Target in Field Search: Distractor in Field - Smith
... Most neurons in the deeper layers of the SC show activity aligned with the visual input and the motor response in single-target tasks. Many of these same neurons show additional discharge that is correlated with higherlevel decision processes in more natural visual tasks. In the case of pop-out sear ...
... Most neurons in the deeper layers of the SC show activity aligned with the visual input and the motor response in single-target tasks. Many of these same neurons show additional discharge that is correlated with higherlevel decision processes in more natural visual tasks. In the case of pop-out sear ...
CLASS 10 CONTROL AND CO – ORDINATION Instructions:
... Mid brain- It connects Fore brain and Hind brain. Controls reflex of eyes & ears Hind brain- Connects the Fore brain & Hind brai Cerebellum – Controls & coordinates muscular movements, maintaining body posture and equilibrium. Pons- Acts as a bridge between brain & spinal cord Medulla oblongata- Con ...
... Mid brain- It connects Fore brain and Hind brain. Controls reflex of eyes & ears Hind brain- Connects the Fore brain & Hind brai Cerebellum – Controls & coordinates muscular movements, maintaining body posture and equilibrium. Pons- Acts as a bridge between brain & spinal cord Medulla oblongata- Con ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... If something causes the membrane’s permeability to Na+ to increase, the membrane potential will move toward ENa and away from EK. ...
... If something causes the membrane’s permeability to Na+ to increase, the membrane potential will move toward ENa and away from EK. ...
Physiology – Excitable Tissue – 11th May 2010
... 28. Choose the incorrect statement regarding the Golgi tendon organ. a. is the receptor for the inverse stretch reflex b. there are 3-25 muscle fibres per tendon organ c. involved in regulation of the velocity of the muscle contraction d. stimulation leads to production of EPSPs (excitatory postsyna ...
... 28. Choose the incorrect statement regarding the Golgi tendon organ. a. is the receptor for the inverse stretch reflex b. there are 3-25 muscle fibres per tendon organ c. involved in regulation of the velocity of the muscle contraction d. stimulation leads to production of EPSPs (excitatory postsyna ...
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior
... • The nervous system is never at rest. There is always a job for it to do. Even when you are sleeping the nervous system is busy regulating your body functions. The nervous system controls your emotions, movements, thinking and behavior. ...
... • The nervous system is never at rest. There is always a job for it to do. Even when you are sleeping the nervous system is busy regulating your body functions. The nervous system controls your emotions, movements, thinking and behavior. ...
1. If a significant amount of Cl - entered the body of a motor neuron
... 15. When the sodium potassium pump breaks down a molecule of ATP, ______ K+ ions are moved into the cell and ______ Na+ are moved out of the cell. a. 2-3 b. 3-2 c. 3-4 d. 4-3 e. None of the above 16. The influx of sodium will cause the membrane potential of a neuron to: a. Increase b. Decrease c. S ...
... 15. When the sodium potassium pump breaks down a molecule of ATP, ______ K+ ions are moved into the cell and ______ Na+ are moved out of the cell. a. 2-3 b. 3-2 c. 3-4 d. 4-3 e. None of the above 16. The influx of sodium will cause the membrane potential of a neuron to: a. Increase b. Decrease c. S ...
intro to psych ch3 biological bases of behavior
... between the neurons over which messages pass ...
... between the neurons over which messages pass ...
Nervous Tissue
... • Formation of new neurons from stem cells was not thought to occur in humans – 1992 a growth factor was found that stimulates adult mice brain cells to multiply – 1998 new neurons found to form within adult human hippocampus (area important for learning) ...
... • Formation of new neurons from stem cells was not thought to occur in humans – 1992 a growth factor was found that stimulates adult mice brain cells to multiply – 1998 new neurons found to form within adult human hippocampus (area important for learning) ...
Final Exam - Creighton Biology
... Which of the following is not believed to be a tropic hormone? sss. Adrenocorticotropic hormone ttt. Gonadotropin releasing hormone uuu. Luteinizing hormone vvv. Prolactin releasing hormone www. All of the above are tropic hormones. In adults, long bones no longer increase in length because xxx. gro ...
