Discrete Modeling of Multi-Transmitter Neural Networks with Neuron
... Goeritz, & Otopalik, 2015). It is supposed that, for cognitive functions, there may be “cognitive pattern generators”, analogs of the familiar generators of motor commands (Graybiel, 1997). 1. Neurons can be recruited into an ensemble either permanently or transienty, from time to time, the latter m ...
... Goeritz, & Otopalik, 2015). It is supposed that, for cognitive functions, there may be “cognitive pattern generators”, analogs of the familiar generators of motor commands (Graybiel, 1997). 1. Neurons can be recruited into an ensemble either permanently or transienty, from time to time, the latter m ...
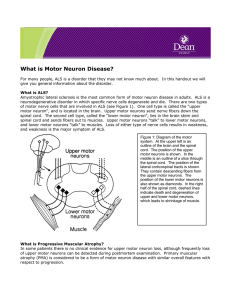
What is Motor Neuron
... Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS) refers to rare patients who have no clinical evidence for lower motor neuron involvement. However, most patients who initially have only upper motor neuron signs eventually develop lower motor neuron signs and go to have ALS. Thus, to be certain that a patient has PLS ...
... Primary lateral sclerosis (PLS) refers to rare patients who have no clinical evidence for lower motor neuron involvement. However, most patients who initially have only upper motor neuron signs eventually develop lower motor neuron signs and go to have ALS. Thus, to be certain that a patient has PLS ...
Week 2 Lecture Notes
... after the tone was heard. 3 -- Synchronizing with a rhythm. Here the tones were presented regularly with a frequency of 1 Hz. The subject was told to press the air cushion 90 in synchrony with the stimulus. ...
... after the tone was heard. 3 -- Synchronizing with a rhythm. Here the tones were presented regularly with a frequency of 1 Hz. The subject was told to press the air cushion 90 in synchrony with the stimulus. ...
Modeling large cortical networks with growing self
... RF-LISSOM focuses on the two-dimensional topographic organization of the cortex, modeling a cortical area as an N × N sheet of neurons and the retina as an R × R sheet of ganglion cells. Neurons receive afferent connections from broad patches of radius rA on the retina, and receive lateral excitator ...
... RF-LISSOM focuses on the two-dimensional topographic organization of the cortex, modeling a cortical area as an N × N sheet of neurons and the retina as an R × R sheet of ganglion cells. Neurons receive afferent connections from broad patches of radius rA on the retina, and receive lateral excitator ...
ling411-11-Columns - OWL-Space
... Similarly.. Neurons of a hypercolumn may have similar response features, upon which others that differ may be superimposed Result is maxicolumns in the hypercolumn sharing certain basic features while differing with respect to others Such maxicolumns may be further subdivided into functional ...
... Similarly.. Neurons of a hypercolumn may have similar response features, upon which others that differ may be superimposed Result is maxicolumns in the hypercolumn sharing certain basic features while differing with respect to others Such maxicolumns may be further subdivided into functional ...
control systems of the body - chapter 11
... [ Bruce Lee was so fast that they actually had to SLOW the film down so you could see his moves. In general, women have faster reflexes than men. ] ...
... [ Bruce Lee was so fast that they actually had to SLOW the film down so you could see his moves. In general, women have faster reflexes than men. ] ...
Exploration of Variability of Arkypallidal and Prototypical Projections
... injected into the mouse brain. The helper virus will bind to Cre positive cells and transfer their genome so that Cre positive cells exclusively express an avian-specific retroviral receptor (TVA) and G. TVA is the receptor that makes it possible for the rabies virus to bind to the cells and the fun ...
... injected into the mouse brain. The helper virus will bind to Cre positive cells and transfer their genome so that Cre positive cells exclusively express an avian-specific retroviral receptor (TVA) and G. TVA is the receptor that makes it possible for the rabies virus to bind to the cells and the fun ...
Note - Reza Shadmehr
... Slide 2. Recall that muscles are composed of two types of muscle fibers: extrafusal and intrafusal. Extrafusal fibers are much larger than the intrafusal fibers. Extrafusal fibers are responsible for the main force generating function of the muscles. .Intrafusal fibers are part of the sensory system ...
... Slide 2. Recall that muscles are composed of two types of muscle fibers: extrafusal and intrafusal. Extrafusal fibers are much larger than the intrafusal fibers. Extrafusal fibers are responsible for the main force generating function of the muscles. .Intrafusal fibers are part of the sensory system ...
The Nervous System workbooklet
... Neurons are surrounded by a cell membrane. Neurons have a nucleus that contains genes. Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other organelles. Neurons carry out basic cellular processes such as protein synthesis and ...
... Neurons are surrounded by a cell membrane. Neurons have a nucleus that contains genes. Neurons contain cytoplasm, mitochondria and other organelles. Neurons carry out basic cellular processes such as protein synthesis and ...
The Central Nervous System
... • Fiber tracts are classified according to the direction in which they run – Commisures connect corresponding gray areas of two hemispheres enabling them to function as a whole • The largest is the corpus collosum – Association fibers connect different parts of the same hemisphere – Projection fiber ...
