primary motor cortex - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... sensorimotor system have patterns of activity programmed into them and complex movements are produced by activating these programs. Cerebellum and basal ganglia then serve to coordinate the various programs. ...
... sensorimotor system have patterns of activity programmed into them and complex movements are produced by activating these programs. Cerebellum and basal ganglia then serve to coordinate the various programs. ...
Document
... 1st - Strongly involved in the top-down control of eye movement, 2nd – involved in spatial working memory ...
... 1st - Strongly involved in the top-down control of eye movement, 2nd – involved in spatial working memory ...
Lectures on mathematical neuroscience
... Action potentials are measurable events The timings or firing rate of action potentials can encode information - place cells in hippocampus - coincidence detection for sound localization - orientation selectivity in visual cortex ...
... Action potentials are measurable events The timings or firing rate of action potentials can encode information - place cells in hippocampus - coincidence detection for sound localization - orientation selectivity in visual cortex ...
Fate specification and patterning
... • Through patterning mechanisms, the nervous system is differentiated into specialized regions/areas. • Patterning is initiated by graded signals (morphogens) that regulate discrete domains of gene expression along an axis (A-P or D-V). • Finer scaled patterning occurs within the initial broad do ...
... • Through patterning mechanisms, the nervous system is differentiated into specialized regions/areas. • Patterning is initiated by graded signals (morphogens) that regulate discrete domains of gene expression along an axis (A-P or D-V). • Finer scaled patterning occurs within the initial broad do ...
Learning Objectives
... Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. ...
... Know the main structures of neurons and the structural differences among neurons. ...
Central nervous system
... sorting a complex set of paths and connections • Processing of information takes place in simple clusters of neurons called ganglia or a more complex organization of neurons called a brain ...
... sorting a complex set of paths and connections • Processing of information takes place in simple clusters of neurons called ganglia or a more complex organization of neurons called a brain ...
Object Recognition and Learning using the BioRC Biomimetic Real
... Moderately-Large Neurons – a hypothetical argument If we decide instead to model the same exact computation with simpler neurons that only have 300 inputs, there are “N choose M” or “10,000 choose 300” combinations of inputs that make the neural circuit fire at the final output. Thus, we require N!/ ...
... Moderately-Large Neurons – a hypothetical argument If we decide instead to model the same exact computation with simpler neurons that only have 300 inputs, there are “N choose M” or “10,000 choose 300” combinations of inputs that make the neural circuit fire at the final output. Thus, we require N!/ ...
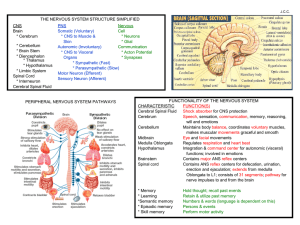
CNS Brain * Cerebrum * Cerebellum * Brain Stem * Diencephalon
... Maintains body balance, coordinates voluntary muscles, makes muscular movements graceful and smooth Midbrain Eye and facial movements Medulla Oblongata Regulates respiration and heart beat Hypothalamus Integration & command center for autonomic (visceral) functions; involved in emotions Brainstem Co ...
... Maintains body balance, coordinates voluntary muscles, makes muscular movements graceful and smooth Midbrain Eye and facial movements Medulla Oblongata Regulates respiration and heart beat Hypothalamus Integration & command center for autonomic (visceral) functions; involved in emotions Brainstem Co ...
Neural Tissue - Decker
... Highly branched dendrites at one end, one axon at the other end with the soma in the middle ...
... Highly branched dendrites at one end, one axon at the other end with the soma in the middle ...
Module 04
... other nearby neurons for much the same reason that people live in cities—it is easier to have brief, quick interactions with other people when they are nearby. Learning occurs as feedback builds and strengthens these neural connections (neurons that fire together wire together). . . . information hi ...
... other nearby neurons for much the same reason that people live in cities—it is easier to have brief, quick interactions with other people when they are nearby. Learning occurs as feedback builds and strengthens these neural connections (neurons that fire together wire together). . . . information hi ...
Chapter 5: The First Two Years
... billion neurons, but not enough dendrites and synapses • During the first months and years, major spurts of growth and refinement in axons, dendrites, and synapses occur (connections are being made) • Transient Exuberance is the great increase in the number of dendrites that occurs in an infant’s br ...
... billion neurons, but not enough dendrites and synapses • During the first months and years, major spurts of growth and refinement in axons, dendrites, and synapses occur (connections are being made) • Transient Exuberance is the great increase in the number of dendrites that occurs in an infant’s br ...
Brain Anatomy PPT
... In the somatosensory cortex and motor cortex neurons are distributed according to the part of the body that generates sensory input or receives motor input Frontal lobe ...
... In the somatosensory cortex and motor cortex neurons are distributed according to the part of the body that generates sensory input or receives motor input Frontal lobe ...
An octopaminergic system in the CNS of the snails, Lymnaea
... the neuronal transmission. However, the synaptic connections formed by either OC neurons or N3p interneurons are not identical, as they make different synaptic connections with both motoneurons (B3) and feeding interneurons (N2). CGC: The cerebral, serotonergic CGC neurons excite the OC cells, but t ...
