Chapter 11 Solutions to Five Crises
... Berlin over the Soviet zone. The United States, Britain, and France managed to fly in 8,000 tons of goods very day, enough to feed, clothe, and supply the city of 2,500,000. As many as 1,071 planes in one day (almost one a minute) flew into West Berlin. The airlift brought West Berliners sufficient ...
... Berlin over the Soviet zone. The United States, Britain, and France managed to fly in 8,000 tons of goods very day, enough to feed, clothe, and supply the city of 2,500,000. As many as 1,071 planes in one day (almost one a minute) flew into West Berlin. The airlift brought West Berliners sufficient ...
Document
... “If you want to, go ahead and fight in the jungles of Vietnam," Khrushchev said. "The French fought there for seven years and still had to quit in the end. Perhaps the Americans will be able to stick it out for a little longer, but eventually they will have to quit, too." - Nikita Krushchev ...
... “If you want to, go ahead and fight in the jungles of Vietnam," Khrushchev said. "The French fought there for seven years and still had to quit in the end. Perhaps the Americans will be able to stick it out for a little longer, but eventually they will have to quit, too." - Nikita Krushchev ...
Military, Reagan & Gorbachev, and Collapse of the Soviet Union
... Glasnost: means “POLITICAL OPENESS” (freedom of speech) Perestroika: means “RESTRUCTURING”, an economic policy to allow LIMITED free enterprise ...
... Glasnost: means “POLITICAL OPENESS” (freedom of speech) Perestroika: means “RESTRUCTURING”, an economic policy to allow LIMITED free enterprise ...
The Cold War - Bibb County Schools
... • Occupied the largest country in the world, 3rd largest population, & the 2nd largest economy • Had military and space technology, a worldwide spy network (the KGB), & one of the largest stockpiles of nuclear weapons in the world ...
... • Occupied the largest country in the world, 3rd largest population, & the 2nd largest economy • Had military and space technology, a worldwide spy network (the KGB), & one of the largest stockpiles of nuclear weapons in the world ...
Cold War OBJ. 2 - Petal School District
... E. The Four Powers Agreements fell apart when the United States, Britain, and France decide to pool their occupation zones together and form the Republic of Germany. The Soviet reaction included the complete isolation of the Western half of the City of Berlin. The United States led “West” decided tr ...
... E. The Four Powers Agreements fell apart when the United States, Britain, and France decide to pool their occupation zones together and form the Republic of Germany. The Soviet reaction included the complete isolation of the Western half of the City of Berlin. The United States led “West” decided tr ...
Document
... spread their influence to other nations. B. The Potsdam Conference 1. Truman’s first meeting with world leaders after he became president was a wartime conference of the Big Three at Potsdam, Germany: ...
... spread their influence to other nations. B. The Potsdam Conference 1. Truman’s first meeting with world leaders after he became president was a wartime conference of the Big Three at Potsdam, Germany: ...
BELL QUIZ: USE PAGES 605-608
... though they were allies in WWII. WHY? 1) Soviets upset about not being invited to Treaty of Versailles (peace treaty ending WWI). 2) Soviets were stripped of their colonies in Finland, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. 3) Soviets resent the U.S. delay in attacking Germany in Europe. (didn’t happen unt ...
... though they were allies in WWII. WHY? 1) Soviets upset about not being invited to Treaty of Versailles (peace treaty ending WWI). 2) Soviets were stripped of their colonies in Finland, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. 3) Soviets resent the U.S. delay in attacking Germany in Europe. (didn’t happen unt ...
Document
... • Stalin used Churchill’s words to help persuade his people that the United States and Great Britain were their enemies. • He also used this as an excuse to rebuild the military. ...
... • Stalin used Churchill’s words to help persuade his people that the United States and Great Britain were their enemies. • He also used this as an excuse to rebuild the military. ...
Soviet Acts of Aggression during the Cold War
... important policies and events from each country during this time period. Typed preferred, 450-550 words. ...
... important policies and events from each country during this time period. Typed preferred, 450-550 words. ...
Restructuring the Post-War World
... Marshall Plan: Cold War: NATO: Warsaw Pact: Brinkmanship: United Nations: Allies Become Enemies Yalta Conference: A Postwar Plan In February 1945, British, American, Soviet leaders meet at Yalta They agree to divide ______________________ into zones of occupation when WWII ends Soviet leader _______ ...
