Design a Neuron
... messages from the inside and outside world to my CNS. Opposite of motor neuron. The structure of the neuron varies depending on the sense, taste, touch, hearing, smell, and sight. ...
... messages from the inside and outside world to my CNS. Opposite of motor neuron. The structure of the neuron varies depending on the sense, taste, touch, hearing, smell, and sight. ...
Nervous System
... EPSP and IPSP • What channel is opened by an excitatory synapse? • Na+ • What channels is opened by an inhibitory neurotransmitter? • K+ • How is the regulation of the postsynaptic membrane’s gated channels different from the gated channels found along the axon? • These channels are chemically sen ...
... EPSP and IPSP • What channel is opened by an excitatory synapse? • Na+ • What channels is opened by an inhibitory neurotransmitter? • K+ • How is the regulation of the postsynaptic membrane’s gated channels different from the gated channels found along the axon? • These channels are chemically sen ...
E1 – Stimulus and response - IBDPBiology-Dnl
... receptors, sensory neurons, relay neurons, motor neurons, synapses and effectors in the response of animals to stimuli. E.1.3 Draw and label a diagram of a reflex arc for a pain withdrawal reflex, including the spinal cord and its spinal nerves, the receptor cell, sensory neuron, relay neuron, mot ...
... receptors, sensory neurons, relay neurons, motor neurons, synapses and effectors in the response of animals to stimuli. E.1.3 Draw and label a diagram of a reflex arc for a pain withdrawal reflex, including the spinal cord and its spinal nerves, the receptor cell, sensory neuron, relay neuron, mot ...
here
... Signals in the synapse are transmitted chemically. When an electrical impulse reaches the end of the neuron (the pre-synaptic terminal) it triggers the release of neurotransmitters from tiny sacs known as vesicles. These neurotransmitters diffuse across the gap and are taken up by receptors. T ...
... Signals in the synapse are transmitted chemically. When an electrical impulse reaches the end of the neuron (the pre-synaptic terminal) it triggers the release of neurotransmitters from tiny sacs known as vesicles. These neurotransmitters diffuse across the gap and are taken up by receptors. T ...
Nerve Cells and Electrical Signaling
... 4) Every cell within the body has a potential difference across its membrane. Discuss the role of potassium ions in creating that potential difference across the cell membrane at rest. Include in your discussion a description of equilibrium potential. 5) Several ions are responsible for resting memb ...
... 4) Every cell within the body has a potential difference across its membrane. Discuss the role of potassium ions in creating that potential difference across the cell membrane at rest. Include in your discussion a description of equilibrium potential. 5) Several ions are responsible for resting memb ...
Chapter 7: The Nervous System
... Synapse - junction between two communicating neurons Nerve pathway - nerve impulse travels from neuron to neuron Dendrite → cell body → along axon -> synapse (gap) → dendrite ...
... Synapse - junction between two communicating neurons Nerve pathway - nerve impulse travels from neuron to neuron Dendrite → cell body → along axon -> synapse (gap) → dendrite ...
Nervous System
... An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by the axon of another neuron or by the environment. Na+ pores open and the flood of Na+ ions makes the inside positive. This reversal of charges, from negative to positive is called a nerve impulse, or an action potential. ...
... An impulse begins when a neuron is stimulated by the axon of another neuron or by the environment. Na+ pores open and the flood of Na+ ions makes the inside positive. This reversal of charges, from negative to positive is called a nerve impulse, or an action potential. ...
Nervous System - APBio
... Bending of the hairs increases the frequency of action potentials in the sensory neurons – the neurons carry sensations to the brain through the auditory nerve ...
... Bending of the hairs increases the frequency of action potentials in the sensory neurons – the neurons carry sensations to the brain through the auditory nerve ...
The Nervous System
... -Wave of depolarization only moves in 1 directions from the dendrites to the cell body to the axon -Original stimulation must be above threshold level in order for an impulse to be started (all or nothing) Transmission of impulses between neurons -Communication between cells occurs at synapses (gap ...
... -Wave of depolarization only moves in 1 directions from the dendrites to the cell body to the axon -Original stimulation must be above threshold level in order for an impulse to be started (all or nothing) Transmission of impulses between neurons -Communication between cells occurs at synapses (gap ...
nervous system 2 notes - Hicksville Public Schools
... I will drop a dollar bill between your open fingers. If you are able to catch the dollar, it is yours. ...
... I will drop a dollar bill between your open fingers. If you are able to catch the dollar, it is yours. ...
Option E Neurobiology and Behaviour
... ¾ Responses may increase survival and reproduction; ¾ Responses show adaptive significance by improving fitness; ¾ Fitness is the genetic contribution of an individual to later generations; ¾ Natural selection acts on differences that have a genetic basis; ¾ Response patterns that improve fitness ge ...
... ¾ Responses may increase survival and reproduction; ¾ Responses show adaptive significance by improving fitness; ¾ Fitness is the genetic contribution of an individual to later generations; ¾ Natural selection acts on differences that have a genetic basis; ¾ Response patterns that improve fitness ge ...