... the neuronal transmission. However, the synaptic connections formed by either OC neurons or N3p interneurons are not identical, as they make different synaptic connections with both motoneurons (B3) and feeding interneurons (N2). CGC: The cerebral, serotonergic CGC neurons excite the OC cells, but t ...
presentation5
... Premotor cortex, parietal areas and the superior temporal sulcus (STS) neurons are activated during action observation ...
... Premotor cortex, parietal areas and the superior temporal sulcus (STS) neurons are activated during action observation ...
Brain_stemCh45
... Function: facilitation of spinal motor neurons in legs for postural support and patterned stereotyped movements ...
... Function: facilitation of spinal motor neurons in legs for postural support and patterned stereotyped movements ...
Nervous System - teacherver.com
... Three Overlapping Functions 1) Much like a sentry, it uses its millions of sensory receptors to monitor changes occurring both inside and outside the body. These changes are called stimuli and the gathered information is called sensory input. 2) It processes and interprets the sensory input and mak ...
... Three Overlapping Functions 1) Much like a sentry, it uses its millions of sensory receptors to monitor changes occurring both inside and outside the body. These changes are called stimuli and the gathered information is called sensory input. 2) It processes and interprets the sensory input and mak ...
features of mercury toxic influence mechanism
... which is involved in maintaining the accuracy of motion, fine motor skills, maintenance of posture and causes the clinical picture of micromercurialism. Data on the growth of vascular motility at lower levels of magnesium allow to perceive degenerative changes of neurons and glia not only as immedia ...
... which is involved in maintaining the accuracy of motion, fine motor skills, maintenance of posture and causes the clinical picture of micromercurialism. Data on the growth of vascular motility at lower levels of magnesium allow to perceive degenerative changes of neurons and glia not only as immedia ...
ch 16 sensory motor systems
... merges into the next. Each stage has been identified by EEG recordings . 2) Most dreaming occurs during rapid eye movement sleep. C. Learning and Memory 1. Learning is the ability to acquire new knowledge or skills through instruction or experience. Memory is the process by which that knowledge is r ...
... merges into the next. Each stage has been identified by EEG recordings . 2) Most dreaming occurs during rapid eye movement sleep. C. Learning and Memory 1. Learning is the ability to acquire new knowledge or skills through instruction or experience. Memory is the process by which that knowledge is r ...
Invited Re vie W The distribution of cholinergic neurons in the
... Summary. Choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), the enzyme responsible for the biosynthesis of acetylcholine, is presently the most specific marker for identifying cholinergic neurons in the central and peripheral nervous systems. The present article reviews immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization ...
... Summary. Choline acetyltransferase (ChAT), the enzyme responsible for the biosynthesis of acetylcholine, is presently the most specific marker for identifying cholinergic neurons in the central and peripheral nervous systems. The present article reviews immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization ...
Neurocognition Cognitive Neuroscience/neuropsychology
... can be considered at two levels of description… a) neuronal - one or a small collection of individual neurons b) neural systems - a large number of neurons that serve a similar function (localization of function); usually referred to by a collective name (e.g., cortex, temporal lobe, etc.) ...
... can be considered at two levels of description… a) neuronal - one or a small collection of individual neurons b) neural systems - a large number of neurons that serve a similar function (localization of function); usually referred to by a collective name (e.g., cortex, temporal lobe, etc.) ...
Biological and Psychology Why are psychologists concerned about
... Forebrain - Largest and most complex regions of the brain (Thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system, cerebrum, or cerebral cortex) Thalamus - Relay station for much sensory information ...
... Forebrain - Largest and most complex regions of the brain (Thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system, cerebrum, or cerebral cortex) Thalamus - Relay station for much sensory information ...
Biology 621 - Chapter 12 Midterm Exam Review
... called the involuntary nervous system. ___ 24. ____ neurons carry impulses from receptors to the spinal cord. 25. What are the two major division of the peripheral nervous system? ____&___ 26 Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the brain and spinal cord.____ 27.The __ is the basic functio ...
... called the involuntary nervous system. ___ 24. ____ neurons carry impulses from receptors to the spinal cord. 25. What are the two major division of the peripheral nervous system? ____&___ 26 Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the brain and spinal cord.____ 27.The __ is the basic functio ...
Neurophysiology-Organization of central nervous system
... make synapses, these synapses modulate the sensation by stimulate or inhibit them. so synapses are very imp. Areas for regulation of impulses &these areas where dugs act on. (We will take this in details in 3 lectures Later) *Fifth : levels of control: 1) level of spinal cord: -It is area of reflex ...
... make synapses, these synapses modulate the sensation by stimulate or inhibit them. so synapses are very imp. Areas for regulation of impulses &these areas where dugs act on. (We will take this in details in 3 lectures Later) *Fifth : levels of control: 1) level of spinal cord: -It is area of reflex ...
Biology General Knowledge 3 iQuiz
... Nerve cells or neurons that bring messages to muscles are called … ...
... Nerve cells or neurons that bring messages to muscles are called … ...