The cutaneous sensory system Neuroscience and Biobehavioral
... entire body from the neck down; sensations from the face are relayed via cranial nerves, with both parts sharing a common central organization. As with other sensory modalities, information is relayed from entry level cortex to higher order neural systems controlling perception, attention and emotio ...
... entire body from the neck down; sensations from the face are relayed via cranial nerves, with both parts sharing a common central organization. As with other sensory modalities, information is relayed from entry level cortex to higher order neural systems controlling perception, attention and emotio ...
TalkHumaine_grandjean
... modulate attentional processes and could thus orient the ressources of organism (or ECAs …) on specific events or objects. ...
... modulate attentional processes and could thus orient the ressources of organism (or ECAs …) on specific events or objects. ...
A1982ND73700001
... basic parameters of the VEPs at a time when little was known in this field. In the carefully collected bibliography there were only six articles dealing directly with the VEPs studied accidentally in limited groups of subjects while the cited publication represented a systematic study of a rather la ...
... basic parameters of the VEPs at a time when little was known in this field. In the carefully collected bibliography there were only six articles dealing directly with the VEPs studied accidentally in limited groups of subjects while the cited publication represented a systematic study of a rather la ...
the potential for abuse: addiction
... (Hyman, 2005). The VTA is composed of various types of neurons that include a specific cluster of dopaminergic neurons that communicate foremost with the nucleus accumbens via the medial forebrain bundle (Hyman, 2005). Although the number of dopaminergic neurons housed in the VTA is miniscule compar ...
... (Hyman, 2005). The VTA is composed of various types of neurons that include a specific cluster of dopaminergic neurons that communicate foremost with the nucleus accumbens via the medial forebrain bundle (Hyman, 2005). Although the number of dopaminergic neurons housed in the VTA is miniscule compar ...
Interneurons and triadic circuitry of the thalamus
... F2 terminal, and this increases inhibition in the relay cell. This will reduce the responsiveness, or gain, of the relay cell to retinal inputs and, because of the temporal properties of mGlu5 receptors, this reduced contrast gain will last for a second or so even after the retinal afferent firing r ...
... F2 terminal, and this increases inhibition in the relay cell. This will reduce the responsiveness, or gain, of the relay cell to retinal inputs and, because of the temporal properties of mGlu5 receptors, this reduced contrast gain will last for a second or so even after the retinal afferent firing r ...
Teacher Materials - Scope, Sequence, and Coordination
... have evolved to ensure reproductive success. Animals often live in unpredictable environments, and so their behavior must be flexible enough to deal with uncertainty and change. Plants also respond to stimuli. Multicellular animals have nervous systems to generate behavior. Nervous systems are forme ...
... have evolved to ensure reproductive success. Animals often live in unpredictable environments, and so their behavior must be flexible enough to deal with uncertainty and change. Plants also respond to stimuli. Multicellular animals have nervous systems to generate behavior. Nervous systems are forme ...
4-22-05
... • The way it is: sensing, analysis, and action are ongoing and overlapping processes. • Sensations begin as different forms of energy that are detected by sensory receptors. – This energy is converted to action potentials that travel to appropriate regions of the brain. • The limbic region plays a m ...
... • The way it is: sensing, analysis, and action are ongoing and overlapping processes. • Sensations begin as different forms of energy that are detected by sensory receptors. – This energy is converted to action potentials that travel to appropriate regions of the brain. • The limbic region plays a m ...
Characterization of DREAM isoforms in astrocytes and neurons
... isoforms of DREAM (A and B) were produced by alternative splicing. Our study is to observe the characterization of DREAM isoforms expression and distribution in astrocytes and neurons. Methods Expression of DREAM A and B mRNA in primary culture of neural cells (astrocytes, GABAergic neuron and gluta ...
... isoforms of DREAM (A and B) were produced by alternative splicing. Our study is to observe the characterization of DREAM isoforms expression and distribution in astrocytes and neurons. Methods Expression of DREAM A and B mRNA in primary culture of neural cells (astrocytes, GABAergic neuron and gluta ...
Introduction to Psychology: Final Exam
... B 18. A description of how certain molecular shapes are required to fit into receptor sites at synapses. C 19. A chemical manufactured in the nervous system and used to send messages between neurons. E 20. An actual chemical found in the brain, lack of which may lead to depression and require the us ...
... B 18. A description of how certain molecular shapes are required to fit into receptor sites at synapses. C 19. A chemical manufactured in the nervous system and used to send messages between neurons. E 20. An actual chemical found in the brain, lack of which may lead to depression and require the us ...
Responses to Rare Visual Target and Distractor Stimuli Using Event
... standard stimuli. ¦Z¦ ⬎ 3.09; region of interest (ROI), P ⬍ 0.005. B: response to target stimuli plotted as in A. C: regions with significant trend in distractor response amplitude across successive distractor repetitions. ¦Z¦ ⬎ 4.0; ROI, P ⬍ 0.005. D: medial frontal gyrus ROI for successive distrac ...
... standard stimuli. ¦Z¦ ⬎ 3.09; region of interest (ROI), P ⬍ 0.005. B: response to target stimuli plotted as in A. C: regions with significant trend in distractor response amplitude across successive distractor repetitions. ¦Z¦ ⬎ 4.0; ROI, P ⬍ 0.005. D: medial frontal gyrus ROI for successive distrac ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP ...
