document
... representation on the medial surface of the hemisphere, called the supplementary motor area (SMA). As defined in this study, M1 and SMA each included several of the currently defined cortical motor areas. (B) Intracortical microstimulation of M1 in an owl monkey produced this map, consisting of a co ...
... representation on the medial surface of the hemisphere, called the supplementary motor area (SMA). As defined in this study, M1 and SMA each included several of the currently defined cortical motor areas. (B) Intracortical microstimulation of M1 in an owl monkey produced this map, consisting of a co ...
Slide ()
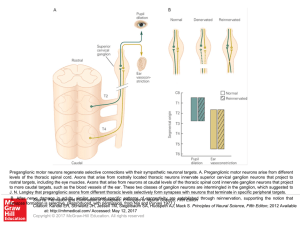
... levels of the thoracic spinal cord. Axons that arise from rostrally located thoracic neurons innervate superior cervical ganglion neurons that project to rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons ...
... levels of the thoracic spinal cord. Axons that arise from rostrally located thoracic neurons innervate superior cervical ganglion neurons that project to rostral targets, including the eye muscles. Axons that arise from neurons at caudal levels of the thoracic spinal cord innervate ganglion neurons ...
Brain Gas
... species. They are far and away the most successful multicellular organisms on the planet, and understanding how they do anything will contribute to our understanding of their success. From an economic standpoint, honey bees are the primary pollinators of many crops and honey bees’ ability to pollina ...
... species. They are far and away the most successful multicellular organisms on the planet, and understanding how they do anything will contribute to our understanding of their success. From an economic standpoint, honey bees are the primary pollinators of many crops and honey bees’ ability to pollina ...
Artificial Intelligence CSC 361
... fibers (surrounding the cell body) that receive messages The dendrites are very receptive to connections from other neurons. The dendrites carry signals from the synapses to the soma. ...
... fibers (surrounding the cell body) that receive messages The dendrites are very receptive to connections from other neurons. The dendrites carry signals from the synapses to the soma. ...
Lecture 12
... Touch Physiology (cont’d) • kinesthetic receptors: – neurological patient Ian Waterman • cutaneous nerves connecting Waterman’s kinesthetic mechanoreceptors to brain destroyed by viral infection • lacked kinesthetic senses, dependent on vision to tell limb positions ...
... Touch Physiology (cont’d) • kinesthetic receptors: – neurological patient Ian Waterman • cutaneous nerves connecting Waterman’s kinesthetic mechanoreceptors to brain destroyed by viral infection • lacked kinesthetic senses, dependent on vision to tell limb positions ...
The CELL MEMBRANE (PLASMA MEMBRANE) as a
... Permeable membranes: Both water and the solute move freely across the membrane. In which case is it really a “membrane” at all? Since everything gets through it’s not really a barrier…. Impermeable membranes: Neither water nor solute can move across the membrane. NOTHING gets in or out. This membran ...
... Permeable membranes: Both water and the solute move freely across the membrane. In which case is it really a “membrane” at all? Since everything gets through it’s not really a barrier…. Impermeable membranes: Neither water nor solute can move across the membrane. NOTHING gets in or out. This membran ...
Cells, Tissues
... -Extensions of cell body, specialized to increase the surface area for incoming signals -Synaptic contacts are made on them -Some synaptic sites on them look like sharp projections called dendritic spines gemmules -Proximal ends has some Nissl bodies ...
... -Extensions of cell body, specialized to increase the surface area for incoming signals -Synaptic contacts are made on them -Some synaptic sites on them look like sharp projections called dendritic spines gemmules -Proximal ends has some Nissl bodies ...
Chapter 13 - s3.amazonaws.com
... • If predatory, evert proboscis (pharynx) through mouth to capture prey and bring back to burrow • Others are herbivores and scavengers or filter feeders Digestion • Contain long, straight intestine used to defecate ...
... • If predatory, evert proboscis (pharynx) through mouth to capture prey and bring back to burrow • Others are herbivores and scavengers or filter feeders Digestion • Contain long, straight intestine used to defecate ...
HORMONES AND BEHAVIOR 1. The Neuroendocrine System: Sum
... located in gastrointestinal tract and enteric nervous system sense _________________, and provide this information to nucleus of the solitary tract via the vagus nerve - Cholecystokinin (CCK): peptide released from ______________________________________ _______ - responds to both volume and caloric ...
... located in gastrointestinal tract and enteric nervous system sense _________________, and provide this information to nucleus of the solitary tract via the vagus nerve - Cholecystokinin (CCK): peptide released from ______________________________________ _______ - responds to both volume and caloric ...
Chocolate Chip Cookie Review
... 2. When you lift up your cookie, what kind of neurons transmit instructions to your muscles? 3. Of what system are these neurons a part of? 4. When you touch your cookie, the sensation of touch involves what action on the part of individual neurons? 5. What part of the neuron receives the stimulus? ...
... 2. When you lift up your cookie, what kind of neurons transmit instructions to your muscles? 3. Of what system are these neurons a part of? 4. When you touch your cookie, the sensation of touch involves what action on the part of individual neurons? 5. What part of the neuron receives the stimulus? ...
