Nervous Nellie Circuit Lesson Summary: Neurons, or nerve cells
... 8. Ask students to describe how they knew which neurons were excitatory and inhibitory. 9. Ask students to write a reflection paragraph that describes how working with the Virtual Neurons software helped them learn about neurons and neuronal communication. 10. Ask for volunteers to share their refle ...
... 8. Ask students to describe how they knew which neurons were excitatory and inhibitory. 9. Ask students to write a reflection paragraph that describes how working with the Virtual Neurons software helped them learn about neurons and neuronal communication. 10. Ask for volunteers to share their refle ...
The Nervous System
... are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... are needed to see this picture. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
Occular Dominance Columns
... Ocular Dominance Columns • The striate cortex is composed of repeating units that contain all the neuronal components to analyze a small region of visual space for a variety of different stimulus attributes. ...
... Ocular Dominance Columns • The striate cortex is composed of repeating units that contain all the neuronal components to analyze a small region of visual space for a variety of different stimulus attributes. ...
File
... 1. This lobe of the cerebrum houses your intellect, emotions, and consciousness: 2. This region of the brain acts as a relay station for sensory input: 3. These neurons transfer impulses from the brain to skeletal muscle: 4. This allows communication between the left and right hemispheres of the cer ...
... 1. This lobe of the cerebrum houses your intellect, emotions, and consciousness: 2. This region of the brain acts as a relay station for sensory input: 3. These neurons transfer impulses from the brain to skeletal muscle: 4. This allows communication between the left and right hemispheres of the cer ...
The Nervous System
... 3. What part of the brain helps a basketball player maintain her balance while driving for a lay-up? 4. What part of the body protects the spinal cord? To which body system does this body part belong? 5. Explain how the peripheral nervous system connects to the central nervous system. 6. If a spider ...
... 3. What part of the brain helps a basketball player maintain her balance while driving for a lay-up? 4. What part of the body protects the spinal cord? To which body system does this body part belong? 5. Explain how the peripheral nervous system connects to the central nervous system. 6. If a spider ...
UNIT 2 REVIEW GUIDE *Be able to identify/label parts of the neuron
... 25. Which division of the nervous system consists of just the brain and ...
... 25. Which division of the nervous system consists of just the brain and ...
Are We Paying Attention Yet?
... Unaffected by cue: 48% Depressed by the cue: 42% Enhanced by the cue: 10% This suggests that the sensitivity of parietal neurons decrement at a given location after that location has been selected ...
... Unaffected by cue: 48% Depressed by the cue: 42% Enhanced by the cue: 10% This suggests that the sensitivity of parietal neurons decrement at a given location after that location has been selected ...
Introduction - Florida Atlantic University
... opposite side of the body Other brain regions control movements via connections with primary motor cortex 1.14 ...
... opposite side of the body Other brain regions control movements via connections with primary motor cortex 1.14 ...
The Body and the Brain neurons first
... Some neurons are as small as an inch in length. Others, like the neurons that run through our legs, can be several feet long. Myelin is a white fatty substance that insulates and protects the axon. The myelin casing also helps to speed up the transmission of the message. The fibers at the end of the ...
... Some neurons are as small as an inch in length. Others, like the neurons that run through our legs, can be several feet long. Myelin is a white fatty substance that insulates and protects the axon. The myelin casing also helps to speed up the transmission of the message. The fibers at the end of the ...
The Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter
... Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells, neurons and glial cells. Neurons are the primary type of cell that most anyone associates with the nervous system. They are responsible for the computation and communication that the nervous system provides. They are electrically active and release c ...
... Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells, neurons and glial cells. Neurons are the primary type of cell that most anyone associates with the nervous system. They are responsible for the computation and communication that the nervous system provides. They are electrically active and release c ...
questions from - AP Psychology: 6(A)
... to the muscles through the motor neurons are called __________. 27. Cameron touches a hot iron and immediately pulls his hand away. His quick response occurs because __________. 28. Jack suffered a brain injury as a result of hitting his head while waterskiing. One of the problems that developed was ...
... to the muscles through the motor neurons are called __________. 27. Cameron touches a hot iron and immediately pulls his hand away. His quick response occurs because __________. 28. Jack suffered a brain injury as a result of hitting his head while waterskiing. One of the problems that developed was ...
Brainfunction - Oakton Community College
... our brain PET Scans: measure amount of glucose being metabolized in different areas of the brain EEG: measure electric charges coming from surface of the brain ...
... our brain PET Scans: measure amount of glucose being metabolized in different areas of the brain EEG: measure electric charges coming from surface of the brain ...
