Introduction
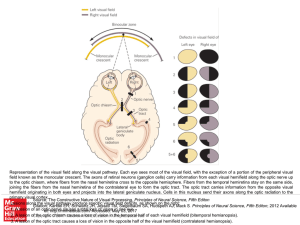
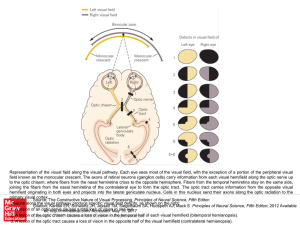
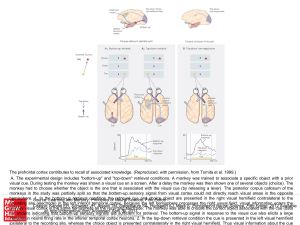
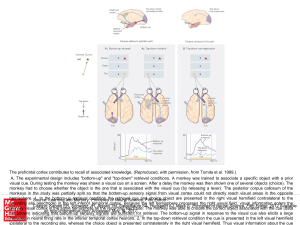
... Visual pathways to the brain. (a) Input from the right half of the visual field strikes the left side of each retina and is transmitted to the left hemisphere (shown in red). Input from the left half of the visual field strikes the right side of each retina and is transmitted to the right hemisphere ...
... Visual pathways to the brain. (a) Input from the right half of the visual field strikes the left side of each retina and is transmitted to the left hemisphere (shown in red). Input from the left half of the visual field strikes the right side of each retina and is transmitted to the right hemisphere ...
Slide ()
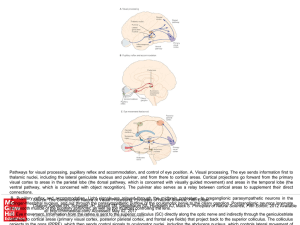
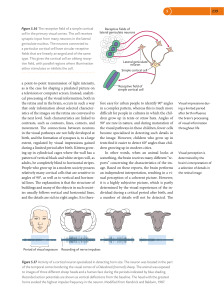
... Pathways for visual processing, pupillary reflex and accommodation, and control of eye position. A. Visual processing. The eye sends information first to thalamic nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus and pulvinar, and from there to cortical areas. Cortical projections go forward from the ...
... Pathways for visual processing, pupillary reflex and accommodation, and control of eye position. A. Visual processing. The eye sends information first to thalamic nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus and pulvinar, and from there to cortical areas. Cortical projections go forward from the ...
Learning to Control Robotic Systems Presented at
... general estimation is performed around a small operating system. •Self-organizing map gives a holistic approach to learn the inverse Jacobian from the vision space to joint space over the entire workspace. •The accurate positioning of the end-effector is achieved with SOM as ...
... general estimation is performed around a small operating system. •Self-organizing map gives a holistic approach to learn the inverse Jacobian from the vision space to joint space over the entire workspace. •The accurate positioning of the end-effector is achieved with SOM as ...