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP ...
The Nervous System - Christian Fenger Academy High School
... 9. Which best describes the peripheral nervous system? a. the basic unit of the nervous system b. the center of memory, speech, and abstract thought c. the link between the body and the brain and spinal cord d. the control center of the body 10. Which is the most important step you can take to care ...
... 9. Which best describes the peripheral nervous system? a. the basic unit of the nervous system b. the center of memory, speech, and abstract thought c. the link between the body and the brain and spinal cord d. the control center of the body 10. Which is the most important step you can take to care ...
Marieb_ch7a
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP ...
... Potassium ions rush out of the neuron after sodium ions rush in, which repolarizes the membrane The sodium-potassium pump restores the original configuration This action requires ATP ...
19. Senses General and Special
... receptors are primarily stretch receptors in the smooth muscle of these organs. Most of the time we are unaware of these receptors, but when the smooth muscle stretches to a certain point (e.g., when eating a large meal stretches our stomach wall), we may become aware of these sensations. Interocept ...
... receptors are primarily stretch receptors in the smooth muscle of these organs. Most of the time we are unaware of these receptors, but when the smooth muscle stretches to a certain point (e.g., when eating a large meal stretches our stomach wall), we may become aware of these sensations. Interocept ...
Forea Wang
... laboratories strives to understand how neuronal responses come to be shaped by patterned input from the environment, there remains no direct method for producing controlled input patterns to a neuron and measuring its functional responses and adaptations. Recently, a new system was developed in the ...
... laboratories strives to understand how neuronal responses come to be shaped by patterned input from the environment, there remains no direct method for producing controlled input patterns to a neuron and measuring its functional responses and adaptations. Recently, a new system was developed in the ...
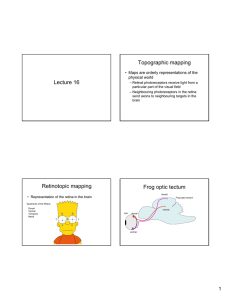
Lecture 16 Topographic mapping Retinotopic mapping Frog optic
... Neurons that express high levels of ligand go to areas of the tectum with high levels of receptor • Ephrin acts as attractive cue! ...
... Neurons that express high levels of ligand go to areas of the tectum with high levels of receptor • Ephrin acts as attractive cue! ...
Nervous_system_Tissue_Overview0
... Sensory Receptors Ends of dendrites are associated with specialized receptors Cutaneous receptors: pressure, pain, heat, cold Proprioceptors: muscles & tendons: amount of stretch or tension Specialized receptors in sense organs: sight, hearing, smell, taste, equilibrium ...
... Sensory Receptors Ends of dendrites are associated with specialized receptors Cutaneous receptors: pressure, pain, heat, cold Proprioceptors: muscles & tendons: amount of stretch or tension Specialized receptors in sense organs: sight, hearing, smell, taste, equilibrium ...
Supplement to: Modulation of Intracortical Synaptic Potentials by
... Through the investigation of synaptic transmission between pairs of layer 5 pyramidal cells maintained in slices in vitro, we answer all three of these questions. First, we demonstrated that the amplitude of action potential evoked EPSPs between synaptically connected pairs of pyramidal cells is a c ...
... Through the investigation of synaptic transmission between pairs of layer 5 pyramidal cells maintained in slices in vitro, we answer all three of these questions. First, we demonstrated that the amplitude of action potential evoked EPSPs between synaptically connected pairs of pyramidal cells is a c ...
Supplement: Modulation of Intracortical Synaptic Potentials by
... Through the investigation of synaptic transmission between pairs of layer 5 pyramidal cells maintained in slices in vitro, we answer all three of these questions. First, we demonstrated that the amplitude of action potential evoked EPSPs between synaptically connected pairs of pyramidal cells is a c ...
... Through the investigation of synaptic transmission between pairs of layer 5 pyramidal cells maintained in slices in vitro, we answer all three of these questions. First, we demonstrated that the amplitude of action potential evoked EPSPs between synaptically connected pairs of pyramidal cells is a c ...
Respiratory Physiology
... Lungs contain lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages Vocalization Loss of water and heat from body It enhances venous return ( Respiratory pump) The nose as a part of respiratory system, serves as the organ of smell Lungs synthesize certain prostaglandins, histamine, heparin and kallekrein Pulmon ...
... Lungs contain lymphocytes, plasma cells and macrophages Vocalization Loss of water and heat from body It enhances venous return ( Respiratory pump) The nose as a part of respiratory system, serves as the organ of smell Lungs synthesize certain prostaglandins, histamine, heparin and kallekrein Pulmon ...
Answer on Question#47890 - Biology - Other
... sarcomeres shorten. Actin and myosin filaments remain the same size – they simply slide past each other, changing their relative position as the muscle contracts and relaxes. Contraction is triggered when an action potential (the electric signal from neurons that tells muscles to contract) reaches t ...
... sarcomeres shorten. Actin and myosin filaments remain the same size – they simply slide past each other, changing their relative position as the muscle contracts and relaxes. Contraction is triggered when an action potential (the electric signal from neurons that tells muscles to contract) reaches t ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.