Worksheet - Nervous System I Lecture Notes Page
... membrane potential. This is called hyperpolarization. Likewise, if a neurotransmitter opens a Cl- channel then Cl- will flow into the cell, making it more _____________(positive/negative) inside, thereby hyperpolarizing the membrane. In contrast, neurotransmitters that open Na+ channels in the membr ...
... membrane potential. This is called hyperpolarization. Likewise, if a neurotransmitter opens a Cl- channel then Cl- will flow into the cell, making it more _____________(positive/negative) inside, thereby hyperpolarizing the membrane. In contrast, neurotransmitters that open Na+ channels in the membr ...
the autonomic nervous system
... CELLS OF SYMPATHETICALLY INNERVATED ORGANS • ALPHA-2: PRESYNAPTIC TERMINALS OF CHOLINERGIC ...
... CELLS OF SYMPATHETICALLY INNERVATED ORGANS • ALPHA-2: PRESYNAPTIC TERMINALS OF CHOLINERGIC ...
Chapter 48 Nervous System
... Gated potentials are triggered by some change (stimulus) in the neuron's environment. Graded potentials are short-lived, local changes in membrane potential that can be either depolarizations or hyperpolarizations. These changes cause current flows that decrease in magnitude with distance. PRODUCTIO ...
... Gated potentials are triggered by some change (stimulus) in the neuron's environment. Graded potentials are short-lived, local changes in membrane potential that can be either depolarizations or hyperpolarizations. These changes cause current flows that decrease in magnitude with distance. PRODUCTIO ...
AP Psychology
... Biological Bases of Behavior 1. In the 1800's Franz Gall invented the study of phrenology. What is phrenology and what positive outcomes evolved from this study? (Myers) 2. Define neuron and explain the parts found in each cell a. dendrite b. cell body c. axon d. myelin sheath 3. Explain the neuron ...
... Biological Bases of Behavior 1. In the 1800's Franz Gall invented the study of phrenology. What is phrenology and what positive outcomes evolved from this study? (Myers) 2. Define neuron and explain the parts found in each cell a. dendrite b. cell body c. axon d. myelin sheath 3. Explain the neuron ...
Neuroanatomy- anatomy of nerve cell (neuron)
... Axon - longest part of neuron. Myelin sheath- covering around the axon that speeds neural impulses.. Breakdown of Mylin Sheath (MS) is related to Multiple Sclerosis (MS). Terminal Buttons of axon (aka end buttons, terminal branches, synaptic knobs))- branched end of the axon that contains neurotrans ...
... Axon - longest part of neuron. Myelin sheath- covering around the axon that speeds neural impulses.. Breakdown of Mylin Sheath (MS) is related to Multiple Sclerosis (MS). Terminal Buttons of axon (aka end buttons, terminal branches, synaptic knobs))- branched end of the axon that contains neurotrans ...
NOTES FOR CHAPTER 13
... 1. Resting Potential – the inside of the axon is neg. compared to outside * sodium-potassium “pump” maintains this difference at rest ...
... 1. Resting Potential – the inside of the axon is neg. compared to outside * sodium-potassium “pump” maintains this difference at rest ...
Chapter 10: Nervous System I: Basic Structure and Function
... 8. A nerve impulse is the propagation of action potentials along an axon. F. All-or-None Response 1. A nerve impulse is an all-or-nothing response, meaning if a neuron responds at all to a nerve impulse, it responds completely. 2. A greater intensity of stimulation on the neuron produces more impuls ...
... 8. A nerve impulse is the propagation of action potentials along an axon. F. All-or-None Response 1. A nerve impulse is an all-or-nothing response, meaning if a neuron responds at all to a nerve impulse, it responds completely. 2. A greater intensity of stimulation on the neuron produces more impuls ...
Somatic and Special Senses
... surrounded by columnar epithelial cells There are 400 types of olfactory receptor proteins Odorant molecules enter the nasal cavity as gases, dissolve in watery fluids, and then bind to the receptors in different patterns Stimulated olfactory receptors cells send nerve impulses along their axons whi ...
... surrounded by columnar epithelial cells There are 400 types of olfactory receptor proteins Odorant molecules enter the nasal cavity as gases, dissolve in watery fluids, and then bind to the receptors in different patterns Stimulated olfactory receptors cells send nerve impulses along their axons whi ...
A- A- A- K+ A - How Your Brain Works
... • In addition to the resting (K+ leakage) channels, neurons can have a large variety of gated ion channels which will open transiently in the presence of certain stimuli or chemical signals. These gated channels may be permeable to Na+, Cl- or Ca++. • When these gated channels open, the voltage acro ...
... • In addition to the resting (K+ leakage) channels, neurons can have a large variety of gated ion channels which will open transiently in the presence of certain stimuli or chemical signals. These gated channels may be permeable to Na+, Cl- or Ca++. • When these gated channels open, the voltage acro ...
The Nervous System (ppt).
... Nerve impulse = all-or-none response Membrane permeability changes again ...
... Nerve impulse = all-or-none response Membrane permeability changes again ...
Study/Review * Nervous System Part 2 * CNS and PNS
... 2. These cells make myelin on axons of the CNS: _______________________ 3. _________________________ are gaps in the myelin sheath 4. A change in ion/charge distribution across the axon membrane is called ___________________________ ...
