Cold War: Truman-JFK
... totalitarianism and provide market for US goods b. Stalin: control of E. Europe (set up satellite nations) and rebuild the Soviet Union’s economy c. Churchill: Europe has been divided by an “iron curtain” (East and West, communism and capitalism) ...
... totalitarianism and provide market for US goods b. Stalin: control of E. Europe (set up satellite nations) and rebuild the Soviet Union’s economy c. Churchill: Europe has been divided by an “iron curtain” (East and West, communism and capitalism) ...
Origins of the Cold War Listen Listen Listen Listen
... • At a meeting at Yalta in February, Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin agreed on the postwar division of Germany but disagreed on the future of Poland. • In April, representatives of 50 countries, including the United States, adopted the charter for the United Nations, an organization dedicated to co ...
... • At a meeting at Yalta in February, Roosevelt, Churchill, and Stalin agreed on the postwar division of Germany but disagreed on the future of Poland. • In April, representatives of 50 countries, including the United States, adopted the charter for the United Nations, an organization dedicated to co ...
Origins of the Cold War
... • H-bomb—hydrogen bomb—nuclear weapon more powerful than atom bomb • 1952, U.S. explodes first H-bomb; 1953, Soviets explode one ...
... • H-bomb—hydrogen bomb—nuclear weapon more powerful than atom bomb • 1952, U.S. explodes first H-bomb; 1953, Soviets explode one ...
The Beginnings of the Cold War
... Decision to use A-bombs at end of WWII partly influenced by desire to impress Soviet Union Henry Wallace warned of dangerous arms race leading to nuclear war Truman saw nuclear weapons as effective deterrent to Soviet aggression Soviets tested their own A-bomb in Sept. 1949 U.S. began building H-bom ...
... Decision to use A-bombs at end of WWII partly influenced by desire to impress Soviet Union Henry Wallace warned of dangerous arms race leading to nuclear war Truman saw nuclear weapons as effective deterrent to Soviet aggression Soviets tested their own A-bomb in Sept. 1949 U.S. began building H-bom ...
Slide 1
... 4) The Yalta Conference = The last meeting that included President Roosevelt was in February 1945 on the shores of the Black Sea in the resort town of Yalta. The Big Three made numerous agreements concerning the postwar European peace that would later serve as a cause of conflict that quickly dissol ...
... 4) The Yalta Conference = The last meeting that included President Roosevelt was in February 1945 on the shores of the Black Sea in the resort town of Yalta. The Big Three made numerous agreements concerning the postwar European peace that would later serve as a cause of conflict that quickly dissol ...
National Security Policymaking
... 1950’s (with exception of Vietnam War) Reagan added some $32 billion to the defense budget in his first term in office to oppose the Soviet buildup. Strategic Defense Initiative: using computers and other equipment to defend against Soviet missiles ...
... 1950’s (with exception of Vietnam War) Reagan added some $32 billion to the defense budget in his first term in office to oppose the Soviet buildup. Strategic Defense Initiative: using computers and other equipment to defend against Soviet missiles ...
Ancient Rome
... and directors who were not allowed to work on Hollywood films because of their alleged Communist connections. Subversives: people who work secretly inside a country to overthrow the government. ...
... and directors who were not allowed to work on Hollywood films because of their alleged Communist connections. Subversives: people who work secretly inside a country to overthrow the government. ...
Cold War
... Atomic bomb creates tension Originally to be under United Nations control o Soviets refused UN inspections o Soviets develop bomb in 1949 o U.S. begins development of ...
... Atomic bomb creates tension Originally to be under United Nations control o Soviets refused UN inspections o Soviets develop bomb in 1949 o U.S. begins development of ...
The Cold War and the 1950s Test Bank - PHS-Test-Bank
... C. force Germany to pay war reparations. D. maintain international peace through the UN. The Soviet blockade of West Berlin was a response to A. the Marshall Plan. B. the formation of NATO. C. efforts by Western nations to divide Germany. D. efforts by Western nations to reunify Germany. The Soviet ...
... C. force Germany to pay war reparations. D. maintain international peace through the UN. The Soviet blockade of West Berlin was a response to A. the Marshall Plan. B. the formation of NATO. C. efforts by Western nations to divide Germany. D. efforts by Western nations to reunify Germany. The Soviet ...
761 - HCSTechCoach
... A. Used methods of fighting without using military weapons B. Competed to buildup large supplies of weapons C. Gave military and economic aid to weaker nations to gain support D. All of the above 2. _____What is a “hot war”? A. A war fought with military weapons C. Another name for a cold war ...
... A. Used methods of fighting without using military weapons B. Competed to buildup large supplies of weapons C. Gave military and economic aid to weaker nations to gain support D. All of the above 2. _____What is a “hot war”? A. A war fought with military weapons C. Another name for a cold war ...
The Cold War
... • 3) Future of Germany • 4) Economic reconstruction of Europe • 5) International policies toward the atomic bomb and atomic energy ...
... • 3) Future of Germany • 4) Economic reconstruction of Europe • 5) International policies toward the atomic bomb and atomic energy ...
Content
... the South, were able to take advantage of a moment when the Soviet delegate was temporarily absent from a United Nations Security Council meeting to commit the United Nations (UN) to defending South Korea. They called on the UN to apply the principle of collective security and to vote for sanctions ...