... Which of the following is not believed to be a tropic hormone? sss. Adrenocorticotropic hormone ttt. Gonadotropin releasing hormone uuu. Luteinizing hormone vvv. Prolactin releasing hormone www. All of the above are tropic hormones. In adults, long bones no longer increase in length because xxx. gro ...
Plant Responses and Growth
... • Annuals – flowering plants that grow, flower and die in a single year • Biennials – complete life cycle in two years – 1st year germinate, grow roots and very short stems and leaves – 2nd year grow new stems and leaves, produce fruit ...
... • Annuals – flowering plants that grow, flower and die in a single year • Biennials – complete life cycle in two years – 1st year germinate, grow roots and very short stems and leaves – 2nd year grow new stems and leaves, produce fruit ...
Sensation
... membrane that vibrates with the waves) • Middle Ear: transmits eardrum’s vibrations through a piston made of 3 tiny bones (hammer, anvil, & stirrup) to the cochlea (snail shaped tube in inner ear) • Inner Ear: incoming vibrations cause the cochlea to vibrate & jostles the fluid that fills the tube ...
... membrane that vibrates with the waves) • Middle Ear: transmits eardrum’s vibrations through a piston made of 3 tiny bones (hammer, anvil, & stirrup) to the cochlea (snail shaped tube in inner ear) • Inner Ear: incoming vibrations cause the cochlea to vibrate & jostles the fluid that fills the tube ...
brain
... Taste – tongue is the organ of taste • Four types of flavors: sour, sweet, salty and bitter • Different areas of tongues taste different flavors • Taste buds pick up tastes and send them to brain ...
... Taste – tongue is the organ of taste • Four types of flavors: sour, sweet, salty and bitter • Different areas of tongues taste different flavors • Taste buds pick up tastes and send them to brain ...
File
... neuron. Myelin is not part of the structure of the neuron but consists of a thick layer mostly made up of lipids, present at regular intervals along the length of the axon. • Such fibers are called myelinated fibers. • The water-soluble ions carrying the current across the membrane cannot permeate t ...
... neuron. Myelin is not part of the structure of the neuron but consists of a thick layer mostly made up of lipids, present at regular intervals along the length of the axon. • Such fibers are called myelinated fibers. • The water-soluble ions carrying the current across the membrane cannot permeate t ...
Opioids General - IHMC Public Cmaps (3)
... Opioid receptors are part of a large superfamily of membrane-bound receptors that are coupled to G proteins. Each opioid receptor has a unique distribution in the brain, spinal cord, and periphery. Opioids combine reversibly with these receptors and alter the transmission and perception of pain. Oth ...
... Opioid receptors are part of a large superfamily of membrane-bound receptors that are coupled to G proteins. Each opioid receptor has a unique distribution in the brain, spinal cord, and periphery. Opioids combine reversibly with these receptors and alter the transmission and perception of pain. Oth ...
Nervous Regulation
... __________________. The junction between nerves and muscles is called a ______________ junction. ____________________ relay impulses from one neuron to another in the brain and spinal cord. The Synapse The axon ends in a __________________ which contains special chemicals called ________________ ...
... __________________. The junction between nerves and muscles is called a ______________ junction. ____________________ relay impulses from one neuron to another in the brain and spinal cord. The Synapse The axon ends in a __________________ which contains special chemicals called ________________ ...
Nervous System functions
... 1. Sensory Function • Sensory receptors at the ends of peripheral neurons: – Gather info by detecting changes inside and outside the body. • Inside: temperature and oxygen concentration • Outside: light and sound intensities ...
... 1. Sensory Function • Sensory receptors at the ends of peripheral neurons: – Gather info by detecting changes inside and outside the body. • Inside: temperature and oxygen concentration • Outside: light and sound intensities ...
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
... Neurons continued • Synapse: the space between the endings of the axon and the waiting dendrites. • Vesicles: containers in the axon bulb of the neurotransmitters. • Neurotransmitters: the chemicals that propel the message across the synapse from the end of the axon to the awaiting dendrite. Discov ...
