demand/supply shock, per-unit tax, free trade, and trade restrictions on equilibrium price and quantity. 4. Describe the technical and legal barriers to entry that allow existence of a monopoly market structure. 5. ...
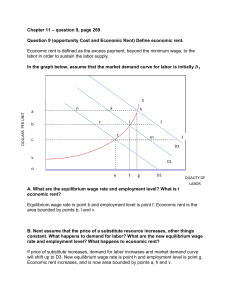
Chapter 11 – question 9, page 269 Question 9 (opportunity Cost and
... Supply labor curve over this range of wages would be vertical, because the quantity of labor supply would not change if substitution effect exactly offsets the income effect. ...
... Supply labor curve over this range of wages would be vertical, because the quantity of labor supply would not change if substitution effect exactly offsets the income effect. ...
Labor Unions - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... alternative wage rates. • The market labor demand includes all the workers the firms are willing and able to hire at alternative wage rates. • Together they determine the equilibrium wage rate, where the quantity of labor supplied equals the quantity of labor demanded. ...
... alternative wage rates. • The market labor demand includes all the workers the firms are willing and able to hire at alternative wage rates. • Together they determine the equilibrium wage rate, where the quantity of labor supplied equals the quantity of labor demanded. ...
Economics of International Migration2 - e
... • Cost-benefit analysis, taking into the account current and future income, employment/deportation probability etc. • Migation perceived as investment ...
... • Cost-benefit analysis, taking into the account current and future income, employment/deportation probability etc. • Migation perceived as investment ...
Ch.5 Vocabulary Quiz _____ Name period A. Law of supply H
... _____1. A tax on the production or sale of a good. _____2. The cost of operating a facility, such as a store or factory. _____3. A chart that lists how much of a good a supplier will offer at different prices. _____4. A cost that does not change, no matter how much of a good is produced. _____5. A g ...
... _____1. A tax on the production or sale of a good. _____2. The cost of operating a facility, such as a store or factory. _____3. A chart that lists how much of a good a supplier will offer at different prices. _____4. A cost that does not change, no matter how much of a good is produced. _____5. A g ...
Honors 102 - Fresno State email
... consequences of the Industrial Revolution in England? How did these changes influence economic theories? 2. Explain David Ricardo’s theory of rent (make sure to give a numerical example). What is the significance of this theory for distribution of income and the rate of profit in economy? 3. What wa ...
... consequences of the Industrial Revolution in England? How did these changes influence economic theories? 2. Explain David Ricardo’s theory of rent (make sure to give a numerical example). What is the significance of this theory for distribution of income and the rate of profit in economy? 3. What wa ...
factor markets 2010
... cheaper capital for the relatively more expensive labor – a switch a to capital ...
... cheaper capital for the relatively more expensive labor – a switch a to capital ...
If two inputs (capital and labor) are gross
... and the daily wage rate is W = $90 per day. The firm should adjust P, or W, or both in order to equate marginal revenue product to the marginal expense of labor. not alter the employment level, as the firm is already earning a profit of $60 for each worker employed. reduce employment because that wi ...
... and the daily wage rate is W = $90 per day. The firm should adjust P, or W, or both in order to equate marginal revenue product to the marginal expense of labor. not alter the employment level, as the firm is already earning a profit of $60 for each worker employed. reduce employment because that wi ...
AP Microeconomics Syllabus
... 1.) Introduction to Economics. In this unit students will be introduced to the economic concepts of scarcity, opportunity cost, and marginal analysis; learn and use the production possibility frontier and circular flow models; and participate in a simulation of the circular flow model and use the pr ...
... 1.) Introduction to Economics. In this unit students will be introduced to the economic concepts of scarcity, opportunity cost, and marginal analysis; learn and use the production possibility frontier and circular flow models; and participate in a simulation of the circular flow model and use the pr ...
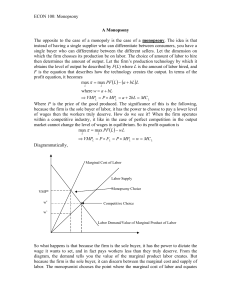
ECON 100: Monopsony A Monopsony The opposite to the case of a
... would be taken advantage of if they are not organized. An example would be the sports franchises, like MLB, NHL, NLL, MLS and NFL. Do you think this provides the rational for why the players are always represented by a players association or union? Could we examine what happens if we have one buyer ...