... the South, were able to take advantage of a moment when the Soviet delegate was temporarily absent from a United Nations Security Council meeting to commit the United Nations (UN) to defending South Korea. They called on the UN to apply the principle of collective security and to vote for sanctions ...
- Toolbox Pro
... Communists. • Announced Vietnamization to slowly withdraw American troops from Vietnam and replace them with Vietnamese soldiers. ...
... Communists. • Announced Vietnamization to slowly withdraw American troops from Vietnam and replace them with Vietnamese soldiers. ...
Name
... 6. The ideological and physical boundary dividing Europe into two separate areas. Warsaw Pact nations on the east side and the NATO nations on the west and south. 9. Countries that remained non-aligned or not moving at all with either the first or second world. 10. Conservatives who opposed reform 1 ...
... 6. The ideological and physical boundary dividing Europe into two separate areas. Warsaw Pact nations on the east side and the NATO nations on the west and south. 9. Countries that remained non-aligned or not moving at all with either the first or second world. 10. Conservatives who opposed reform 1 ...
The Cold War
... States would take what actions necessary to prevent the further spread of communism. ...
... States would take what actions necessary to prevent the further spread of communism. ...
SSUSH20 The student will analyze the domestic and international
... • In late January 1968, the North Vietnamese launched a surprise attack during the Vietnamese New Year. They attacked nearly every U.S. airbase and most major cities. in the South ...
... • In late January 1968, the North Vietnamese launched a surprise attack during the Vietnamese New Year. They attacked nearly every U.S. airbase and most major cities. in the South ...
1. Pick up an answer Document 2. The Cold War 3
... • Glasnost: A policy promoted during the latter half of the 1980s in the Soviet Union by Mikhail Gorbachev in which government secrecy (which had characterized the past several decades of Soviet policy) was discouraged and open discussion and distribution of information was encouraged. The term tra ...
... • Glasnost: A policy promoted during the latter half of the 1980s in the Soviet Union by Mikhail Gorbachev in which government secrecy (which had characterized the past several decades of Soviet policy) was discouraged and open discussion and distribution of information was encouraged. The term tra ...
SSUSH20 The student will analyze the domestic
... • In March 1965, Johnson launched Operation Rolling Thunder, a bombing campaign of the North, and sent more than 180,000 troops to fight in Vietnam ...
... • In March 1965, Johnson launched Operation Rolling Thunder, a bombing campaign of the North, and sent more than 180,000 troops to fight in Vietnam ...
North American Treaty Organization
... Organization – 1949, formed to respond to possible attacks by the Soviet Union. (each member country agreed to treat an attack on any other member as an attack on itself. ...
... Organization – 1949, formed to respond to possible attacks by the Soviet Union. (each member country agreed to treat an attack on any other member as an attack on itself. ...
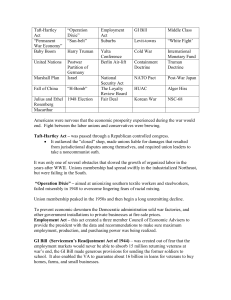
Taft-Hartley Act - Mr. Dunn`s History Class
... was named for United States Secretary of State George Marshall and was largely the creation of State Department officials, especially William L. Clayton and George F. Kennan. The reconstruction plan was developed at a meeting of the participating European states on July 12 1947. The Marshall Plan of ...
... was named for United States Secretary of State George Marshall and was largely the creation of State Department officials, especially William L. Clayton and George F. Kennan. The reconstruction plan was developed at a meeting of the participating European states on July 12 1947. The Marshall Plan of ...
The Cold War - World History
... • The main fear is that the standard of living is so low in Europe, it’s citizens will turn to communism, and fall under Soviet Dominance • Turn to a Partner - How should president Truman react to this problem? ...
... • The main fear is that the standard of living is so low in Europe, it’s citizens will turn to communism, and fall under Soviet Dominance • Turn to a Partner - How should president Truman react to this problem? ...
Cold War Review Sheet
... 2. Describe the ways that the US and the Soviet Union “fought” 3. Which two groups fought a civil war in China both before and after World War II? 4. Which European countries could receive aid through the Marshall Plan? 5. What led the Soviets to blockade West Berlin? 6. What event increased U.S. sp ...
... 2. Describe the ways that the US and the Soviet Union “fought” 3. Which two groups fought a civil war in China both before and after World War II? 4. Which European countries could receive aid through the Marshall Plan? 5. What led the Soviets to blockade West Berlin? 6. What event increased U.S. sp ...
Containment

Containment is a military strategy to stop the expansion of an enemy. It is best known as the Cold War policy of the United States and its allies to prevent the spread of communism abroad. A component of the Cold War, this policy was a response to a series of moves by the Soviet Union to enlarge communist influence in Eastern Europe, China, Korea, Africa, and Vietnam. Containment represented a middle-ground position between detente and rollback, but it let the opponent choose the place and time of any confrontation.The basis of the doctrine was articulated in a 1946 cable by U.S. diplomat George F. Kennan during the post-WWII administration of U.S. President Harry Truman. As a description of U.S. foreign policy, the word originated in a report Kennan submitted to U.S. Defense Secretary James Forrestal in 1947, a report that was later used in a magazine article. It is a translation of the French cordon sanitaire, used to describe Western policy toward the Soviet Union in the 1920s.