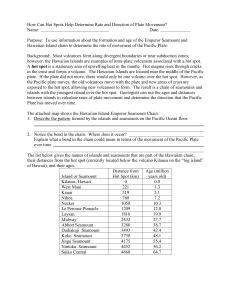
How Can Hot Spots Help Determine Rate and Direction of Plate
... Purpose: To use information about the formation and age of the Emperor Seamount and Hawaiian Island chain to determine the rate of movement of the Pacific Plate. Background: Most volcanoes form along divergent boundaries or near subduction zones; however, the Hawaiian Islands are examples of intra-p ...
... Purpose: To use information about the formation and age of the Emperor Seamount and Hawaiian Island chain to determine the rate of movement of the Pacific Plate. Background: Most volcanoes form along divergent boundaries or near subduction zones; however, the Hawaiian Islands are examples of intra-p ...
Slide 1
... A "bulge" developed on the north side of Mount St. Helens as magma pushed up within the peak. Repeated measurement of the distance to the bulge (as shown here) found growth of up to five feet (1.5 meters) per day. By May 17, part of the volcano's north side had been pushed upwards and outwards over ...
... A "bulge" developed on the north side of Mount St. Helens as magma pushed up within the peak. Repeated measurement of the distance to the bulge (as shown here) found growth of up to five feet (1.5 meters) per day. By May 17, part of the volcano's north side had been pushed upwards and outwards over ...
Geological mapping of the central area of Terceira Island (Azores
... whose aa-type lava flows where extruded to the south. To the north it is worth mentioning three important episodes/eruptions: a) the extensive pahoehoe basaltic lava field emitted from Pico Galiarte (also known as “Pico dos Pedreiros”), that flooded the flat areas near the axial part of the BFZ, but ...
... whose aa-type lava flows where extruded to the south. To the north it is worth mentioning three important episodes/eruptions: a) the extensive pahoehoe basaltic lava field emitted from Pico Galiarte (also known as “Pico dos Pedreiros”), that flooded the flat areas near the axial part of the BFZ, but ...
UGRC 144_Session 5
... Highly fluid lava flows rapidly down a volcano’s slopes. Viscous lava flows more slowly. • Rock fragments, generally called tephra are formed from viscous magma. Tephra includes - volcanic dust, - volcanic ash and - volcanic bombs. • Pyroclastic is the name given to particles produced in volcanic er ...
... Highly fluid lava flows rapidly down a volcano’s slopes. Viscous lava flows more slowly. • Rock fragments, generally called tephra are formed from viscous magma. Tephra includes - volcanic dust, - volcanic ash and - volcanic bombs. • Pyroclastic is the name given to particles produced in volcanic er ...
Restless Earth
... A: Where the plates move parallel to each other, the earths crust is not created or ...
... A: Where the plates move parallel to each other, the earths crust is not created or ...
Earth Shakes, Rattles, and Rolls
... FAULT-BLOCK MOUNTAINS •Consist of huge blocks of the earth's crust that have been tilted or pushed up along a fracture line called a fault •Sierra in California, Arizona is an example. • Created when a plate hits a fault and tips upside down, creating erosion and debris, which is at the base of the ...
... FAULT-BLOCK MOUNTAINS •Consist of huge blocks of the earth's crust that have been tilted or pushed up along a fracture line called a fault •Sierra in California, Arizona is an example. • Created when a plate hits a fault and tips upside down, creating erosion and debris, which is at the base of the ...
Glencoe Earth Science
... volcano has been erupting, but not explosively. In May of 1990, most of the town of Kalapana Gardens was destroyed, but no one was hurt because the lava moved slowly and people could escape. The most recent series of eruptions from Kilauea began in January 1983 and still continues. The island countr ...
... volcano has been erupting, but not explosively. In May of 1990, most of the town of Kalapana Gardens was destroyed, but no one was hurt because the lava moved slowly and people could escape. The most recent series of eruptions from Kilauea began in January 1983 and still continues. The island countr ...