... would be taken advantage of if they are not organized. An example would be the sports franchises, like MLB, NHL, NLL, MLS and NFL. Do you think this provides the rational for why the players are always represented by a players association or union? Could we examine what happens if we have one buyer ...
Model Paper Micro Economic
... 1. Bamford Colin (2002) Economics Cambridge University Press 2. H. Craig Peterson W. Cris Lewis (2004) Managerial Economics Pearson Education (4th edition) 3. Salvator Dominick (2004) Micro Economic Theory and Application New Oxford University Press 4th edition 4. Colander C. David (2006) Economics ...
... 1. Bamford Colin (2002) Economics Cambridge University Press 2. H. Craig Peterson W. Cris Lewis (2004) Managerial Economics Pearson Education (4th edition) 3. Salvator Dominick (2004) Micro Economic Theory and Application New Oxford University Press 4th edition 4. Colander C. David (2006) Economics ...
EASTERN MEDITERRANEAN UNIVERSITY
... average and marginal cost of pipe? b. In long run equilibrium what will be the market equilibrium price and quantity for concrete pipe? How much will each firm produce? How much labor will be hired by each firm and in the market as a whole? ...
... average and marginal cost of pipe? b. In long run equilibrium what will be the market equilibrium price and quantity for concrete pipe? How much will each firm produce? How much labor will be hired by each firm and in the market as a whole? ...
Principles of Economics, Case and Fair,8e
... continue in microeconomics, in Chapter 13 we will define and explore several different kinds of market organization and structure, including monopoly, oligopoly, and monopolistic competition. Because monopolists, oligopolists, monopolistic competitors, and perfect competitors share the objective of ...
... continue in microeconomics, in Chapter 13 we will define and explore several different kinds of market organization and structure, including monopoly, oligopoly, and monopolistic competition. Because monopolists, oligopolists, monopolistic competitors, and perfect competitors share the objective of ...
Module 71 - The Market For Labor
... Shifts in the Supply of Labor • Changes in preferences or social norms • Post-WWII acceptance of women in workplace ...
... Shifts in the Supply of Labor • Changes in preferences or social norms • Post-WWII acceptance of women in workplace ...
Lecture 1: An Introduction to Economics
... If you understand economics you have the potential to: • Better understand the factors that most affect businesses • Better understand human behaviour • Anticipate economic trends, such as interest rate and the share market • Make better choices in your private and work lives • Make better use of k ...
... If you understand economics you have the potential to: • Better understand the factors that most affect businesses • Better understand human behaviour • Anticipate economic trends, such as interest rate and the share market • Make better choices in your private and work lives • Make better use of k ...
Chapter 5 LR Demand for Labor
... will result in entirely new production function. • Technological change has two effects on employment; net impact depends on which is bigger: – 1) DL: better technology allows firms to produce given Q with fewer workers. – 2) DL: better technology costs of production product prices and ...
... will result in entirely new production function. • Technological change has two effects on employment; net impact depends on which is bigger: – 1) DL: better technology allows firms to produce given Q with fewer workers. – 2) DL: better technology costs of production product prices and ...
What is Economics?
... Example: if you choose to buy an iPad, you are exchanging your income for the right to own the iPad. You might also sacrifice other things Can you think of scenarios where you might sacrifice something other than time or money? ...
... Example: if you choose to buy an iPad, you are exchanging your income for the right to own the iPad. You might also sacrifice other things Can you think of scenarios where you might sacrifice something other than time or money? ...
Intro Micro Exam 3, Fall 2006
... 6. Suppose a competitive labor market is in equilibrium. Describe how the following events will affect the labor market and predict changes in equilibrium employment and the market wage. Diagrams are not necessary, but make sure that you provide an explanation for the changes. (5 points each) a. The ...
... 6. Suppose a competitive labor market is in equilibrium. Describe how the following events will affect the labor market and predict changes in equilibrium employment and the market wage. Diagrams are not necessary, but make sure that you provide an explanation for the changes. (5 points each) a. The ...
KIELCE SCHOOL OF ECONOMICS TOURISM AND SOCIAL
... Able to assess the situation in a particular market of the the producer and the consumer perspective using obtained knowledge in the field of microeconomics. Can communicate with the environment and provide a basic understanding of the situation in individual market areas. Can complete and improve o ...
... Able to assess the situation in a particular market of the the producer and the consumer perspective using obtained knowledge in the field of microeconomics. Can communicate with the environment and provide a basic understanding of the situation in individual market areas. Can complete and improve o ...