Body Systems - Bishop Ireton High School
... An impulse has only 1 strength It must be strong enough to start an impulse in a ...
... An impulse has only 1 strength It must be strong enough to start an impulse in a ...
Nervous System - simonbaruchcurriculum
... The network of nerves allows the brain to communicate with every part of the body. Nerves transmit information as electrical impulses from one area of the body to another. Some nerves carry information to the brain. This allows us to see, hear, smell, taste and touch. Other nerves carry information ...
... The network of nerves allows the brain to communicate with every part of the body. Nerves transmit information as electrical impulses from one area of the body to another. Some nerves carry information to the brain. This allows us to see, hear, smell, taste and touch. Other nerves carry information ...
File - Perkins Science
... a. Neurons that conduct impulses but generally can not divide. b. Glial cells (neuroglia) that support the neurons and can not conduct impulses, but can divide ...
... a. Neurons that conduct impulses but generally can not divide. b. Glial cells (neuroglia) that support the neurons and can not conduct impulses, but can divide ...
Axon - Perkins Science
... a. Neurons that conduct impulses but generally can not divide. b. Glial cells (neuroglia) that support the neurons and can not conduct impulses, but can divide ...
... a. Neurons that conduct impulses but generally can not divide. b. Glial cells (neuroglia) that support the neurons and can not conduct impulses, but can divide ...
Midterm 1 - studyfruit
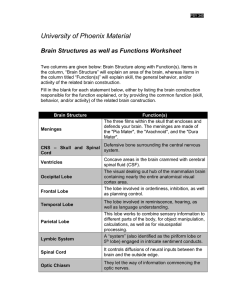
... ○ Phineas Gage- dynamite worker in 1848 who had an iron bar that entered his head under his left eye, passed through his frontal lobe, and exited through the top of his skull ■ was mobile even while the iron bar was in his brain ■ survived for 12 more years after bar was removed from his brain ● los ...
... ○ Phineas Gage- dynamite worker in 1848 who had an iron bar that entered his head under his left eye, passed through his frontal lobe, and exited through the top of his skull ■ was mobile even while the iron bar was in his brain ■ survived for 12 more years after bar was removed from his brain ● los ...
LECTURE FIVE
... Somehow similar to this case: from an eliminativist perspective, the Great French Revolution is not a legitimate label which can pick out a single historical event. Rather, it should be viewed as a label attached to a loose collection of the behaviors of numerous individuals. Though historians nee ...
... Somehow similar to this case: from an eliminativist perspective, the Great French Revolution is not a legitimate label which can pick out a single historical event. Rather, it should be viewed as a label attached to a loose collection of the behaviors of numerous individuals. Though historians nee ...
HP Authorized Customer
... autonomic nervous system and somatic nervous Autonomic System system. Controls essential functions such as blood Medulla Oblongata pressure, breathing, and heart rate. The specific olfactory receptor neurons related to the olfactory nerve are situated in the olfactory mucosa of the nasal hollow spac ...
... autonomic nervous system and somatic nervous Autonomic System system. Controls essential functions such as blood Medulla Oblongata pressure, breathing, and heart rate. The specific olfactory receptor neurons related to the olfactory nerve are situated in the olfactory mucosa of the nasal hollow spac ...
Biology 212: January 30, 2002
... describe: All relevant channels involved, and when they open and close (refer to your “custom drawing” from class) Which ions move when, in which direction, and what they do to the membrane potential 11. Briefly explain how an action potential is propagated down an axon. 12. Describe, step-by-st ...
... describe: All relevant channels involved, and when they open and close (refer to your “custom drawing” from class) Which ions move when, in which direction, and what they do to the membrane potential 11. Briefly explain how an action potential is propagated down an axon. 12. Describe, step-by-st ...
Chapter 3
... • The classes of sensory modalities are general senses and special senses. – The general senses include both somatic and visceral senses, which provide information about conditions within internal organs. – The special senses include the modalities of smell, taste, vision, hearing, and equilibrium. ...
... • The classes of sensory modalities are general senses and special senses. – The general senses include both somatic and visceral senses, which provide information about conditions within internal organs. – The special senses include the modalities of smell, taste, vision, hearing, and equilibrium. ...
HISTOLOGY REVISIT: NEURONS AND NEUROGLIA LEARNING
... Cell body varies in size from 4 micrometer as in granule cells of cerebral cortex to I35 micrometer in anterior horn cells of spinal cord Shape of body may be globular in pseudounipolar cells Spindle shaped in bipolar neurons Vary from pyramidal to globular in multipolar cells ...
... Cell body varies in size from 4 micrometer as in granule cells of cerebral cortex to I35 micrometer in anterior horn cells of spinal cord Shape of body may be globular in pseudounipolar cells Spindle shaped in bipolar neurons Vary from pyramidal to globular in multipolar cells ...
File - Ms Curran`s Leaving Certificate Biology
... Touch Skin contains receptors for touch & temperature These are found in different concentrations in skin at various locations around the body. E.g. very few in the heel of the foot compared to the elbow which has several (this is why parents use their elbow to test the temp of a ...
