seminario - Instituto Cajal
... retrogradely-labeled neurons from both tegmental areas within the PeF, some of which contained Hcrt, and positive Hcrt synapses on dRPO and vRPO neurons. Hcrt-1 application in dRPO provoked an increase in dRPO neurons activity that was blocked with Hcrt-1R antagonists. Iontophoretic application of H ...
... retrogradely-labeled neurons from both tegmental areas within the PeF, some of which contained Hcrt, and positive Hcrt synapses on dRPO and vRPO neurons. Hcrt-1 application in dRPO provoked an increase in dRPO neurons activity that was blocked with Hcrt-1R antagonists. Iontophoretic application of H ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
... Reflex Arcs continued - Interneuron * CNS Gray Matter * Usually one but may be 0 or >1 * Transmits, Inhibits, or Reroutes to Motor Neuron - Motor Neuron (CNS to Effector) - Effector * Muscle or Gland; responds to motor impulse * Response is Reflex (e.g. knee jerk, secretion of digestive juices, pai ...
... Reflex Arcs continued - Interneuron * CNS Gray Matter * Usually one but may be 0 or >1 * Transmits, Inhibits, or Reroutes to Motor Neuron - Motor Neuron (CNS to Effector) - Effector * Muscle or Gland; responds to motor impulse * Response is Reflex (e.g. knee jerk, secretion of digestive juices, pai ...
cardiac muscle
... Spindle shaped cells with a single central nuclei Walls of hollow organs (blood vessels, GI tract, bladder) Involuntary and nonstriated ...
... Spindle shaped cells with a single central nuclei Walls of hollow organs (blood vessels, GI tract, bladder) Involuntary and nonstriated ...
treatments stress
... – one group of anxious patients is given a drug another group is given a placebo- a substance that has no pharmacological effects (i.e. it has no effect on the body). Patients are given medication but do not know whether it is the real thing or the placebo. This enables us to determine whether the e ...
... – one group of anxious patients is given a drug another group is given a placebo- a substance that has no pharmacological effects (i.e. it has no effect on the body). Patients are given medication but do not know whether it is the real thing or the placebo. This enables us to determine whether the e ...
PDF - Cogprints
... Fig. 4. Motor system diagram. In A, sensory-motor integration is implemented through sandglass structures, whose junctions could be Pyramid cells or PCs. The neural network is actually composed of overlapping coding trees. The efferent network is hierarchical and selfsimilar, and motor learning in e ...
... Fig. 4. Motor system diagram. In A, sensory-motor integration is implemented through sandglass structures, whose junctions could be Pyramid cells or PCs. The neural network is actually composed of overlapping coding trees. The efferent network is hierarchical and selfsimilar, and motor learning in e ...
Movement of Fluids and Electrolytes
... distribution of sodium and potassium within the interstitial and the intracellular fluid compartments are via the sodiumpotassium pump. Active transport is necessary to move sodium from the cells to the ECF compartment. The active process of pumping sodium out of the cells forces potassium into the ...
... distribution of sodium and potassium within the interstitial and the intracellular fluid compartments are via the sodiumpotassium pump. Active transport is necessary to move sodium from the cells to the ECF compartment. The active process of pumping sodium out of the cells forces potassium into the ...
The virtue of simplicity
... However, models that work well to explain perceptual phenomena are often difficult to instantiate in ‘wetware.’ For these reasons, a simple model that explains such a complex perceptual problem in neuronally realistic terms provides considerable cause for rejoicing. The model of Rust et al. in this ...
... However, models that work well to explain perceptual phenomena are often difficult to instantiate in ‘wetware.’ For these reasons, a simple model that explains such a complex perceptual problem in neuronally realistic terms provides considerable cause for rejoicing. The model of Rust et al. in this ...
A plastic axonal hotspot
... Neurons generate their output signal — the action potential — in a distinct region of the axon called the initial segment. The location and extent of this trigger zone can be modified by neural activity to control excitability. ...
... Neurons generate their output signal — the action potential — in a distinct region of the axon called the initial segment. The location and extent of this trigger zone can be modified by neural activity to control excitability. ...
Lecture Cranial Nerves 1
... Gross Anatomy: Cranial Nerve Introduction (Grays, pages 807; 848-854) ...
... Gross Anatomy: Cranial Nerve Introduction (Grays, pages 807; 848-854) ...
The Nervous and Endocrine Systems Review Set
... • How does information about how food tastes get to the brain? • A. The chemicals from the food pass from the mouth to the nasal passage and into the brain. • B. Taste receptors on the retina sense the chemicals in food and send vibrations to the brain. • C. Taste buds on the tongue sense chemicals ...
... • How does information about how food tastes get to the brain? • A. The chemicals from the food pass from the mouth to the nasal passage and into the brain. • B. Taste receptors on the retina sense the chemicals in food and send vibrations to the brain. • C. Taste buds on the tongue sense chemicals ...
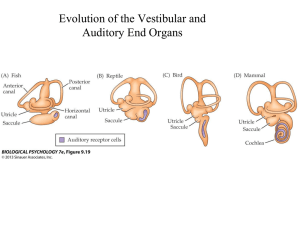
Box 9.1 The Basics of Sound (Part 1)
... Can hear sounds in a range from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter12.html ...
... Can hear sounds in a range from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter12.html ...
Drosophila as a model to study mechanisms underlying alcohol
... (oscillations). These are widely regarded as functionally relevant signals of the brain. Synchronized neuronal networks are also necessary for the locomotor output, independent of its form (swimming, crawling, walking or flying). In all these systems a big effort is made to understand the cellular m ...