... 2. These cells make myelin on axons of the CNS: _______________________ 3. _________________________ are gaps in the myelin sheath 4. A change in ion/charge distribution across the axon membrane is called ___________________________ ...
Nerve Cell Physiology
... It can summate, which means if another stimulus is applied before repolarization is complete, the depolarization of the second stimulus adds onto the depolarization of the first (the 2 depolarizations sum together). رافع عاوي الفياض.د ...
... It can summate, which means if another stimulus is applied before repolarization is complete, the depolarization of the second stimulus adds onto the depolarization of the first (the 2 depolarizations sum together). رافع عاوي الفياض.د ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM - Welcome to SBI4U with Ms. Taman!
... • Brain is found in the skull & serves as overall control center for the nervous system • Spinal Cord is surrounded by vertebrae and extends down the back of the neck, thorax and abdomen – Center of many reflex actions – Provides a link between sensory and motor nerves ...
... • Brain is found in the skull & serves as overall control center for the nervous system • Spinal Cord is surrounded by vertebrae and extends down the back of the neck, thorax and abdomen – Center of many reflex actions – Provides a link between sensory and motor nerves ...
Review (10/25/16) updated
... • Which type of hair cell receives more efferent input from the brain – Outer. If you do not know what efferent means, google it. This should make sense. ...
... • Which type of hair cell receives more efferent input from the brain – Outer. If you do not know what efferent means, google it. This should make sense. ...
unit 2 – nervous system / senses - Greater Atlanta Christian Schools
... -“polarized” b/c of electrical charge difference that exists on each side of the cell membrane - inside cell: -ve ; high amt. of K+ - outside cell: +ve; high amt of Na+ - cell membrane permeability K+ > Na+ - Na+/ K+ exchange pump maintains RMP 3. Stimulated Neuron (action potential) a. nerve (e ...
... -“polarized” b/c of electrical charge difference that exists on each side of the cell membrane - inside cell: -ve ; high amt. of K+ - outside cell: +ve; high amt of Na+ - cell membrane permeability K+ > Na+ - Na+/ K+ exchange pump maintains RMP 3. Stimulated Neuron (action potential) a. nerve (e ...
Complete Nervous System Worksheet
... Nerves - process and send information fast (eg. stepping on a tack) Hormones - process and send information slowly (eg. growth hormone etc) 2. Major components of the nervous system: Two major divisions The central nervous system (CNS) - made up of the spinal cord and brain The peripheral nervous sy ...
... Nerves - process and send information fast (eg. stepping on a tack) Hormones - process and send information slowly (eg. growth hormone etc) 2. Major components of the nervous system: Two major divisions The central nervous system (CNS) - made up of the spinal cord and brain The peripheral nervous sy ...
The Nervous System - leavingcertbiology.net
... Mechanism of the Reflex Arc (cont.) • Some interneurons carry impulse directly to cell bodies of motor neurons located in the spinal cord whereas others carry impulses to the brain • The stimulated motor neurons carry impulses from spinal cord along the ventral root nerve to the effector(s), in thi ...
... Mechanism of the Reflex Arc (cont.) • Some interneurons carry impulse directly to cell bodies of motor neurons located in the spinal cord whereas others carry impulses to the brain • The stimulated motor neurons carry impulses from spinal cord along the ventral root nerve to the effector(s), in thi ...
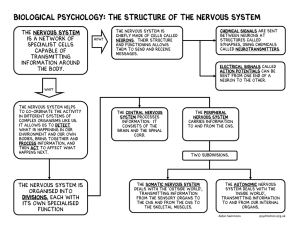
Biological Psychology: The structure of the nervous system
... in different systems of complex organisms like us. It allows us to detect what is happening in our environment and our own bodies, bring together and process information, and ...
... in different systems of complex organisms like us. It allows us to detect what is happening in our environment and our own bodies, bring together and process information, and ...
sympathetic and parasympathetic systems
... The Hypothalamus is the part of the brain that is concerned with homeostasis (maintaining a constant internal environment). The pituitary is a small gland (2 parts, anterior and posterior lobes) that produces a large number of hormones, many of which control the release of hormones from other glands ...
... The Hypothalamus is the part of the brain that is concerned with homeostasis (maintaining a constant internal environment). The pituitary is a small gland (2 parts, anterior and posterior lobes) that produces a large number of hormones, many of which control the release of hormones from other glands ...
Neuron - Schoolwires.net
... with the same intensity. A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. **Toilet flushing example ...
... with the same intensity. A strong stimulus can trigger more neurons to fire, and to fire more often, but it does not affect the action potentials strength or speed. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. **Toilet flushing example ...
The Neuron
... sense, they serve to "feed" the nerve cells. They also provide a structure for guiding and directing the neural signal. Supporting cells also serve the function of "consuming" damaged tissue in a process known as phagocytosis. Not only do they clean up the damaged tissue, but they also fill the spac ...
... sense, they serve to "feed" the nerve cells. They also provide a structure for guiding and directing the neural signal. Supporting cells also serve the function of "consuming" damaged tissue in a process known as phagocytosis. Not only do they clean up the damaged tissue, but they also fill the spac ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.