Mariana Trench - WordPress.com
... WHAT CREATED THE MARIANA TRENCH • IT WAS CREATED BY OCEAN CRUST-TO-OCEAN CRUST SUBDUCTION. • A PHENOMENA IN WHICH A OCEANIC PLATE IS TOPPED BY ANOTHER OCEANIC PLATE. ...
... WHAT CREATED THE MARIANA TRENCH • IT WAS CREATED BY OCEAN CRUST-TO-OCEAN CRUST SUBDUCTION. • A PHENOMENA IN WHICH A OCEANIC PLATE IS TOPPED BY ANOTHER OCEANIC PLATE. ...
OCEAN FLOOR TOPOGRAPHY
... SIGNAL AND RECEIVES THE “ECHO” TO DETERMINE THE RANGE AND ORIENTATION OF OBJECTS. PASSIVE SONAR DOES NOT EMIT A SIGNAL, IT DETECTS SOUND WAVES AND CAN NOT DETERMINE THE RANGE AND ORIENTATION OF OBJECTS. ...
... SIGNAL AND RECEIVES THE “ECHO” TO DETERMINE THE RANGE AND ORIENTATION OF OBJECTS. PASSIVE SONAR DOES NOT EMIT A SIGNAL, IT DETECTS SOUND WAVES AND CAN NOT DETERMINE THE RANGE AND ORIENTATION OF OBJECTS. ...
2014 Fellow, the American Geophysical Union
... (AGU). This year, 62 fellows representing less than 0.1 percent of overall membership were named for their scientific eminence, a major breakthrough, a major discovery, paradigm shifts and/or sustained scientific impact. Egbert is a geophysicist and oceanographer whose studies range from ocean tides ...
... (AGU). This year, 62 fellows representing less than 0.1 percent of overall membership were named for their scientific eminence, a major breakthrough, a major discovery, paradigm shifts and/or sustained scientific impact. Egbert is a geophysicist and oceanographer whose studies range from ocean tides ...
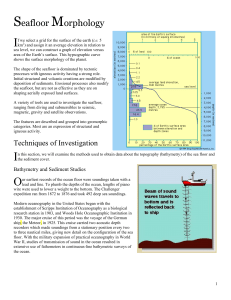
Seafloor Morphology - Department of Geology UPRM
... oceanic ridge and abyssal plains of fine sediment. The Atlantic Ocean has grown during the past 200 million years at the expense of the Pacific Ocean. ...
... oceanic ridge and abyssal plains of fine sediment. The Atlantic Ocean has grown during the past 200 million years at the expense of the Pacific Ocean. ...
Hydrothermal Vents
... Most of us are familiar with "Old Faithful" in Yellowstone National Park. This famous geyser erupts several times a day. It spouts a column of water heated by volcanic rock deep within the Earth's crust. A hydrothermal vent is a geyser on the seafloor. It continuously spews super-hot, mineral-rich w ...
... Most of us are familiar with "Old Faithful" in Yellowstone National Park. This famous geyser erupts several times a day. It spouts a column of water heated by volcanic rock deep within the Earth's crust. A hydrothermal vent is a geyser on the seafloor. It continuously spews super-hot, mineral-rich w ...
exploring_the_ocean
... • Home of many ocean plants and animals because sunlight reaches the bottom. ...
... • Home of many ocean plants and animals because sunlight reaches the bottom. ...
6TH GRADE EARTH SCIENCE LEOCE STUDY GUIDE
... KEY TERMS: climate, ocean currents (surface/deep – density), greenhouse gases, infrared radiation, global winds, evaporation, water cycle, weather, ozone layer, condensation, transpiration, precipitation, salinity, radiation, conduction, and convection STUDENT QUESTIONS: 6. Explain the Sun’s role in ...
... KEY TERMS: climate, ocean currents (surface/deep – density), greenhouse gases, infrared radiation, global winds, evaporation, water cycle, weather, ozone layer, condensation, transpiration, precipitation, salinity, radiation, conduction, and convection STUDENT QUESTIONS: 6. Explain the Sun’s role in ...
Mountain Belts formed at Divergent and Convergent Boundaries
... chaotically mixed in the trench by the faulting and folding caused as they are scraped from the down-going oceanic plate ...
... chaotically mixed in the trench by the faulting and folding caused as they are scraped from the down-going oceanic plate ...
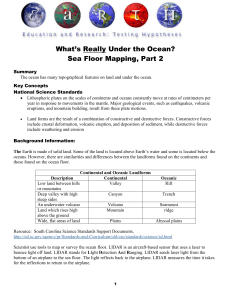
Sea Floor Mapping Lesson Plan Part 2
... Lithospheric plates on the scales of continents and oceans constantly move at rates of centimeters per year in response to movements in the mantle. Major geological events, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain building, result from these plate motions. ...
