But Ma, how do all the body systems fit together?
... But Ma, how do all the body systems fit together? ...
... But Ma, how do all the body systems fit together? ...
MCDB 3650 Take Home Quiz 1 50 points (6) Describe how an
... post-synaptic neuron. What kinds of ways can the postsynaptic neuron respond, and what dictates this response? Consider neurotransmitters, neurotransmitter receptors, multiple inputs, and distance of input(s) from the neuronal cell body in your answer. ...
... post-synaptic neuron. What kinds of ways can the postsynaptic neuron respond, and what dictates this response? Consider neurotransmitters, neurotransmitter receptors, multiple inputs, and distance of input(s) from the neuronal cell body in your answer. ...
Slide ()
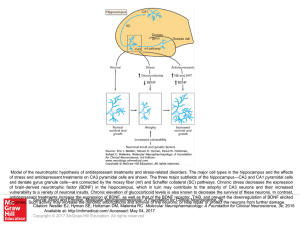
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
... Model of the neurotrophic hypothesis of antidepressant treatments and stress-related disorders. The major cell types in the hippocampus and the effects of stress and antidepressant treatments on CA3 pyramidal cells are shown. The three major subfields of the hippocampus—CA3 and CA1 pyramidal cells a ...
Damage to the frontal lobes can lead to
... sensory organs (skin, eyes, ears, tongue, nose) & internal organs to your brain and spine (CNS) 1. Sensory/afferent nerves: The body’s organs use these to send sensations to the brain e.g. afferent nerves on tongue (taste buds) sense flavor, afferent nerves on skin senses touch, afferent nerves on i ...
... sensory organs (skin, eyes, ears, tongue, nose) & internal organs to your brain and spine (CNS) 1. Sensory/afferent nerves: The body’s organs use these to send sensations to the brain e.g. afferent nerves on tongue (taste buds) sense flavor, afferent nerves on skin senses touch, afferent nerves on i ...
Review questions for unit 2 File
... Draw a diagram that shows the homeostatic regulations in response to a rise in blood calcium. (in response to rising blood glucose, in response to a fall in plasma thyroxine concentration…) Draw a diagram that shows the visual pathways from receptor to interpretation/perception Draw a concept map th ...
... Draw a diagram that shows the homeostatic regulations in response to a rise in blood calcium. (in response to rising blood glucose, in response to a fall in plasma thyroxine concentration…) Draw a diagram that shows the visual pathways from receptor to interpretation/perception Draw a concept map th ...
A2.2.1.TheNeuron
... dial 911. Your heart races as you run out in the street to see if you can be of any help. So much is happening at one time, you feel like your brain is on overload. Just how does your nervous system deal with so much information at one time? Did you realize that a big part of communication between a ...
... dial 911. Your heart races as you run out in the street to see if you can be of any help. So much is happening at one time, you feel like your brain is on overload. Just how does your nervous system deal with so much information at one time? Did you realize that a big part of communication between a ...
Theory of Arachnid Prey Localization
... set of stimulus-locked action potentials (or spikes) [2,5]. For each Rayleigh wave maximum, there is at most one spike per neuron that is transported to a ring-shaped structure [13] in the suboesophageal ganglion (SOG), where the axons from the eight legs meet. We consider M active axons per BCSS an ...
... set of stimulus-locked action potentials (or spikes) [2,5]. For each Rayleigh wave maximum, there is at most one spike per neuron that is transported to a ring-shaped structure [13] in the suboesophageal ganglion (SOG), where the axons from the eight legs meet. We consider M active axons per BCSS an ...
RESTING MEMBRANE POTENTIALS
... The ion channels can be of 2 main types: 1. Leak channels: Include ion channels specific for Na+, K+, Cl- etc. As long as the size of the ion is appropriate, the ion will go through them. 2. Gated channels: The gates are part of the protein channel and can open or close in response to certain stimul ...
... The ion channels can be of 2 main types: 1. Leak channels: Include ion channels specific for Na+, K+, Cl- etc. As long as the size of the ion is appropriate, the ion will go through them. 2. Gated channels: The gates are part of the protein channel and can open or close in response to certain stimul ...
Outline: Muscular System
... neural stimulation: takes place at the __________________________. o ...
... neural stimulation: takes place at the __________________________. o ...
Neuroscience 7a – Neuromuscular, spinal cord
... cause discharge; the action potential travels to the neuromuscular junctions and causes the muscles to contract. It also results in the inhibition of the motoneurons supplying the antagonistic muscle (the lower thigh compartment). This is called reciprocal inhibition. Higher centres in the central n ...
... cause discharge; the action potential travels to the neuromuscular junctions and causes the muscles to contract. It also results in the inhibition of the motoneurons supplying the antagonistic muscle (the lower thigh compartment). This is called reciprocal inhibition. Higher centres in the central n ...
Common Neurotransmitters: Criteria for Neurotransmitters, Key
... Abstract: The criteria, key locations, classifications and functions of common neuro transmitters is reviewed and discussed. Neurotransmitters are the brain chemicals that communicate information throughout our brain and body. They relay signals between neurons. To be neurotransmitter the molecule m ...
... Abstract: The criteria, key locations, classifications and functions of common neuro transmitters is reviewed and discussed. Neurotransmitters are the brain chemicals that communicate information throughout our brain and body. They relay signals between neurons. To be neurotransmitter the molecule m ...
