Neuronal Anatomy - VCC Library
... other cells. 2. Brain: interneurons. Skin: sensory neurons. 3. False. Many nerves have their cell bodies in ganglia, outside the brain and spinal cord. 4. Most protein synthesis would occur in the cell body, where most of the organelles are found. 5. The CNS comprises the spinal cord and the brain w ...
... other cells. 2. Brain: interneurons. Skin: sensory neurons. 3. False. Many nerves have their cell bodies in ganglia, outside the brain and spinal cord. 4. Most protein synthesis would occur in the cell body, where most of the organelles are found. 5. The CNS comprises the spinal cord and the brain w ...
Sensory input: Sensory structures, classification by function
... neuron innervating the cell; these neurons are located in cranial nerves VII, IX, X 6. information from these neurons is routed via the thalamus to the gustatory cortex, where information from smell and pain receptors is integrated with gustatory input ...
... neuron innervating the cell; these neurons are located in cranial nerves VII, IX, X 6. information from these neurons is routed via the thalamus to the gustatory cortex, where information from smell and pain receptors is integrated with gustatory input ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... axon per neuron Rare branches, if present, are called axon collaterals Axonal terminal – branched terminus of an axon ...
... axon per neuron Rare branches, if present, are called axon collaterals Axonal terminal – branched terminus of an axon ...
CH005a NERVOUS SYS - INTRO 10-22
... Bloodborne metabolic wastes, such as urea and creatinine as well as proteins, certain toxins, and most drugs, are prevented from entering brain tissue ...
... Bloodborne metabolic wastes, such as urea and creatinine as well as proteins, certain toxins, and most drugs, are prevented from entering brain tissue ...
Nerves Day 2
... ions diffuse inward, depolarizing the membrane. • About the same time, potassium channels open and potassium ions diffuse outwards, repolarizing the membrane • Rapid change in potential is Action Potential ...
... ions diffuse inward, depolarizing the membrane. • About the same time, potassium channels open and potassium ions diffuse outwards, repolarizing the membrane • Rapid change in potential is Action Potential ...
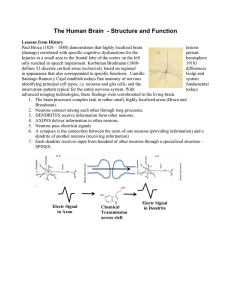
The Human Brain - Structure and Function
... innervation pattern typical for the entire nervous system. With todays advanced imaging technologies, these findings were corroborated in the living brain. 1. The brain processes complex task in rather small, highly localized areas (Broca and Broadman). 2. Neurons connect among each other through lo ...
... innervation pattern typical for the entire nervous system. With todays advanced imaging technologies, these findings were corroborated in the living brain. 1. The brain processes complex task in rather small, highly localized areas (Broca and Broadman). 2. Neurons connect among each other through lo ...
The human brain is a 3 pound mass of fatty tissue that controls all
... When the cell increases its firing rate, it produces more neurotransmitter at its synapse, more strongly influencing the post-synaptic cell. Acetylcholine: This was the first neurotransmitter that was identified (about 75 years ago). Motor neurons release this neurotransmitter onto the skeletal musc ...
... When the cell increases its firing rate, it produces more neurotransmitter at its synapse, more strongly influencing the post-synaptic cell. Acetylcholine: This was the first neurotransmitter that was identified (about 75 years ago). Motor neurons release this neurotransmitter onto the skeletal musc ...
AP – All or nothing
... 3. Temperature – higher temp = faster nerve impulse (rate of diffusion is faster, enzyme activity is faster e.g. ATPase. ...
... 3. Temperature – higher temp = faster nerve impulse (rate of diffusion is faster, enzyme activity is faster e.g. ATPase. ...
Module 10 Guided Notes The Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... Module 10 Guided Notes The Nervous and Endocrine Systems THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. What role does the Central Nervous System play? The decision maker 2. What role does the peripheral nervous system play? Gathers information and transmits decisions made by CNS to other parts of body 3. What role do n ...
... Module 10 Guided Notes The Nervous and Endocrine Systems THE NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. What role does the Central Nervous System play? The decision maker 2. What role does the peripheral nervous system play? Gathers information and transmits decisions made by CNS to other parts of body 3. What role do n ...
Chapter 1: Concepts and Methods in Biology - Rose
... ii. EPSPs and IPSPs decay with time iii. EPSPs and IPSPs decay with distance (relative to axon hillock) b. If voltage at axon hillock exceeds threshold, then action potential is fired 2. Summation–ADDITIVE effect of EPSPs and IPSPs (fig. 48.14) a. Temporal summation–additive effects of PSPs from a s ...