... Touch Skin contains receptors for touch & temperature These are found in different concentrations in skin at various locations around the body. E.g. very few in the heel of the foot compared to the elbow which has several (this is why parents use their elbow to test the temp of a ...
B6 Brain and Mind
... Neurones never ____ each other – there is a small gap between them called a _____. A signal is sent from one _______ to the next by a _______ transmitter across the synapse (called a “neurotransmitter”). These transmitters are then ________ back into the sensory neurone to be used again. This proces ...
... Neurones never ____ each other – there is a small gap between them called a _____. A signal is sent from one _______ to the next by a _______ transmitter across the synapse (called a “neurotransmitter”). These transmitters are then ________ back into the sensory neurone to be used again. This proces ...
Lecture 6
... Neocortex: Cortex means bark in Greek, it lies as a bark over the rest of the brain with a surface of 2000cm^2. At the back is the occipital area important for visual processing (the later takes up 40% of the brain) very high visual resolution (& capability for associative and therefore creative ...
... Neocortex: Cortex means bark in Greek, it lies as a bark over the rest of the brain with a surface of 2000cm^2. At the back is the occipital area important for visual processing (the later takes up 40% of the brain) very high visual resolution (& capability for associative and therefore creative ...
Physiology
... Physiology The Nervous System The human nervous system consists of billions of nerve cells (or neurons)plus supporting (neuroglial) cells. Neurons are able to respond to stimuli (such as touch, sound, light, and so on), conduct impulses, and communicate with each other (and with other types of cells ...
... Physiology The Nervous System The human nervous system consists of billions of nerve cells (or neurons)plus supporting (neuroglial) cells. Neurons are able to respond to stimuli (such as touch, sound, light, and so on), conduct impulses, and communicate with each other (and with other types of cells ...
Synapse
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
Chapter 28
... THE SYNAPSE • The vertebrate nervous system uses dozens of different kinds of neurotransmitters. • They fall into two classes, depending on whether they excite or inhibit the postsynaptic cell. • In an excitatory synapse, the chemically-gated channel is usually a Na+ channel. • This can lead to an ...
... THE SYNAPSE • The vertebrate nervous system uses dozens of different kinds of neurotransmitters. • They fall into two classes, depending on whether they excite or inhibit the postsynaptic cell. • In an excitatory synapse, the chemically-gated channel is usually a Na+ channel. • This can lead to an ...
Notes0112
... These amino acids bind to and activate a cation-permeable channel, causing depolarization in a similar manner to glutamate activation of cation channels in the brain ...
... These amino acids bind to and activate a cation-permeable channel, causing depolarization in a similar manner to glutamate activation of cation channels in the brain ...
Summary - SCIENCE HELP @ ne3me.com
... impulses to the central nervous system. There are five types of sensory receptors. Pain receptors respond to pain. Thermoreceptors respond to temperature. Mechanoreceptors respond to pressure. Chemoreceptors respond to chemicals. Photoreceptors respond to light. Light enters the eye through the pupi ...
... impulses to the central nervous system. There are five types of sensory receptors. Pain receptors respond to pain. Thermoreceptors respond to temperature. Mechanoreceptors respond to pressure. Chemoreceptors respond to chemicals. Photoreceptors respond to light. Light enters the eye through the pupi ...
Nervous System - s3.amazonaws.com
... • Did you know that 1 cm3 of your brain contains about 50 million neurons (nerve cells)? • Each neuron may communicate with thousands of other neurons forming intricate networks that control our functions and store our thoughts. • The nervous system has 3 major functions. – Sensory input moves signa ...
... • Did you know that 1 cm3 of your brain contains about 50 million neurons (nerve cells)? • Each neuron may communicate with thousands of other neurons forming intricate networks that control our functions and store our thoughts. • The nervous system has 3 major functions. – Sensory input moves signa ...
Neurons - University of San Diego Home Pages
... Our example: vertebrate motor neuron • Signal is a neurotransmitter (in other neurons, the signal may be electrical, chemical, mechanical, etc.) • Neurotransmitter must bind to a receptor. • Receptor is a ligand-gated ion channel. • These receptors are concentrated on the dendrites and cell bod ...
... Our example: vertebrate motor neuron • Signal is a neurotransmitter (in other neurons, the signal may be electrical, chemical, mechanical, etc.) • Neurotransmitter must bind to a receptor. • Receptor is a ligand-gated ion channel. • These receptors are concentrated on the dendrites and cell bod ...
Parts of a Neuron…… Neuronal Communication….
... • Very end of the axon where chemicals are released to stimulate the next neighboring neuron located nearby ...
... • Very end of the axon where chemicals are released to stimulate the next neighboring neuron located nearby ...
Nervous system Nervous system
... • Separated from the brain stem by the 4th ventricle – Receives sensory input from the eyes, ears, joints, and muscles – Sends motor impulses out the brain stem to the skeletal muscles • Helps maintain balance and produce smooth ...
... • Separated from the brain stem by the 4th ventricle – Receives sensory input from the eyes, ears, joints, and muscles – Sends motor impulses out the brain stem to the skeletal muscles • Helps maintain balance and produce smooth ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.