PsychScich03
... Neurotransmitters Influence Mental Activity and Behavior • Much of what we know about neurotransmitters has been learned through the study of the effects of drugs and toxins on emotion, thought, and behavior • Drugs and toxins can alter neurotransmitter action: – Agonists:enhance the actions of neu ...
... Neurotransmitters Influence Mental Activity and Behavior • Much of what we know about neurotransmitters has been learned through the study of the effects of drugs and toxins on emotion, thought, and behavior • Drugs and toxins can alter neurotransmitter action: – Agonists:enhance the actions of neu ...
REU Poster - CURENT Education
... Center Program of the National Science Foundation and the Department of Energy under NSF Award Number EEC-1041877 and the CURENT Industry Partnership Program. ...
... Center Program of the National Science Foundation and the Department of Energy under NSF Award Number EEC-1041877 and the CURENT Industry Partnership Program. ...
Anikeeva
... Schematic for activation of heat sensitive calcium ion channels through conversion of EM field into localized heat ...
... Schematic for activation of heat sensitive calcium ion channels through conversion of EM field into localized heat ...
motor unit
... weak contraction called a “twitch” Greater tension can be produced by repeated stimulation of the muscle fiber before it relaxes. Two twitches from two action potentials add together or sum to produce greater tension. This twitch summation is similar to temporal summation of EPSPs at the postsynapti ...
... weak contraction called a “twitch” Greater tension can be produced by repeated stimulation of the muscle fiber before it relaxes. Two twitches from two action potentials add together or sum to produce greater tension. This twitch summation is similar to temporal summation of EPSPs at the postsynapti ...
Central Auditory Pathways
... The IAM also carries fibers from the utricle, saccule, and semicircular canals that form the vestibular portion of the VIII nerve The vestibular and auditory portions of the VIII N. separate at the cerebellopontine ...
... The IAM also carries fibers from the utricle, saccule, and semicircular canals that form the vestibular portion of the VIII nerve The vestibular and auditory portions of the VIII N. separate at the cerebellopontine ...
Flyer - Energy Kinesiology Association
... discoveries show that the Glial Cells – the other half of the Nervous System - are actively involved in Neurotransmission as well as Neurons! Now research has exploded showing in detail the exact nature of the powerful role Glial Cells play in Neurotransmission, causing a revolution in our understan ...
... discoveries show that the Glial Cells – the other half of the Nervous System - are actively involved in Neurotransmission as well as Neurons! Now research has exploded showing in detail the exact nature of the powerful role Glial Cells play in Neurotransmission, causing a revolution in our understan ...
Nervous System - Anderson School District One
... nerves that your go from spinal the cord called central spinal nervous nerves. to system Spinal your nerves are skeletal made up of muscles. bundles of The sensory autonomic and motor system neurons controls bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious R ...
... nerves that your go from spinal the cord called central spinal nervous nerves. to system Spinal your nerves are skeletal made up of muscles. bundles of The sensory autonomic and motor system neurons controls bound involuntary together by actionsconnective those not tissue. For under this conscious R ...
unit 6 - nervous system / special senses
... B. When the neuron is stimulated, (by another neuron, light in the eye or a touch on the skin), a phase known as depolarization occurs. The sodium channels (gates) in the cell membrane open. This allows sodium to diffuse quickly into the axon. The inward rush of sodium ions changes the charge of the ...
... B. When the neuron is stimulated, (by another neuron, light in the eye or a touch on the skin), a phase known as depolarization occurs. The sodium channels (gates) in the cell membrane open. This allows sodium to diffuse quickly into the axon. The inward rush of sodium ions changes the charge of the ...
AP Practice unit 3 and 4
... 30. An exhausted forest ranger may notice the faintest scent of a forest fire, whereas much stronger but less important odors fail to catch her attention. This fact would be of greatest relevance to A) the Young-Helmholtz theory. B) opponent-process theory. C) signal detection theory. D) frequency t ...
... 30. An exhausted forest ranger may notice the faintest scent of a forest fire, whereas much stronger but less important odors fail to catch her attention. This fact would be of greatest relevance to A) the Young-Helmholtz theory. B) opponent-process theory. C) signal detection theory. D) frequency t ...
1 - davis.k12.ut.us
... in the cell membrane open. This allows sodium to diffuse quickly into the axon. The inward rush of sodium ions changes the charge of the membrane. The inside now becomes positive while the outside become negative. This allows the neuron to transmit the action potential which continues down the lengt ...
... in the cell membrane open. This allows sodium to diffuse quickly into the axon. The inward rush of sodium ions changes the charge of the membrane. The inside now becomes positive while the outside become negative. This allows the neuron to transmit the action potential which continues down the lengt ...
Of nerves and neurons - Case Western Reserve University
... neural damage and nerve activity impact the adult nervous system. Here, he talks about the trigger that sparked his interest in neurological research, and his studies on nerve injury When and why did you first become interested in the adult nervous system? I attended Harvard College, USA, with the i ...
... neural damage and nerve activity impact the adult nervous system. Here, he talks about the trigger that sparked his interest in neurological research, and his studies on nerve injury When and why did you first become interested in the adult nervous system? I attended Harvard College, USA, with the i ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.