... Marshall Plan: Cold War: NATO: Warsaw Pact: Brinkmanship: United Nations: Allies Become Enemies Yalta Conference: A Postwar Plan In February 1945, British, American, Soviet leaders meet at Yalta They agree to divide ______________________ into zones of occupation when WWII ends Soviet leader _______ ...
THE COLD WAR
... Soviet Union controlled the eastern portion and most of Eastern Europe. The Allies also divided the German capital of Berlin into West Berlin and East Berlin. (see map) The western Allies saw this arrangement as temporary. They wanted Germany and all of Europe to be independent, free democracies. Th ...
... Soviet Union controlled the eastern portion and most of Eastern Europe. The Allies also divided the German capital of Berlin into West Berlin and East Berlin. (see map) The western Allies saw this arrangement as temporary. They wanted Germany and all of Europe to be independent, free democracies. Th ...
europe-20th-century
... In 1985, a progressive leader named Mikhail Gorbachev came to power in the USSR. HE al so recognized that the Soviet economy was failing. He knew that his country could not afford to keep up with Regan’s military programs. He made several changes. His programs allowed more political openness and per ...
... In 1985, a progressive leader named Mikhail Gorbachev came to power in the USSR. HE al so recognized that the Soviet economy was failing. He knew that his country could not afford to keep up with Regan’s military programs. He made several changes. His programs allowed more political openness and per ...
Objective: To examine the causes of the Cold War
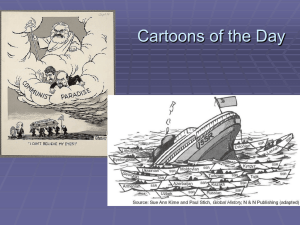
... make sure that these nations would not be forced to turn to war or communism to provide for their starving people. It is considered This political cartoon by Daniel Fitzpatrick one of the most successful aid from July 20, 1947, shows how the projects in U.S. history. ...
... make sure that these nations would not be forced to turn to war or communism to provide for their starving people. It is considered This political cartoon by Daniel Fitzpatrick one of the most successful aid from July 20, 1947, shows how the projects in U.S. history. ...
Origins of the Cold War, Part I
... arrangement of Europe following the end of the war Peace meant different things to each leader: – Stalin – an increase in Soviet power and safeguards against further attacks – Churchill – a free and democratic Europe with Britain at its head – Roosevelt – world democracy headed by the U.S. ...
... arrangement of Europe following the end of the war Peace meant different things to each leader: – Stalin – an increase in Soviet power and safeguards against further attacks – Churchill – a free and democratic Europe with Britain at its head – Roosevelt – world democracy headed by the U.S. ...
AP World History
... Divergent forms of government—communism, fascism, democracy—were rivals for most of the 20th century. The century ended with democracy in the ascendant. Spain, Portugal, and Greece, along with all Latin American countries except Cuba, adopted democratic forms of government. South Korea, Taiwan, and ...
... Divergent forms of government—communism, fascism, democracy—were rivals for most of the 20th century. The century ended with democracy in the ascendant. Spain, Portugal, and Greece, along with all Latin American countries except Cuba, adopted democratic forms of government. South Korea, Taiwan, and ...
In March 1985 Gorbachev was chosen as leader of
... These reforms became known as perestroika (restructuring). • Through perestroika he began to introduce elements of capitalism into the Soviet economy. For example, some citizens were allowed to own businesses while the government still operated most of them. ...
... These reforms became known as perestroika (restructuring). • Through perestroika he began to introduce elements of capitalism into the Soviet economy. For example, some citizens were allowed to own businesses while the government still operated most of them. ...
The Cold War: Military, Reagan & Gorbachev, and Collapse of the
... A STRONG military was key to America’s success in the Cold War During the Cold War, MILLIONS of Americans served in the military, defending freedom in wars and conflicts ...
... A STRONG military was key to America’s success in the Cold War During the Cold War, MILLIONS of Americans served in the military, defending freedom in wars and conflicts ...
