The autonomic nervous system
... nervous system (other division is somatic nervous system) - It influences the function of internal organs - It acts largely unconsciously ...
... nervous system (other division is somatic nervous system) - It influences the function of internal organs - It acts largely unconsciously ...
Ascending tracts
... Carries sensations of pain, temperature, light touch, and pressure. Cell body of the 1st order neurone lies in the dorsal root ganglion . The central process enters the spinal cord through the dorsal root. The 2nd order neuron cell bodies lie in the contralateral dorsal hone. The axons decussat ...
... Carries sensations of pain, temperature, light touch, and pressure. Cell body of the 1st order neurone lies in the dorsal root ganglion . The central process enters the spinal cord through the dorsal root. The 2nd order neuron cell bodies lie in the contralateral dorsal hone. The axons decussat ...
PP1
... Prenatal Development Prenatal Period: the 9 months b/w conception and birth. A zygote is a fertilized egg with 100 cells that become increasingly diverse. At about 14 days the zygote turns into an embryo (a and b). ...
... Prenatal Development Prenatal Period: the 9 months b/w conception and birth. A zygote is a fertilized egg with 100 cells that become increasingly diverse. At about 14 days the zygote turns into an embryo (a and b). ...
Spinal Cord
... Decussate in medulla into medial lemniscal tract Allows discriminative touch and proprioception Uses 1st, 2nd, & 3rd order neurons 1st order neurons synapse with interneruons at level of spine entry creating reflex arcs ...
... Decussate in medulla into medial lemniscal tract Allows discriminative touch and proprioception Uses 1st, 2nd, & 3rd order neurons 1st order neurons synapse with interneruons at level of spine entry creating reflex arcs ...
General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive system
... • Ampulla of ductus deferens: releases up to 150 million sperm cells ...
... • Ampulla of ductus deferens: releases up to 150 million sperm cells ...
Reinforcement learning in populations of spiking neurons
... mechanism for achieving reliable behavioral responses despite neuronal variability. However, standard reinforcement learning slows down with increasing population size, as the global reward signal becomes less and less related to the performance of any single neuron. We found that learning speeds up ...
... mechanism for achieving reliable behavioral responses despite neuronal variability. However, standard reinforcement learning slows down with increasing population size, as the global reward signal becomes less and less related to the performance of any single neuron. We found that learning speeds up ...
Chapter 14-Nervous Tissue
... • Interneurons integrate response to sensory input • communication between sensory and motor neurons • lie entirely within CNS • multipolar structures Cell body Afferent of sensory (input) transmission neuron ...
... • Interneurons integrate response to sensory input • communication between sensory and motor neurons • lie entirely within CNS • multipolar structures Cell body Afferent of sensory (input) transmission neuron ...
2 Guided Notes for PPT 7, Hearing and Sight
... Sensory fibers begin at the bases of the hair cells in the cochlea. Cell bodies form the __________________________ Axons lead away from the cochlea as the ______________________________________________________ This cochlea nerve joins with the ________________________________________________to form ...
... Sensory fibers begin at the bases of the hair cells in the cochlea. Cell bodies form the __________________________ Axons lead away from the cochlea as the ______________________________________________________ This cochlea nerve joins with the ________________________________________________to form ...
Digital Selection and Analogue Amplification Coexist in a cortex-inspired silicon circuit
... letters to nature excitatory neurons, and returns inhibition to them. This simple architecture and similar variants have been used previously to model response properties of neurons in cortex5±9 and other10±12 brain areas. The output of each excitatory neuron is an electrical current that is positi ...
... letters to nature excitatory neurons, and returns inhibition to them. This simple architecture and similar variants have been used previously to model response properties of neurons in cortex5±9 and other10±12 brain areas. The output of each excitatory neuron is an electrical current that is positi ...
1749-7221-5-5-S2
... IN THE FIRST DAYS SCHWANN CELL PROLIPHERATE INSIDE THE ENDONEURAL TUBE : AFTER SOME DAYS THE PROXXIMAL STUMP OF THE AXON SENDS OUT SOME SPROUTS SOME OF WHICH ARE TOO THIN AND WILL BE ELIMINATED SOME OTHER WILL BE STOPPED BY FIBROBLASTIC PROLIFERATION OTHERS , MORE HEARTY WILL PROCEED INTO THE ENDONE ...
... IN THE FIRST DAYS SCHWANN CELL PROLIPHERATE INSIDE THE ENDONEURAL TUBE : AFTER SOME DAYS THE PROXXIMAL STUMP OF THE AXON SENDS OUT SOME SPROUTS SOME OF WHICH ARE TOO THIN AND WILL BE ELIMINATED SOME OTHER WILL BE STOPPED BY FIBROBLASTIC PROLIFERATION OTHERS , MORE HEARTY WILL PROCEED INTO THE ENDONE ...
