Nervous system - Lancaster High School
... Membrane potentials change quickly 2. Chemical Neurotransmitters Most vertebrates ...
... Membrane potentials change quickly 2. Chemical Neurotransmitters Most vertebrates ...
Fundamentals of Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... A neuron has a cell body. Many smaller branched appendages are called Dendrites. Dendrites bring in information (nerve impulse) to the cell body. A single longer appendage is called Axon. It takes information away from cell body. It branches at the end into terminal knobs. A terminal knob secretes a ...
... A neuron has a cell body. Many smaller branched appendages are called Dendrites. Dendrites bring in information (nerve impulse) to the cell body. A single longer appendage is called Axon. It takes information away from cell body. It branches at the end into terminal knobs. A terminal knob secretes a ...
UNIT 4 – HOMEOSTASIS 8.1 – Human Body Systems and H
... - An action potential cannot cross the synaptic cleft between neurons therefore the nerve impulse is carried across by chemicals called neurotransmitters. - Once an action potential reaches the area of the terminal button, it initiates the following sequence of events. 1) Calcium ions (Ca2+) diffuse ...
... - An action potential cannot cross the synaptic cleft between neurons therefore the nerve impulse is carried across by chemicals called neurotransmitters. - Once an action potential reaches the area of the terminal button, it initiates the following sequence of events. 1) Calcium ions (Ca2+) diffuse ...
Nervous System
... 3. axon- long, fibrous part of neuron; conducts nerve impulses away from cell body 4. at the end of the axon, the impulse travels across the synapse, a tiny gap separating the axon of one neuron from the dendrite of another. Once the impulse reaches the end of the axon, it is able to jump the gap by ...
... 3. axon- long, fibrous part of neuron; conducts nerve impulses away from cell body 4. at the end of the axon, the impulse travels across the synapse, a tiny gap separating the axon of one neuron from the dendrite of another. Once the impulse reaches the end of the axon, it is able to jump the gap by ...
Bio 211 Lecture 18
... • absolute - time when threshold stimulus does not start another action potential (Na+ channels inactivated) • relative – time when stronger threshold stimulus can start another action potential (Na+ channels restored, K+ channels begin ...
... • absolute - time when threshold stimulus does not start another action potential (Na+ channels inactivated) • relative – time when stronger threshold stimulus can start another action potential (Na+ channels restored, K+ channels begin ...
Major Divisions in the Central Nervous System
... 7. axis cylinder – composed of neurofibrils – carry impulse throughout neuron 8. nodes of ranvier – gaps between successive schwann cells 9. motor end plate – (axon terminals) site where neurotransmitters are stored and released through the synapse to an effector 10. axon – carry impulses away from ...
... 7. axis cylinder – composed of neurofibrils – carry impulse throughout neuron 8. nodes of ranvier – gaps between successive schwann cells 9. motor end plate – (axon terminals) site where neurotransmitters are stored and released through the synapse to an effector 10. axon – carry impulses away from ...
Lecture 2: Basics and definitions - Homepages | The University of
... • UNITs: nerve cells called neurons, many different types and are extremely complex • around 1011 neurons in the brain (depending on counting technique) each with 103 connections • INTERACTIONs: signal is conveyed by action potentials, interactions could be chemical (release or receive neurotransmit ...
... • UNITs: nerve cells called neurons, many different types and are extremely complex • around 1011 neurons in the brain (depending on counting technique) each with 103 connections • INTERACTIONs: signal is conveyed by action potentials, interactions could be chemical (release or receive neurotransmit ...
Chapter 3 Neuroscience and Behavior
... Messages between neurons are transmitted by chemical messengers called neurotransmitters: little chemical messengers Neurotransmitters are held in the synaptic vesicles , little sacs in the axon terminal When an action potential reaches the axon terminal, the synaptic vesicles release their neurotra ...
... Messages between neurons are transmitted by chemical messengers called neurotransmitters: little chemical messengers Neurotransmitters are held in the synaptic vesicles , little sacs in the axon terminal When an action potential reaches the axon terminal, the synaptic vesicles release their neurotra ...
Slide 1
... An efferent or motor neuron conducts impulses from CNS to PNS Voluntary Control – in somatic nervous system Involuntary control – in autonomic nervous system ...
... An efferent or motor neuron conducts impulses from CNS to PNS Voluntary Control – in somatic nervous system Involuntary control – in autonomic nervous system ...