Doc Snapshot The Cold War-The Communist Perspective
... The capitalist world headed by the U.S.A. turned with all its strength to the task of reinforcing its weakened links and retaining them in the system of imperialism. To suppress the revolutionary movement it resorted to armed force, economic pressure and direct interference in the internal affairs o ...
... The capitalist world headed by the U.S.A. turned with all its strength to the task of reinforcing its weakened links and retaining them in the system of imperialism. To suppress the revolutionary movement it resorted to armed force, economic pressure and direct interference in the internal affairs o ...
The Cold War: The Communist Perspective B
... The capitalist world headed by the U.S.A. turned with all its strength to the task of reinforcing its weakened links and retaining them in the system of imperialism. To suppress the revolutionary movement it resorted to armed force, economic pressure and direct interference in the internal affairs o ...
... The capitalist world headed by the U.S.A. turned with all its strength to the task of reinforcing its weakened links and retaining them in the system of imperialism. To suppress the revolutionary movement it resorted to armed force, economic pressure and direct interference in the internal affairs o ...
The Cold War - Effingham County Schools
... and dictatorships around the world • Occupied the largest country in the world, 3rd largest population, & the 2nd largest economy • Had military and space technology, a worldwide spy network (the KGB), & one of the largest stockpiles of nuclear weapons in the world ...
... and dictatorships around the world • Occupied the largest country in the world, 3rd largest population, & the 2nd largest economy • Had military and space technology, a worldwide spy network (the KGB), & one of the largest stockpiles of nuclear weapons in the world ...
Name: Hour: ______ Ideological Foundations of the Cold War After
... While ideology cannot entirely explain the origins of the cold war, it may help explain why the cold war became so enduring and contentious. Both nations held dramatically different worldviews, nurtured by their domestic values. The Soviet Union envisioned a world-wide global revolution leading to a ...
... While ideology cannot entirely explain the origins of the cold war, it may help explain why the cold war became so enduring and contentious. Both nations held dramatically different worldviews, nurtured by their domestic values. The Soviet Union envisioned a world-wide global revolution leading to a ...
Chapter 26: Cold War Conflicts The Cold War
... a. As VP, Truman was not included in policy decisions--was not told about atom bomb D. The Potsdam Conference 1. July 1945 conference with U.S., Great Britain, USSR 2. Stalin does not allow free, multiparty elections in Poland--bans democratic parties II. Tension Mounts A. Bargaining at Potsdam 1. T ...
... a. As VP, Truman was not included in policy decisions--was not told about atom bomb D. The Potsdam Conference 1. July 1945 conference with U.S., Great Britain, USSR 2. Stalin does not allow free, multiparty elections in Poland--bans democratic parties II. Tension Mounts A. Bargaining at Potsdam 1. T ...
Origins of the Cold War
... across the Continent. Behind that line lie all the capitals of the ancient states of Central and Eastern Europe. Warsaw, Berlin, Prague, Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade, Bucharest and Sofia; all these famous cities and the populations around them lie in what I must call the Soviet sphere, and all are sub ...
... across the Continent. Behind that line lie all the capitals of the ancient states of Central and Eastern Europe. Warsaw, Berlin, Prague, Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade, Bucharest and Sofia; all these famous cities and the populations around them lie in what I must call the Soviet sphere, and all are sub ...
Chapter 15 - 1945 - Present
... •Germany was divided between Western and Eastern Europe. -West Germany was part of Western Europe and democratic. -East Germany was part of Eastern Europe and Communist. ...
... •Germany was divided between Western and Eastern Europe. -West Germany was part of Western Europe and democratic. -East Germany was part of Eastern Europe and Communist. ...
A Nation Faces Conflict, 1939-1960 - Background
... The most alarming development for Americans, however, was the Cuban Revolution in 1959, when revolutionary Fidel Castro established a communist government a mere 90 miles from the coast of Florida and promptly signed an alliance with the Soviet Union. Under the auspices of the Central Intelligence ...
... The most alarming development for Americans, however, was the Cuban Revolution in 1959, when revolutionary Fidel Castro established a communist government a mere 90 miles from the coast of Florida and promptly signed an alliance with the Soviet Union. Under the auspices of the Central Intelligence ...