... ii. EPSPs and IPSPs decay with time iii. EPSPs and IPSPs decay with distance (relative to axon hillock) b. If voltage at axon hillock exceeds threshold, then action potential is fired 2. Summation–ADDITIVE effect of EPSPs and IPSPs (fig. 48.14) a. Temporal summation–additive effects of PSPs from a s ...
Untitled 2
... - In the brain finer dendrites are highly specialised for collecting information, bristling with dendrites spines which represent points of close contact - synapses - with other neurons ...
... - In the brain finer dendrites are highly specialised for collecting information, bristling with dendrites spines which represent points of close contact - synapses - with other neurons ...
Term - k20 learn
... One of the organs of the nervous system, the body’s central “computer” that receives, integrates, and sends messages. ...
... One of the organs of the nervous system, the body’s central “computer” that receives, integrates, and sends messages. ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... a. __________ (α) adrenergic receptors are the most common sympathetic receptor; they respond _________ to NE and weakly to epinephrine; α receptors are found in many _________ b. ____ (β) adrenergic receptors have two main subtypes β1 and β2 1) ___ receptors respond ___________ to NE and epinephrin ...
... a. __________ (α) adrenergic receptors are the most common sympathetic receptor; they respond _________ to NE and weakly to epinephrine; α receptors are found in many _________ b. ____ (β) adrenergic receptors have two main subtypes β1 and β2 1) ___ receptors respond ___________ to NE and epinephrin ...
Andrea Sookchan Jasmine Hodge Billy Chang
... •These cells carry messages (impulse) throughout the nervous system. ...
... •These cells carry messages (impulse) throughout the nervous system. ...
Nervous System Communication
... • Nerve impulse is started by a stimulus • Stimuli cause movements of ions through membrane • Threshold potential – Sufficient stimulation to depolarize membrane ...
... • Nerve impulse is started by a stimulus • Stimuli cause movements of ions through membrane • Threshold potential – Sufficient stimulation to depolarize membrane ...
to find the lecture notes for lecture 6 nervous tissue click here
... – Opening of chloride channels (inward) or potassium channels (outward) ...
... – Opening of chloride channels (inward) or potassium channels (outward) ...
fleming_Oct
... Many resemble activities of neurotransmitters Caffeine Constricts blood vessels in the brain Interferes with the effects of the neurotransmitter adenosine (ANTAG) Alcohol-multiple effects on brain NTs Inhibits flow of sodium across the membrane Expands the surface of membranes Decreases serotonin ac ...
... Many resemble activities of neurotransmitters Caffeine Constricts blood vessels in the brain Interferes with the effects of the neurotransmitter adenosine (ANTAG) Alcohol-multiple effects on brain NTs Inhibits flow of sodium across the membrane Expands the surface of membranes Decreases serotonin ac ...
Guided Notes for the Nervous System-
... 5.There are two subdivisions of the PNS. The sensory, or afferent, division consists of nerve fibers that convey impulses to the central nervous system from sensory receptors located in various parts of the body. The motor, or efferent, division carries impulses from the CNS to effector organs, the ...
... 5.There are two subdivisions of the PNS. The sensory, or afferent, division consists of nerve fibers that convey impulses to the central nervous system from sensory receptors located in various parts of the body. The motor, or efferent, division carries impulses from the CNS to effector organs, the ...
I) Mark right or false beside each sentence and correct the wrong
... 9- The postganglionic fibre of parasympathetic nervous system releases acetylcholine that binds muscarinic receptors on the effector organs. ( ) ﺻﺢ 10- The postganglionic fibre of sympathetic nervous system releases norepinephrine that binds adrenergic receptors on the effector organs. ( )ﺻﺢ 11- ...
... 9- The postganglionic fibre of parasympathetic nervous system releases acetylcholine that binds muscarinic receptors on the effector organs. ( ) ﺻﺢ 10- The postganglionic fibre of sympathetic nervous system releases norepinephrine that binds adrenergic receptors on the effector organs. ( )ﺻﺢ 11- ...
HUMAN ANATOMY
... • Axon – is the long (sometimes up to the 1 m or more) extension, which sends outgoing signals to the cells. ...
... • Axon – is the long (sometimes up to the 1 m or more) extension, which sends outgoing signals to the cells. ...
Nervous System Part 1
... If the cell only had K + channels the equilibrium potential of the cell would be ...
... If the cell only had K + channels the equilibrium potential of the cell would be ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.