AP Biology Campbell 8th Edition Chapter 1 Study Guide
... • The rising phase of the action potential ends when the positive feedback loop is interrupted. • Two processes break the loop: 1. the inactivation of the voltage-gated sodium channels. 2. the opening of the voltage-gated potassium channels. • The voltage-gated sodium channels have two gates: 1. A v ...
... • The rising phase of the action potential ends when the positive feedback loop is interrupted. • Two processes break the loop: 1. the inactivation of the voltage-gated sodium channels. 2. the opening of the voltage-gated potassium channels. • The voltage-gated sodium channels have two gates: 1. A v ...
Nervous tissue
... Re-read today’s lecture, highlight all vocabulary you do not understand, and look up terms. ...
... Re-read today’s lecture, highlight all vocabulary you do not understand, and look up terms. ...
Control of Movement
... Biomechanical properties 206 bones, 200-300 muscles Different joints for different movement Muscle binds to bones via collagen, surrounded by protective tissue Muscle cell membrane – Sarcolemma Myofibrils – Thin filaments (actin), Thick filaments (myozin) -> create stipes Functional stru ...
... Biomechanical properties 206 bones, 200-300 muscles Different joints for different movement Muscle binds to bones via collagen, surrounded by protective tissue Muscle cell membrane – Sarcolemma Myofibrils – Thin filaments (actin), Thick filaments (myozin) -> create stipes Functional stru ...
abstract english
... brain functions, however direct evidence for these theories is still lacking. Therefore more insight in the cellular mechanism as well as how variations in genes influence brain waves might help understanding when and why these waves occur. Brain waves only occur when large groups of brain cells ( ...
... brain functions, however direct evidence for these theories is still lacking. Therefore more insight in the cellular mechanism as well as how variations in genes influence brain waves might help understanding when and why these waves occur. Brain waves only occur when large groups of brain cells ( ...
Motor System & Behavior
... for all movement. Movement can be generated from: - sensory signals in the muscle spindle like the stretch reflex - sensory signals from skin as in the pain withdrawal response - involuntary signals from the brainstem for posture, keeping us upright without conscious attention - signals from the bra ...
... for all movement. Movement can be generated from: - sensory signals in the muscle spindle like the stretch reflex - sensory signals from skin as in the pain withdrawal response - involuntary signals from the brainstem for posture, keeping us upright without conscious attention - signals from the bra ...
SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM Composed of somatic parts of CNS
... Greatly outnumber the presynaptic fibers within the paravertebral ganglia ...
... Greatly outnumber the presynaptic fibers within the paravertebral ganglia ...
Topic Option A Neurobio
... 6. Ganglion cells send messages to the brain via the iris, vitreous humour, retina, fovea, optic nerve optic nerve. and blind spot. 7. The information from the right field of vision 16. Skill: Annotation of a diagram of the retina to from both eyes is sent to the left part of the show the cell types ...
... 6. Ganglion cells send messages to the brain via the iris, vitreous humour, retina, fovea, optic nerve optic nerve. and blind spot. 7. The information from the right field of vision 16. Skill: Annotation of a diagram of the retina to from both eyes is sent to the left part of the show the cell types ...
Practice Questions for Exam 2 As you prepare for the exam you
... 70) Paralytic shellfish poisoning is caused by microorganisms that produce what specific toxin? What does this toxin bind to? 71) How does heavy metal poisoning damage the nervous system? 72) Name the three types of membrane gated channels: 73) The minimum stimulus that initiates an action potential ...
... 70) Paralytic shellfish poisoning is caused by microorganisms that produce what specific toxin? What does this toxin bind to? 71) How does heavy metal poisoning damage the nervous system? 72) Name the three types of membrane gated channels: 73) The minimum stimulus that initiates an action potential ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
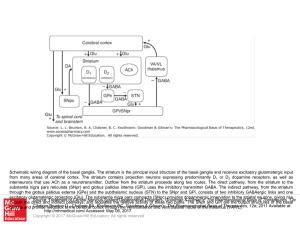
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
... Schematic wiring diagram of the basal ganglia. The striatum is the principal input structure of the basal ganglia and receives excitatory glutamatergic input from many areas of cerebral cortex. The striatum contains projection neurons expressing predominantly D1 or D2 dopamine receptors, as well as ...
Spinal Cord Reflexes
... activation of reflexes. For example, alternating activation of Ia stretch reflex in flexors and extensors of limb, and FRA reflex with ...
... activation of reflexes. For example, alternating activation of Ia stretch reflex in flexors and extensors of limb, and FRA reflex with ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM AND REFLEXES Introduction:
... eyes. When a bright light stimulates the retina of the eye, impulses are carried to the brain by sensory neurons. In the brain, the impulses are transmitted to interneurons which determine an appropriate response which is carried out by motor neurons that cause the muscles of the iris to contract. C ...
... eyes. When a bright light stimulates the retina of the eye, impulses are carried to the brain by sensory neurons. In the brain, the impulses are transmitted to interneurons which determine an appropriate response which is carried out by motor neurons that cause the muscles of the iris to contract. C ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.