... • Fiber tracts are classified according to the direction in which they run – Commisures connect corresponding gray areas of two hemispheres enabling them to function as a whole • The largest is the corpus collosum – Association fibers connect different parts of the same hemisphere – Projection fiber ...
Anatomical and physiological bases of consciousness and sleep
... • Single cell- synaptic potential - action potential • Neuronal aggregate -EEG ...
... • Single cell- synaptic potential - action potential • Neuronal aggregate -EEG ...
Cortico-Basal Ganglia Interactions in Huntington`s Disease
... The striatum (caudate nucleus and putamen) receives major excitatory glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex. The cortical information, which is passed to the striatum from the primary motor, primary sensory, premotor and associative motor cortices, can be processed through two different route ...
... The striatum (caudate nucleus and putamen) receives major excitatory glutamatergic inputs from the cerebral cortex. The cortical information, which is passed to the striatum from the primary motor, primary sensory, premotor and associative motor cortices, can be processed through two different route ...
UNIT 4 – HOMEOSTASIS 8.1 – Human Body Systems and H
... miminum level of a stimulus required to produce a response (usually 50 mV) ...
... miminum level of a stimulus required to produce a response (usually 50 mV) ...
Drivers and modulators from push-pull and balanced synaptic input
... subtractive effect of the conductance increase cancels the additive effect of the current variance increase, leaving the divisive gain change. Of relevance for the connection with the idea of driver and modulator inputs (Sherman and Guillery, 1998) is the fact that mixed multiplicative/divisive and ...
... subtractive effect of the conductance increase cancels the additive effect of the current variance increase, leaving the divisive gain change. Of relevance for the connection with the idea of driver and modulator inputs (Sherman and Guillery, 1998) is the fact that mixed multiplicative/divisive and ...
Bio_246_files/Clinical Considerations of the Nervous System
... Spinal Cord Trauma: Transection • Cross sectioning of the spinal cord at any level results in total motor and sensory loss in regions inferior to the cut • Paraplegia – transection between T1 and L1 • Quadriplegia – transection in the cervical ...
... Spinal Cord Trauma: Transection • Cross sectioning of the spinal cord at any level results in total motor and sensory loss in regions inferior to the cut • Paraplegia – transection between T1 and L1 • Quadriplegia – transection in the cervical ...
Practice Questions for Neuro Anatomy Lectures 4,5,6,7 Which of the
... To the brain via spinal cord; brain interprets stimuli and generates a response ...
... To the brain via spinal cord; brain interprets stimuli and generates a response ...
Unit 3 Summary
... The ANS is different from the somatic nervous system because the somatic nervous system initiates or causes movement or change (in skeletal muscles), whereas the ANS modifies and changes the activities of muscles, organs and glands to meet whatever demands face the body at the time. While most chang ...
... The ANS is different from the somatic nervous system because the somatic nervous system initiates or causes movement or change (in skeletal muscles), whereas the ANS modifies and changes the activities of muscles, organs and glands to meet whatever demands face the body at the time. While most chang ...
PowerPoint Nervous System
... Two types of neurons: Sensory neurons gather information about what is happening in and around the body. ...
... Two types of neurons: Sensory neurons gather information about what is happening in and around the body. ...
Dear Notetaker:
... a. “Retinotopic organization” means that parts of the visual world that are spatially adjacent to each other are processed by neurons that are spatial adjacent b. However, in this pathway, two adjacent neurons in the ventral pathway might be processing parts of the visual world that are very far awa ...
... a. “Retinotopic organization” means that parts of the visual world that are spatially adjacent to each other are processed by neurons that are spatial adjacent b. However, in this pathway, two adjacent neurons in the ventral pathway might be processing parts of the visual world that are very far awa ...
Time-delay-induced phase-transition to synchrony in coupled
... pling, the stable in-phase synchronization coexists with antiphase bursting within a broad range of initial conditions and parameter values of the network.29 For delayed coupling with small delays, this will be true also. In Fig. 5, we show that the phase-transitions can also occur even when the bif ...
... pling, the stable in-phase synchronization coexists with antiphase bursting within a broad range of initial conditions and parameter values of the network.29 For delayed coupling with small delays, this will be true also. In Fig. 5, we show that the phase-transitions can also occur even when the bif ...
Slide 1
... Nerve cell that lies between a sensory neuron and motor neuron in a reflex arc Confined entirely within the CNS ...
... Nerve cell that lies between a sensory neuron and motor neuron in a reflex arc Confined entirely within the CNS ...
Nervous System
... their structure. They are capable of response to their environment but not in this way. 2) This is the start of cephalization (development of the brain). Cnidarians have the simplest nervous system of the Animal Kingdom, they have a network of nerves that conducts signals from sensory cells to muscl ...
... their structure. They are capable of response to their environment but not in this way. 2) This is the start of cephalization (development of the brain). Cnidarians have the simplest nervous system of the Animal Kingdom, they have a network of nerves that conducts signals from sensory cells to muscl ...