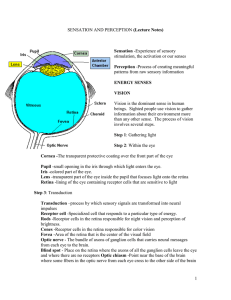
- Eye, Brain, and Vision
... the membrane from inside to outside, of packages of special chemicals call neurotransmitters. About twenty transmitter chemicals have been identified, and to judge from the rate of new discoveries the total number may exceed fifty. Transmitter molecules are much smaller than protein molecules but ar ...
... the membrane from inside to outside, of packages of special chemicals call neurotransmitters. About twenty transmitter chemicals have been identified, and to judge from the rate of new discoveries the total number may exceed fifty. Transmitter molecules are much smaller than protein molecules but ar ...
Document
... • Postsynaptic potentials fall into two categories – Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) are depolarizations that bring the membrane potential toward threshold – Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) are hyperpolarizations that move the membrane potential farther from threshold ...
... • Postsynaptic potentials fall into two categories – Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) are depolarizations that bring the membrane potential toward threshold – Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) are hyperpolarizations that move the membrane potential farther from threshold ...
File
... contains sense receptors for sound Organ of Corti -Structure on the surface of the basilar membrane that contains the receptors cells for hearing Auditory nerve -The bundle of neurons that carries signals from each ear to the brain PITCH THEORIES- As with color vision, two different theories describ ...
... contains sense receptors for sound Organ of Corti -Structure on the surface of the basilar membrane that contains the receptors cells for hearing Auditory nerve -The bundle of neurons that carries signals from each ear to the brain PITCH THEORIES- As with color vision, two different theories describ ...
Vertebrate Nervous System
... Astrocytes not responsible only for transmitting nutrients but also inflammatory signals and neurotrophic and protective factor Important cell for normal functioning of the nervous system Without astrocytes you would have significant damage to your functions ...
... Astrocytes not responsible only for transmitting nutrients but also inflammatory signals and neurotrophic and protective factor Important cell for normal functioning of the nervous system Without astrocytes you would have significant damage to your functions ...
The BRAIN - davis.k12.ut.us
... The axon is not actively conducting nerve impulses. Sodium is the ion found in the greatest concentration in the extracellular fluid. Potassium is the ion found in the greatest concentration in the intracellular fluid. The outside charge of the polarized membrane is positive while the inside charge ...
... The axon is not actively conducting nerve impulses. Sodium is the ion found in the greatest concentration in the extracellular fluid. Potassium is the ion found in the greatest concentration in the intracellular fluid. The outside charge of the polarized membrane is positive while the inside charge ...
Drugs and the Nervous System
... Drugs and the Nervous System Drug: Any substance, other than food, that changes the structure or function of the body ALL drugs (prescription, over the counter and illegal) have potential to do harm if abused or used improperly. Drugs differ in ways they affect the body. (kill bacteria, treat diseas ...
... Drugs and the Nervous System Drug: Any substance, other than food, that changes the structure or function of the body ALL drugs (prescription, over the counter and illegal) have potential to do harm if abused or used improperly. Drugs differ in ways they affect the body. (kill bacteria, treat diseas ...
M. Woodin
... that enable the measurement of this flow and the potential changes related to them ...
... that enable the measurement of this flow and the potential changes related to them ...
Biological Bases Powerpoint – Neurons
... Like a neuron, a toilet operates on the all-ornone principle – it always flushes with the same intensity, no matter how much force you apply to the handle ...
... Like a neuron, a toilet operates on the all-ornone principle – it always flushes with the same intensity, no matter how much force you apply to the handle ...
Somatic senses
... and has connection with it Integrates sensory information like temperature and pressure coming from the primary somatosensory cortex. Forms understanding of the stimulus like size, texture, and relationship of parts Ex.: putting the hand in the pocket and feeling something. The center integrat ...
... and has connection with it Integrates sensory information like temperature and pressure coming from the primary somatosensory cortex. Forms understanding of the stimulus like size, texture, and relationship of parts Ex.: putting the hand in the pocket and feeling something. The center integrat ...
LPN-C
... • Certain peripheral nerves perform specialized functions and form the autonomic nervous system; they control various activities that occur automatically or involuntarily such as the contraction of smooth muscle in the walls of the digestive system. – The autonomic system is further divided into the ...
... • Certain peripheral nerves perform specialized functions and form the autonomic nervous system; they control various activities that occur automatically or involuntarily such as the contraction of smooth muscle in the walls of the digestive system. – The autonomic system is further divided into the ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.