... Lithospheric plates on the scales of continents and oceans constantly move at rates of centimeters per year in response to movements in the mantle. Major geological events, such as earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and mountain building, result from these plate motions. ...
1824 - Lunar and Planetary Institute
... “uphill,'' away from regions of thick ice, and pool in regions where the ice is thin. By allowing the hot, dense interior water to contact regions where the ice is thick (hence increasing the heat flux and causing melting), and forcing it away from regions where the ice is thin (decreasing the heat ...
... “uphill,'' away from regions of thick ice, and pool in regions where the ice is thin. By allowing the hot, dense interior water to contact regions where the ice is thick (hence increasing the heat flux and causing melting), and forcing it away from regions where the ice is thin (decreasing the heat ...
CHAPTER 11 The global ocean
... +5° C below a shallow thermocline. The pycnocline, or zone of density increase below a shallow surface layer, is initially more sensitive to changes in salinity but ultimately controlled by the greater range of temperatures. ...
... +5° C below a shallow thermocline. The pycnocline, or zone of density increase below a shallow surface layer, is initially more sensitive to changes in salinity but ultimately controlled by the greater range of temperatures. ...
Plate Tectonics
... basins. Gas and dust from large volcanoes can change the atmosphere. The solid crust of the earth—including both the continents and the ocean basins— consists of separate plates that ride on a denser, hot, gradually deformable layer of the earth. The crust sections move very slowly, pressing against ...
... basins. Gas and dust from large volcanoes can change the atmosphere. The solid crust of the earth—including both the continents and the ocean basins— consists of separate plates that ride on a denser, hot, gradually deformable layer of the earth. The crust sections move very slowly, pressing against ...
Ch 9 4 Testing Plate Tectonics
... deep-focus earthquakes and ocean trenches. Also, the absence of deep-focus earthquakes along the oceanic ridge system was shown to be consistent with the new theory Scientists have found that intermediate and deep focus earthquakes occur within the subducting plate as it goes into the mantle Sha ...
... deep-focus earthquakes and ocean trenches. Also, the absence of deep-focus earthquakes along the oceanic ridge system was shown to be consistent with the new theory Scientists have found that intermediate and deep focus earthquakes occur within the subducting plate as it goes into the mantle Sha ...
plate - PAMS-Doyle
... Earth’s Spreading Ocean Floor Midocean ridges form the single largest mountain range in the world 80,000 km long and 3 km high Lava erupts to form new sea floor and spread As it spreads it takes continents with it This explained the mechanism for continental drift! ...
... Earth’s Spreading Ocean Floor Midocean ridges form the single largest mountain range in the world 80,000 km long and 3 km high Lava erupts to form new sea floor and spread As it spreads it takes continents with it This explained the mechanism for continental drift! ...
6TH GRADE EARTH SCIENCE LEOCE STUDY GUIDE
... KEY TERMS: climate, ocean currents (surface/deep – density), greenhouse gases, infrared radiation, global winds, evaporation, water cycle, weather, ozone layer, condensation, transpiration, precipitation, salinity, radiation, conduction, and convection STUDENT QUESTIONS: 6. Explain the Sun’s role in ...
... KEY TERMS: climate, ocean currents (surface/deep – density), greenhouse gases, infrared radiation, global winds, evaporation, water cycle, weather, ozone layer, condensation, transpiration, precipitation, salinity, radiation, conduction, and convection STUDENT QUESTIONS: 6. Explain the Sun’s role in ...
Weather Powerpoint
... Warm air rises and then cools so it cannot hold the moisture; therefore, it falls to earth as some type of precipitation. Cold: holds less moisture Cold air sinks and becomes warmer so it can hold more moisture. Due to this there will be little ...
... Warm air rises and then cools so it cannot hold the moisture; therefore, it falls to earth as some type of precipitation. Cold: holds less moisture Cold air sinks and becomes warmer so it can hold more moisture. Due to this there will be little ...
Hydrosphere - Greenon Local Schools
... The rich Antarctic waters are pulled away from the shore and become part of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, also known as West Wind Drift. This current, the strongest ocean current on earth, is partially diverted by the southern tip of South America, forming the Humboldt Current off the coast of ...
... The rich Antarctic waters are pulled away from the shore and become part of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, also known as West Wind Drift. This current, the strongest ocean current on earth, is partially diverted by the southern tip of South America, forming the Humboldt Current off the coast of ...
The Sea Floor
... – Magma oozes from the thinner oceanic crust – Cools and creates a seamount – Eventually breaks the surface ...
... – Magma oozes from the thinner oceanic crust – Cools and creates a seamount – Eventually breaks the surface ...