Chapter 12 – Volcanoes
... volcano has been erupting, but not explosively. In May of 1990, most of the town of Kalapana Gardens was destroyed, but no one was hurt because the lava moved slowly and people could escape. The most recent series of eruptions from Kilauea began in January 1983 and still continues. The island countr ...
... volcano has been erupting, but not explosively. In May of 1990, most of the town of Kalapana Gardens was destroyed, but no one was hurt because the lava moved slowly and people could escape. The most recent series of eruptions from Kilauea began in January 1983 and still continues. The island countr ...
Unit Two Part Two Notes
... Mechanisms of Plate Motion ◆ Slab-Pull and Ridge-Push • Slab-pull is a mechanism that contributes to plate motion in which cool, dense oceanic crust sinks into the mantle and “pulls” the trailing lithosphere along. It is thought to be the primary downward arm of convective flow in the mantle. ...
... Mechanisms of Plate Motion ◆ Slab-Pull and Ridge-Push • Slab-pull is a mechanism that contributes to plate motion in which cool, dense oceanic crust sinks into the mantle and “pulls” the trailing lithosphere along. It is thought to be the primary downward arm of convective flow in the mantle. ...
2013年1月12日托福写作真题回忆
... puzzle. Some plates carry islands or continents, others form the seafloor. All are slowly moving because the plates float on a denser sem-iliquid mantle, the layer between the crust and Earth’s core. The plates have edges that are spreading ridges (where two plates are moving apart and new seafloor ...
... puzzle. Some plates carry islands or continents, others form the seafloor. All are slowly moving because the plates float on a denser sem-iliquid mantle, the layer between the crust and Earth’s core. The plates have edges that are spreading ridges (where two plates are moving apart and new seafloor ...
Understanding Plate Boundaries - Merrillville Community School
... Colliding plates create convergent (kun-VER-junt) boundaries. What happens along a convergent boundary depends on the type of lithosphere at the edge of each of the colliding plates. The earth’s lithosphere—which includes the crust and solid upper mantle—varies over the surface of the earth. This is ...
... Colliding plates create convergent (kun-VER-junt) boundaries. What happens along a convergent boundary depends on the type of lithosphere at the edge of each of the colliding plates. The earth’s lithosphere—which includes the crust and solid upper mantle—varies over the surface of the earth. This is ...
Period
... What type of landform forms when two pieces of continental crust pull apart? What type of plate boundary is this called? Two plates slip past each other at a ___________________________________ boundary. What happens when two oceanic plates collide? What type of plate boundary is this called? What h ...
... What type of landform forms when two pieces of continental crust pull apart? What type of plate boundary is this called? Two plates slip past each other at a ___________________________________ boundary. What happens when two oceanic plates collide? What type of plate boundary is this called? What h ...
Lesson Sample Part 2
... 3. Write the dates of the eruption beside the mark. Notice how many of these eruptions occur on or near plate boundaries. The Science You Just Used If melted rock is above ground, it’s called Lava, underground the same rock is Magma. Volcanic Eruptions happens when conditions create Pressure or Forc ...
... 3. Write the dates of the eruption beside the mark. Notice how many of these eruptions occur on or near plate boundaries. The Science You Just Used If melted rock is above ground, it’s called Lava, underground the same rock is Magma. Volcanic Eruptions happens when conditions create Pressure or Forc ...
Understanding Plate Motions - My Science Class / FrontPage
... On 9 June 1994, a magnitude-8.3 earthquake struck about 320 km northeast of La Paz, Bolivia, at a depth of 636 km. This earthquake, within the subduction zone between the Nazca Plate and the South American Plate, was one of deepest and largest subduction earthquakes recorded in South America. Fortu ...
... On 9 June 1994, a magnitude-8.3 earthquake struck about 320 km northeast of La Paz, Bolivia, at a depth of 636 km. This earthquake, within the subduction zone between the Nazca Plate and the South American Plate, was one of deepest and largest subduction earthquakes recorded in South America. Fortu ...