Slide - Reza Shadmehr
... A neuron can produce only one kind of neurotransmitter at its synapse. The post-synaptic neuron will have receptors for this neurotransmitter that will either cause an increase or decrease in membrane potential. Acetylcholine (ACh) Released by neurons that control muscles (motor neurons), neurons th ...
... A neuron can produce only one kind of neurotransmitter at its synapse. The post-synaptic neuron will have receptors for this neurotransmitter that will either cause an increase or decrease in membrane potential. Acetylcholine (ACh) Released by neurons that control muscles (motor neurons), neurons th ...
Slide ()
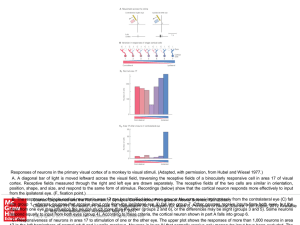
... A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. Receptive fields measured through the right and left eye are drawn separately. The receptive fields of the two cells are similar in orie ...
... A. A diagonal bar of light is moved leftward across the visual field, traversing the receptive fields of a binocularly responsive cell in area 17 of visual cortex. Receptive fields measured through the right and left eye are drawn separately. The receptive fields of the two cells are similar in orie ...
Organization of the nervous system
... determines whether it will fire •Axon:Extending fiber that conducts impulses away from the cell body and transmits to other cells. ...
... determines whether it will fire •Axon:Extending fiber that conducts impulses away from the cell body and transmits to other cells. ...
Nervous System: Levels of Organization Review and
... Compare the structure of myelinated vs. unmyelinated axons. Distinguish between white matter and gray matter. Describe the transmembrane potential or voltage across the cell membrane and how it is measured. Contrast the relative concentrations of ions in body solutions inside and outside of a cell ( ...
... Compare the structure of myelinated vs. unmyelinated axons. Distinguish between white matter and gray matter. Describe the transmembrane potential or voltage across the cell membrane and how it is measured. Contrast the relative concentrations of ions in body solutions inside and outside of a cell ( ...
Neurons
... Within a neuron, the transmission of information is usually electrical. Between neurons, the transmission of information is usually chemical. When the signal is electrical, two neurons communicate physically through gap junctions. Synchronicity among the neurons is thereby maintained as the juncti ...
... Within a neuron, the transmission of information is usually electrical. Between neurons, the transmission of information is usually chemical. When the signal is electrical, two neurons communicate physically through gap junctions. Synchronicity among the neurons is thereby maintained as the juncti ...
Exploring the Human Nervous System
... Saltatory conduction is faster than conduction on unmyelinated neurons. ...
... Saltatory conduction is faster than conduction on unmyelinated neurons. ...
hwk-4-pg-521 - WordPress.com
... Schwann cells, which produce the myelin sheath, and the glial cells, which provide nutritional and structural support for neurons. They facilitate the transmission of nerve impulses via neurons but do not provide nerve transmission themselves. 4. Reflexes have evolved to occur without the need for t ...
... Schwann cells, which produce the myelin sheath, and the glial cells, which provide nutritional and structural support for neurons. They facilitate the transmission of nerve impulses via neurons but do not provide nerve transmission themselves. 4. Reflexes have evolved to occur without the need for t ...
Central nervous system (CNS)
... regulates the amount of water in your blood. About the size of a marble and found at the base of the cerebrum. It also releases HGH—controls how fast everything grows. Releases hormones that control all other glands. Referred to as the “master gland”. ...
... regulates the amount of water in your blood. About the size of a marble and found at the base of the cerebrum. It also releases HGH—controls how fast everything grows. Releases hormones that control all other glands. Referred to as the “master gland”. ...
The Nervous System - Needham.K12.ma.us
... within a Neuron! • The change in charge that travels from the dendrite of a neuron down the axon. • Can be represented on a graph as a nerve impluse: ...
... within a Neuron! • The change in charge that travels from the dendrite of a neuron down the axon. • Can be represented on a graph as a nerve impluse: ...
Reflex Arc - WordPress.com
... Reflexes are automatic - don’t have to think about them Message doesn’t have to go to brain for response to occur, sent directly to spinal cord Since there is no processing, reactions can be very quick ...
... Reflexes are automatic - don’t have to think about them Message doesn’t have to go to brain for response to occur, sent directly to spinal cord Since there is no processing, reactions can be very quick ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.