How the shape of ocean floors can affect speed and height of tsunami
... Thailand, Malaysia and the Maldives, it slowed. The more it became compressed, the more it grew in height. As it reached the shore it grew into a monster. ...
... Thailand, Malaysia and the Maldives, it slowed. The more it became compressed, the more it grew in height. As it reached the shore it grew into a monster. ...
Reporting Category 3 Assessed Curriculum Vocabulary
... The sun is the only star in our solar system. There are many other stars that make up other galaxies. Conduct an investigation about wavelengths and the electromagnetic spectrum ...
... The sun is the only star in our solar system. There are many other stars that make up other galaxies. Conduct an investigation about wavelengths and the electromagnetic spectrum ...
Earth Systems
... Look at the world map 1. Earth’s surface is not smooth. What do you think causes variations in its surface? 2. Is the Earth changing? List any evidence (features or processes) that it is or is not ...
... Look at the world map 1. Earth’s surface is not smooth. What do you think causes variations in its surface? 2. Is the Earth changing? List any evidence (features or processes) that it is or is not ...
Flowing water ecosystems, such as streams and rivers, are also
... In lakes and ponds, the open water zone extending to the depth of light penetration is referred to as the ________ In lakes and ponds, the deepest zone beneath the compensation depth of light is referred to as the ________ zone. In lakes and ponds, the ________ zone supports the richest diversity of ...
... In lakes and ponds, the open water zone extending to the depth of light penetration is referred to as the ________ In lakes and ponds, the deepest zone beneath the compensation depth of light is referred to as the ________ zone. In lakes and ponds, the ________ zone supports the richest diversity of ...
Unit 3 Geology - Manatee School For the Arts / Homepage
... Geology of the Ocean, Water, Waves, and Tides MRS. STAHL MARINE BIOLOGY ...
... Geology of the Ocean, Water, Waves, and Tides MRS. STAHL MARINE BIOLOGY ...
Factors Affecting Ocean Surface Currents
... As the temperature changes, this water becomes denser and returns back towards the equator as cold deep water rises/upwells completing the “belt” This influences global climate by converting warm water to cold, releasing heat to the atmosphere. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/content /chp ...
... As the temperature changes, this water becomes denser and returns back towards the equator as cold deep water rises/upwells completing the “belt” This influences global climate by converting warm water to cold, releasing heat to the atmosphere. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/content /chp ...
Ocean

An ocean (from Ancient Greek Ὠκεανός, transc. Okeanós, the sea of classical antiquity) is a body of saline water that composes much of a planet's hydrosphere. On Earth, an ocean is one of the major conventional divisions of the World Ocean, which covers almost 71% of its surface. These are, in descending order by area, the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic Oceans. The word sea is often used interchangeably with ""ocean"" in American English but, strictly speaking, a sea is a body of saline water (generally a division of the world ocean) partly or fully enclosed by land.Saline water covers approximately 72% of the planet's surface (~3.6×108 km2) and is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas, with the ocean covering approximately 71% of Earth's surface. The ocean contains 97% of Earth's water, and oceanographers have stated that only 5% of the World Ocean has been explored. The total volume is approximately 1.35 billion cubic kilometers (320 million cu mi) with an average depth of nearly 3,700 meters (12,100 ft).As it is the principal component of Earth's hydrosphere, the world ocean is integral to all known life, forms part of the carbon cycle, and influences climate and weather patterns. It is the habitat of 230,000 known species, although much of the oceans depths remain unexplored, and over two million marine species are estimated to exist. The origin of Earth's oceans remains unknown; oceans are thought to have formed in the Hadean period and may have been the impetus for the emergence of life.Extraterrestrial oceans may be composed of water or other elements and compounds. The only confirmed large stable bodies of extraterrestrial surface liquids are the lakes of Titan, although there is evidence for the existence of oceans elsewhere in the Solar System. Early in their geologic histories, Mars and Venus are theorized to have had large water oceans. The Mars ocean hypothesis suggests that nearly a third of the surface of Mars was once covered by water, and a runaway greenhouse effect may have boiled away the global ocean of Venus. Compounds such as salts and ammonia dissolved in water lower its freezing point, so that water might exist in large quantities in extraterrestrial environments as brine or convecting ice. Unconfirmed oceans are speculated beneath the surface of many dwarf planets and natural satellites; notably, the ocean of Europa is estimated to have over twice the water volume of Earth. The Solar System's giant planets are also thought to have liquid atmospheric layers of yet to be confirmed compositions. Oceans may also exist on exoplanets and exomoons, including surface oceans of liquid water within a circumstellar habitable zone. Ocean planets are a hypothetical type of planet with a surface completely covered with liquid.