Earthquake and Volcano Readings
... will continue to have strong earthquakes. Most of the earthquakes in the United States occur in the Western U.S. Movement of the Pacific seafloor causes the earthquakes in Alaska. Most of California's earthquakes are caused by slippage of the crust along the San Andreas Fault. This major strike-slip ...
... will continue to have strong earthquakes. Most of the earthquakes in the United States occur in the Western U.S. Movement of the Pacific seafloor causes the earthquakes in Alaska. Most of California's earthquakes are caused by slippage of the crust along the San Andreas Fault. This major strike-slip ...
GEOL 10: Environmental Geology Activity 9: Topographic Maps and
... and sedimentary material are being shoved downward, toward the east, underneath North America. This down‐going material undergoes metamorphism as it becomes exposed to progressively higher pressures and temperatures in the interior of the earth beneath North America. Temperatures at depths of the ...
... and sedimentary material are being shoved downward, toward the east, underneath North America. This down‐going material undergoes metamorphism as it becomes exposed to progressively higher pressures and temperatures in the interior of the earth beneath North America. Temperatures at depths of the ...
Seismic activity of the Nevados de Chillán volcanic complex after the
... Couplings between large magnitude subduction zone earthquakes and the subsequent response of their respective volcanic arcs are generally accepted, but the mechanisms driving this coupling are not known. The 2010 Maule earthquake (Mw8.8) ruptured approximately 500 km along strike in the south-centra ...
... Couplings between large magnitude subduction zone earthquakes and the subsequent response of their respective volcanic arcs are generally accepted, but the mechanisms driving this coupling are not known. The 2010 Maule earthquake (Mw8.8) ruptured approximately 500 km along strike in the south-centra ...
Internal Forces Shaping the Earth
... RING OF FIRE The Ring of Fire, a zone around the rim of the Pacific Ocean, is the location of the vast majority of active volcanoes. You can see the zone on the map on page 37. Eight major tectonic plates meet in this zone. Volcanic action and earthquakes occur frequently there. Other volcanoes are ...
... RING OF FIRE The Ring of Fire, a zone around the rim of the Pacific Ocean, is the location of the vast majority of active volcanoes. You can see the zone on the map on page 37. Eight major tectonic plates meet in this zone. Volcanic action and earthquakes occur frequently there. Other volcanoes are ...
Birth and growth of an atoll
... parts of the world where plates are continuously being created or destroyed. We are located on a plate (Fig. 10) at the South Pacific ridge, which moves in a north-westerly direction at an average speed of approximately 10 cm per year towards a trench where it will be swallowed up. This speed, altho ...
... parts of the world where plates are continuously being created or destroyed. We are located on a plate (Fig. 10) at the South Pacific ridge, which moves in a north-westerly direction at an average speed of approximately 10 cm per year towards a trench where it will be swallowed up. This speed, altho ...
Volcanoes
... volcano has been erupting, but not explosively. In May of 1990, most of the town of Kalapana Gardens was destroyed, but no one was hurt because the lava moved slowly and people could escape. The most recent series of eruptions from Kilauea began in January 1983 and still continues. The island countr ...
... volcano has been erupting, but not explosively. In May of 1990, most of the town of Kalapana Gardens was destroyed, but no one was hurt because the lava moved slowly and people could escape. The most recent series of eruptions from Kilauea began in January 1983 and still continues. The island countr ...
Americas - Tectonic Plates - Central Michigan University
... “Why do you think Los Angeles, Mexico City, and Lima, Peru were built in such dangerous places?” ...
... “Why do you think Los Angeles, Mexico City, and Lima, Peru were built in such dangerous places?” ...
my fineshed pro
... packed a bag. I also took 2 irreplaceable items from my grandmother and put these in the trunk of my car after backing it into the driveway for an easy exit if needed. For the next two hours, I followed everything that I knew to do including going to the ATM machine and getting some cash out and get ...