Cold War

The Cold War was a state of political and military tension after World War II between powers in the Western Bloc (the United States, its NATO allies and others) and powers in the Eastern Bloc (the Soviet Union and its allies in the Warsaw Pact).Historians have not fully agreed on the dates, but 1947–1991 is common. It was termed as ""cold"" because there was no large-scale fighting directly between the two sides, although there were major regional wars, known as proxy wars, in Korea, Vietnam and Afghanistan that the two sides supported. The Cold War split the temporary wartime alliance against Nazi Germany, leaving the USSR and the US as two superpowers with profound economic and political differences: the former being a single-party Marxist–Leninist state operating planned economy and controlled press while professing state atheism and owning exclusively the right to establish and govern communities, and the latter being a capitalist state with generally free elections and press, which also granted freedom of religion and freedom of association to its citizens. A self-proclaimed neutral bloc arose with the Non-Aligned Movement founded by Egypt, India, Indonesia and Yugoslavia; this faction rejected association with either the US-led West or the Soviet-led East. The two superpowers never engaged directly in full-scale armed combat but they each armed heavily in preparation for a possible all-out nuclear world war. Each side had a nuclear deterrent that deterred an attack by the other side, on the basis that such an attack would lead to total destruction of the attacker: the doctrine of mutually assured destruction (MAD). Aside from the development of the two sides' nuclear arsenals, and deployment of conventional military forces, the struggle for dominance was expressed via proxy wars around the globe, psychological warfare, massive propaganda campaigns and espionage, rivalry at sports events, and technological competitions such as the Space Race.The first phase of the Cold War began in the first two years after the end of the Second World War in 1945. The USSR consolidated its control over the states of the Eastern Bloc while the United States began a strategy of global containment to challenge Soviet power, extending military and financial aid to the countries of Western Europe (for example, supporting the anti-Communist side in the Greek Civil War) and creating the NATO alliance. The Berlin Blockade (1948–49) was the first major crisis of the Cold War.With victory of the Communist side in the Chinese Civil War and the outbreak of the Korean War (1950–53), the conflict expanded. The USSR and USA competed for influence in Latin America and decolonizing states of Africa, the Middle East and Southeast Asia. Meanwhile, the Hungarian Revolution of 1956 was stopped by the Soviets. The expansion and escalation sparked more crises, such as the Suez Crisis (1956), the Berlin Crisis of 1961, and the Cuban Missile Crisis of 1962. Following this last crisis a new phase began that saw the Sino-Soviet split complicate relations within the Communist sphere while US allies, particularly France, demonstrated greater independence of action. The USSR crushed the 1968 Prague Spring liberalization program in Czechoslovakia, and the Vietnam War (1955–1975) ended with a defeat of the US-backed Republic of South Vietnam, prompting further adjustments.By the 1970s, both sides had become interested in accommodations to create a more stable and predictable international system, inaugurating a period of détente that saw Strategic Arms Limitation Talks and the US opening relations with the People's Republic of China as a strategic counterweight to the Soviet Union. Détente collapsed at the end of the decade with the Soviet war in Afghanistan beginning in 1979.The early 1980s were another period of elevated tension, with the Soviet downing of Korean Air Lines Flight 007 (1983), and the ""Able Archer"" NATO military exercises (1983). The United States increased diplomatic, military, and economic pressures on the Soviet Union, at a time when the communist state was already suffering from economic stagnation. In the mid-1980s, the new Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbachev introduced the liberalizing reforms of perestroika (""reorganization"", 1987) and glasnost (""openness"", c. 1985) and ended Soviet involvement in Afghanistan. Pressures for national independence grew stronger in Eastern Europe, especially Poland. Gorbachev meanwhile refused to use Soviet troops to bolster the faltering Warsaw Pact regimes as had occurred in the past. The result in 1989 was a wave of revolutions that peacefully (with the exception of the Romanian Revolution) overthrew all of the Communist regimes of Central and Eastern Europe. The Communist Party of the Soviet Union itself lost control and was banned following an abortive coup attempt in August 1991. This in turn led to the formal dissolution of the USSR in December 1991 and the collapse of Communist regimes in other countries such as Mongolia, Cambodia and South Yemen. The United States remained as the world's only superpower.The Cold War and its events have left a significant legacy, and it is often referred to in popular culture, especially in media featuring themes of espionage (such as the internationally successful James Bond film series) and the threat of nuclear warfare.