File
... fibre Acetylcholine released between a motor neuron and a heart muscle fibre Neurotransmitters can be removed ...
... fibre Acetylcholine released between a motor neuron and a heart muscle fibre Neurotransmitters can be removed ...
Slide ()
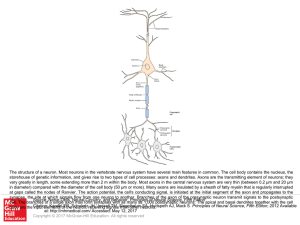
... storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; they vary greatly in length, some extending more than 2 m within the body. Most axons in the central nervous system are very thin (between 0.2 μm and ...
... storehouse of genetic information, and gives rise to two types of cell processes: axons and dendrites. Axons are the transmitting element of neurons; they vary greatly in length, some extending more than 2 m within the body. Most axons in the central nervous system are very thin (between 0.2 μm and ...
Ch. 35.2
... TOWARD the cell body Long fibers AXON carry impulses AWAY from the cell body Neurons may have many dendrites by only one axon Form NERVES when axons and dendrites are clustered together ...
... TOWARD the cell body Long fibers AXON carry impulses AWAY from the cell body Neurons may have many dendrites by only one axon Form NERVES when axons and dendrites are clustered together ...
Nervous System
... The nervous system runs on electricity • Current- The movement of charge (electrons or ions) • Voltage- potential energy stored in a charge disparity over distance • Nervous system uses ions (Na+, K+, Cl-, Ca++) to send signals from one neuron to another ...
... The nervous system runs on electricity • Current- The movement of charge (electrons or ions) • Voltage- potential energy stored in a charge disparity over distance • Nervous system uses ions (Na+, K+, Cl-, Ca++) to send signals from one neuron to another ...
The Senses
... • Produces a receptor potential, a graded change in response to opening or closing ion channels • Neurotransmitter release is increased to signal the CNS ▫ The rate change in action potentials signals the brain ...
... • Produces a receptor potential, a graded change in response to opening or closing ion channels • Neurotransmitter release is increased to signal the CNS ▫ The rate change in action potentials signals the brain ...
Message Transmission
... • This is a nerve cell that is ready to work. • The cell membrane is more permeable to K+ than to Na+, so more positives are leaving than entering. Add the Na+ K+ pump ( a mechanism in the cell membrane that shunts the Na+ back out) and the inside is decidedly negative and the outside is definitely ...
... • This is a nerve cell that is ready to work. • The cell membrane is more permeable to K+ than to Na+, so more positives are leaving than entering. Add the Na+ K+ pump ( a mechanism in the cell membrane that shunts the Na+ back out) and the inside is decidedly negative and the outside is definitely ...
Chapter 48: Nervous System
... Neurotransmitter binds to channel (the receptor), it opens and allows ions to diffuse across the membrane Result- postsynaptic potential (change in membrane potential) Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) membrane potential brought down to threshold Inhibitiory postsynaptic potentials (IPS ...
... Neurotransmitter binds to channel (the receptor), it opens and allows ions to diffuse across the membrane Result- postsynaptic potential (change in membrane potential) Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) membrane potential brought down to threshold Inhibitiory postsynaptic potentials (IPS ...
“Put that in the Form of a Question, Please!”
... on outside). When in action potential, polarity switches and cell becomes more positive on inside as ion channels open up and Na+ ions flood in? ...
... on outside). When in action potential, polarity switches and cell becomes more positive on inside as ion channels open up and Na+ ions flood in? ...
Nervous System Objectives
... 10. Label a diagram of a synaptic region and tell where neurotransmitters are released, direction of impulse travel, ion flow, and fusion of the neurotransmitter occur. 11. Identify the types of receptors and the structures found in the vision and hearing receptors. 12. Elaborate on the nervous syst ...
... 10. Label a diagram of a synaptic region and tell where neurotransmitters are released, direction of impulse travel, ion flow, and fusion of the neurotransmitter occur. 11. Identify the types of receptors and the structures found in the vision and hearing receptors. 12. Elaborate on the nervous syst ...
Unit VIII: Animal Structure and Function, Part II
... info. To spinal cord 4. Synapses with motor neuron in spinal cord 5. Motor neuron conveys signal to quadriceps 6. Synapse with interneuron in spinal cord 7. Interneurons inhibit other motor neurons (hamstring) 8. Prevents the hamstring from contracting ...
... info. To spinal cord 4. Synapses with motor neuron in spinal cord 5. Motor neuron conveys signal to quadriceps 6. Synapse with interneuron in spinal cord 7. Interneurons inhibit other motor neurons (hamstring) 8. Prevents the hamstring from contracting ...
Chapter 48: Nervous System
... Voltage-gated ion channels: channels that open and close in response to membrane potential changes. These ion channels are responsible the action potential Potassium channels: closed when resting, opens slowly in response to depolarization Sodium channels: (two types of gates) Activation: clos ...
... Voltage-gated ion channels: channels that open and close in response to membrane potential changes. These ion channels are responsible the action potential Potassium channels: closed when resting, opens slowly in response to depolarization Sodium channels: (two types of gates) Activation: clos ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.