... (oscillations). These are widely regarded as functionally relevant signals of the brain. Synchronized neuronal networks are also necessary for the locomotor output, independent of its form (swimming, crawling, walking or flying). In all these systems a big effort is made to understand the cellular m ...
Feeding Pathways
... Hunger vs. Satiety Controlled by communication between the gut and parasympathetic nervous system ...
... Hunger vs. Satiety Controlled by communication between the gut and parasympathetic nervous system ...
Regulation of respiration
... Peripheral chemoreceptors Chemosensory neurons that respond to changes in blood pH and gas content are located in the aorta and in the carotid sinuses; these sensory afferent neurons alter CNS regulation l ti off the rate of ventilation. ...
... Peripheral chemoreceptors Chemosensory neurons that respond to changes in blood pH and gas content are located in the aorta and in the carotid sinuses; these sensory afferent neurons alter CNS regulation l ti off the rate of ventilation. ...
The Action Potential, Synaptic Transmission, and Maintenance of
... Ions can flow across the nerve cell membrane through three types of ion channels: nongated (leakage), ligand-gated, and voltage-gated (Fig. 3.3). Nongated ion channels are always open. They are responsible for the influx of Na⫹ and efflux of K⫹ when the neuron is in its resting state. Ligandgated io ...
... Ions can flow across the nerve cell membrane through three types of ion channels: nongated (leakage), ligand-gated, and voltage-gated (Fig. 3.3). Nongated ion channels are always open. They are responsible for the influx of Na⫹ and efflux of K⫹ when the neuron is in its resting state. Ligandgated io ...
Neurons and Circuits - UT Computer Science
... connected to each other in circuits. Such circuits are obviously doing many different kinds of functions, but our plan is just to sample two of these to convey the general idea. A nerve cell has three main components, its dendrites, its soma or body, and its axon. The dendrites are a tree-like struc ...
... connected to each other in circuits. Such circuits are obviously doing many different kinds of functions, but our plan is just to sample two of these to convey the general idea. A nerve cell has three main components, its dendrites, its soma or body, and its axon. The dendrites are a tree-like struc ...
52 Nerve Tissue
... arise from the base of a major dendrite. Axons usually are much longer and more slender than dendrites and may or may not give rise to side branches called collaterals, which, unlike dendritic branches, usually leave the parent axon at right angles. Axons also differ in that the diameter is constant ...
... arise from the base of a major dendrite. Axons usually are much longer and more slender than dendrites and may or may not give rise to side branches called collaterals, which, unlike dendritic branches, usually leave the parent axon at right angles. Axons also differ in that the diameter is constant ...
15. ANS (Stick Figure) Anat Lecture
... The rule of thumb is: The more Sym stimulation, the more constriction of blood vessels (except for blood vessels that supply skeletal muscle!). So this means your blood pressure will go up when you get excited!!! Please Note: Skeletal muscle is controlled by the Somatic (soma = body) nervous system ...
... The rule of thumb is: The more Sym stimulation, the more constriction of blood vessels (except for blood vessels that supply skeletal muscle!). So this means your blood pressure will go up when you get excited!!! Please Note: Skeletal muscle is controlled by the Somatic (soma = body) nervous system ...
How Do Neurons Communicate?
... granular substances in the terminal, which are vesicles containing the neurotransmitter. The dark band of material just inside the dendrite provides the receptors for the neurotransmitter. The terminal and the dendrite are separated by a small space. The drawing in Figure 5-4 illustrates the three m ...
... granular substances in the terminal, which are vesicles containing the neurotransmitter. The dark band of material just inside the dendrite provides the receptors for the neurotransmitter. The terminal and the dendrite are separated by a small space. The drawing in Figure 5-4 illustrates the three m ...
chapter32_part2shorter
... • A reflex is an automatic response to a stimulus, a movement or other action that does not require thought • Examples: Stretch reflex, knee-jerk reflex, withdrawal reflex • Spinal reflexes do not involve the brain • Sensory signals flow to the spinal cord, which commands a response by way of motor ...
... • A reflex is an automatic response to a stimulus, a movement or other action that does not require thought • Examples: Stretch reflex, knee-jerk reflex, withdrawal reflex • Spinal reflexes do not involve the brain • Sensory signals flow to the spinal cord, which commands a response by way of motor ...
What and Where Pathways
... Figure 4.8 (a) Response of a complex cell recorded from the visual cortex of a cat. The stimulus bar is moved back and forth across the receptive field. The cell fires best when the bar is positioned with a specific orientation and is moved in a specific direction (*). (From Hubel and Wiesel, 1959. ...
... Figure 4.8 (a) Response of a complex cell recorded from the visual cortex of a cat. The stimulus bar is moved back and forth across the receptive field. The cell fires best when the bar is positioned with a specific orientation and is moved in a specific direction (*). (From Hubel and Wiesel, 1959. ...
Multiple Choice - 32 points total In each of the questions, select the
... E) All of the above are true. 8)_____ C_____A synapse that uses the amino acid glutamate as a neurotransmitter A) contains glutamate receptors in the presynaptic membrane. B) responds directly to increases in glutamate in the blood caused by eating a meal high in protein. C) requires calcium entry i ...
... E) All of the above are true. 8)_____ C_____A synapse that uses the amino acid glutamate as a neurotransmitter A) contains glutamate receptors in the presynaptic membrane. B) responds directly to increases in glutamate in the blood caused by eating a meal high in protein. C) requires calcium entry i ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.