... Neurons continued • Synapse: the space between the endings of the axon and the waiting dendrites. • Vesicles: containers in the axon bulb of the neurotransmitters. • Neurotransmitters: the chemicals that propel the message across the synapse from the end of the axon to the awaiting dendrite. Discov ...
Unit 3 Biology of Behavior The Neuron Dendrites: Tree
... Temporal Lobes: Contain the primary auditory cortex (audition) and areas for the senses of smell (olfaction) and taste (gustatory sense). The LEFT temporal lobe contains Wernicke's Area which control language comprehension and expression. Occipital Lobes: Contains the Primary Visual Cortex. Associat ...
... Temporal Lobes: Contain the primary auditory cortex (audition) and areas for the senses of smell (olfaction) and taste (gustatory sense). The LEFT temporal lobe contains Wernicke's Area which control language comprehension and expression. Occipital Lobes: Contains the Primary Visual Cortex. Associat ...
Unit 5 Homeostasis Study Guide Homeostasis: maintaining a
... Ectotherm: cold-blooded animals that either allow their body temperature to match that of the environment or use behaviors to semi-regulate it (e.g. lay in the sun or shade) Cell signaling ...
... Ectotherm: cold-blooded animals that either allow their body temperature to match that of the environment or use behaviors to semi-regulate it (e.g. lay in the sun or shade) Cell signaling ...
Slide ()
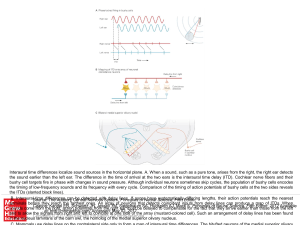
... the sound earlier than the left ear. The difference in the time of arrival at the two ears is the interaural time delay (ITD). Cochlear nerve fibers and their bushy cell targets fire in phase with changes in sound pressure. Although individual neurons sometimes skip cycles, the population of bushy c ...
... the sound earlier than the left ear. The difference in the time of arrival at the two ears is the interaural time delay (ITD). Cochlear nerve fibers and their bushy cell targets fire in phase with changes in sound pressure. Although individual neurons sometimes skip cycles, the population of bushy c ...
The Biology of Mind take
... Nerves consist of neural “cables” containing many axons. They are part of the peripheral nervous system and connect muscles, glands, and sense organs to the central nervous system. ...
... Nerves consist of neural “cables” containing many axons. They are part of the peripheral nervous system and connect muscles, glands, and sense organs to the central nervous system. ...
The Biology of Mind take 2
... Nerves consist of neural “cables” containing many axons. They are part of the peripheral nervous system and connect muscles, glands, and sense organs to the central nervous system. ...
... Nerves consist of neural “cables” containing many axons. They are part of the peripheral nervous system and connect muscles, glands, and sense organs to the central nervous system. ...
Biology 30 – Notes Neurotransmitters and the Brain, September 15
... 4. Midbrain – found about the pons in the brainstem. It relays visual and auditory information between areas of the hindbrain and forebrain. It also plays an important role in eye movement and control of skeletal muscles. 5. Medulla oblongata – sits at the base of the brainstem, it connects the brai ...
... 4. Midbrain – found about the pons in the brainstem. It relays visual and auditory information between areas of the hindbrain and forebrain. It also plays an important role in eye movement and control of skeletal muscles. 5. Medulla oblongata – sits at the base of the brainstem, it connects the brai ...
File
... same postsynaptic neuron add together. The combination of EPSPs through spatial and temporal summation can trigger an action potential. • Through summation, an IPSP can counter the effect of an EPSP. The summed effect of EPSPs and IPSPs determines whether an axon hillock will reach threshold and gen ...
... same postsynaptic neuron add together. The combination of EPSPs through spatial and temporal summation can trigger an action potential. • Through summation, an IPSP can counter the effect of an EPSP. The summed effect of EPSPs and IPSPs determines whether an axon hillock will reach threshold and gen ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.