... packed a bag. I also took 2 irreplaceable items from my grandmother and put these in the trunk of my car after backing it into the driveway for an easy exit if needed. For the next two hours, I followed everything that I knew to do including going to the ATM machine and getting some cash out and get ...
Volcanic Crisis: The Soufrière Hills Volcano, Montserrat
... During the early 1990s, many small earthquakes were detected beneath Montserrat. Most were too small to be felt, but seismologists realized that they were caused by magma forcing its way up through the crust. Scientists arrived on Montserrat with seismometers to carefully monitor activity. ash depos ...
... During the early 1990s, many small earthquakes were detected beneath Montserrat. Most were too small to be felt, but seismologists realized that they were caused by magma forcing its way up through the crust. Scientists arrived on Montserrat with seismometers to carefully monitor activity. ash depos ...
World of quakes - Science Learning Hub
... 5. Now give each group Part 2 – Specialists working together instructions and World map showing main tectonic plates (if the map is a transparency, they can lay it over and line it up with their data maps). 6. In their groups of 4, students look at their map and answer Part 2 questions. Where on the ...
... 5. Now give each group Part 2 – Specialists working together instructions and World map showing main tectonic plates (if the map is a transparency, they can lay it over and line it up with their data maps). 6. In their groups of 4, students look at their map and answer Part 2 questions. Where on the ...
Ring of Fire
The Ring of Fire is an area in the basin of the Pacific Ocean where a large number of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur. In a 40,000 km (25,000 mi) horseshoe shape, it is associated with a nearly continuous series of oceanic trenches, volcanic arcs, and volcanic belts and/or plate movements. It has 452 volcanoes and is home to over 75% of the world's active and dormant volcanoes. The Ring of Fire is sometimes called the circum-Pacific belt.About 90% of the world's earthquakes and 81% of the world's largest earthquakes occur along the Ring of Fire. The next most seismically active region (5–6% of earthquakes and 17% of the world's largest earthquakes) is the Alpide belt, which extends from Java to the northern Atlantic Ocean via the Himalayas and southern Europe.All but 3 of the world's 25 largest volcanic eruptions of the last 11,700 years occurred at volcanoes in the Ring of Fire.The Ring of Fire is a direct result of plate tectonics and the movement and collisions of lithospheric plates. The eastern section of the ring is the result of the Nazca Plate and the Cocos Plate being subducted beneath the westward moving South American Plate. The Cocos Plate is being subducted beneath the Caribbean Plate, in Central America. A portion of the Pacific Plate along with the small Juan de Fuca Plate are being subducted beneath the North American Plate. Along the northern portion, the northwestward-moving Pacific plate is being subducted beneath the Aleutian Islands arc. Farther west, the Pacific plate is being subducted along the Kamchatka Peninsula arcs on south past Japan. The southern portion is more complex, with a number of smaller tectonic plates in collision with the Pacific plate from the Mariana Islands, the Philippines, Bougainville, Tonga, and New Zealand; this portion excludes Australia, since it lies in the center of its tectonic plate. Indonesia lies between the Ring of Fire along the northeastern islands adjacent to and including New Guinea and the Alpide belt along the south and west from Sumatra, Java, Bali, Flores, and Timor. The famous and very active San Andreas Fault zone of California is a transform fault which offsets a portion of the East Pacific Rise under southwestern United States and Mexico. The motion of the fault generates numerous small earthquakes, at multiple times a day, most of which are too small to be felt. The active Queen Charlotte Fault on the west coast of the Haida Gwaii, British Columbia, Canada, has generated three large earthquakes during the 20th century: a magnitude 7 event in 1929; a magnitude 8.1 in 1949 (Canada's largest recorded earthquake); and a magnitude 7.4 in 1970.