Study Design
... Stability of the body To maintain balance the center of gravity needs to be maintained above the supporting base of the body and this is achieved through coordinated contraction and relaxation of postural muscles in response to positional changes. Successful balance depends on the ability to sense p ...
... Stability of the body To maintain balance the center of gravity needs to be maintained above the supporting base of the body and this is achieved through coordinated contraction and relaxation of postural muscles in response to positional changes. Successful balance depends on the ability to sense p ...
Samantha Zarati - A critical review of computational neurological models
... Each approach has its own unique benefits and challenges: • Software such as NEURON is operable on different simulators and is easy-to-use for biologists unfamiliar with programming, but it is difficult to reproduce and results are difficult to communicate due to nonstandard methods. – This can be i ...
... Each approach has its own unique benefits and challenges: • Software such as NEURON is operable on different simulators and is easy-to-use for biologists unfamiliar with programming, but it is difficult to reproduce and results are difficult to communicate due to nonstandard methods. – This can be i ...
How do Human Sensors Work?
... These neurons respond differently to different pitches. Pitches range from low (such as from drums) to high (such as from bells). All these signals are sent individually to the auditory cortex in your brain. The auditory cortex integrates all the frequencies correctly and helps your brain unders ...
... These neurons respond differently to different pitches. Pitches range from low (such as from drums) to high (such as from bells). All these signals are sent individually to the auditory cortex in your brain. The auditory cortex integrates all the frequencies correctly and helps your brain unders ...
Visual Coding and the Retinal Receptors
... activity by a particular nerve always conveys the same type of information to the brain. – Example: impulses in one neuron indicate light; impulses in another neuron indicate sound. • The brain does not duplicate what we see. • Which neurons respond, the amount of response, and the timing of respons ...
... activity by a particular nerve always conveys the same type of information to the brain. – Example: impulses in one neuron indicate light; impulses in another neuron indicate sound. • The brain does not duplicate what we see. • Which neurons respond, the amount of response, and the timing of respons ...
Systemogenesis.
... by the formation of a hippocamapl-dependent memory, but also participate in it. The new cells are about 1-2 weeks of age when they become involved in the learned response. This ability to undergo rapid structural change may be a characteristic of immature neurons that makes them ideally suited f ...
... by the formation of a hippocamapl-dependent memory, but also participate in it. The new cells are about 1-2 weeks of age when they become involved in the learned response. This ability to undergo rapid structural change may be a characteristic of immature neurons that makes them ideally suited f ...
Nervous System - IHMC Public Cmaps
... because in such case there will be no coordination between different body functions and they will all act separately. Nervous system not only controls the voluntary functions of human body that are directed by human will, but it also controls those functions that are below the level of consciousness ...
... because in such case there will be no coordination between different body functions and they will all act separately. Nervous system not only controls the voluntary functions of human body that are directed by human will, but it also controls those functions that are below the level of consciousness ...
This Week in The Journal - The Journal of Neuroscience
... further enhanced by increased uptake of glutamine. Having previously identified the glutamine transporter SNAT1 as a target of MeCP2-mediated transcriptional repression, Jin et al. now report that SNAT1 levels were elevated approximately threefold in MeCP2deficient microglia compared to wild-type. I ...
... further enhanced by increased uptake of glutamine. Having previously identified the glutamine transporter SNAT1 as a target of MeCP2-mediated transcriptional repression, Jin et al. now report that SNAT1 levels were elevated approximately threefold in MeCP2deficient microglia compared to wild-type. I ...
You submitted this quiz on Tue 6 May 2014 6:55 PM CDT. You got a
... Inorrect0.00 Gut mobility requires peripheral autonomic ganglion neurons, which could be impaired by the new toxin. Total ...
... Inorrect0.00 Gut mobility requires peripheral autonomic ganglion neurons, which could be impaired by the new toxin. Total ...
Lesson 1
... Multiple representations of information can be located within different areas of the human brain, yet specific regions of the brain seem most critical in handling particular functions. This localization of structure and function has been identified for numerous regions. I. Areas below the neocortex ...
... Multiple representations of information can be located within different areas of the human brain, yet specific regions of the brain seem most critical in handling particular functions. This localization of structure and function has been identified for numerous regions. I. Areas below the neocortex ...
pain - Dog2Doc.com
... • ACTH/B-lipotropin is released from the anterior pituitary in response to pain – broken down into Bendorphins and corticosteroids • Mechanism of action – similar to enkephalins to block ascending nerve impulses ...
... • ACTH/B-lipotropin is released from the anterior pituitary in response to pain – broken down into Bendorphins and corticosteroids • Mechanism of action – similar to enkephalins to block ascending nerve impulses ...
Lesson 1
... Multiple representations of information can be located within different areas of the human brain, yet specific regions of the brain seem most critical in handling particular functions. This localization of structure and function has been identified for numerous regions. I. Areas below the neocortex ...
... Multiple representations of information can be located within different areas of the human brain, yet specific regions of the brain seem most critical in handling particular functions. This localization of structure and function has been identified for numerous regions. I. Areas below the neocortex ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.