Parts of the Peripheral Nervous System
... To Darwin, similarities of this response pattern indicated that these different species evolved from a common ancestor, which possessed the same behavioral trait. B/c Behavior reflects the activity of the nervous system we can infer that the brain mechanisms that underlie this fear reaction may be s ...
... To Darwin, similarities of this response pattern indicated that these different species evolved from a common ancestor, which possessed the same behavioral trait. B/c Behavior reflects the activity of the nervous system we can infer that the brain mechanisms that underlie this fear reaction may be s ...
Nerve Fiber Classification Nerve fibers are classified according to:
... Reflexes are rapid, automatic responses to stimuli. The stimulus always causes the same response (stereotyped and dependable) ...
... Reflexes are rapid, automatic responses to stimuli. The stimulus always causes the same response (stereotyped and dependable) ...
File
... Background and Objectives: The consequences of injury in adult central nervous systems (CNS) are often devastating and irreversible. In the cricket (Gryllus bimaculatus), unilateral deafferentation of the auditory neurons of the prothoracic ganglia induces these cells to send dendrites across the mi ...
... Background and Objectives: The consequences of injury in adult central nervous systems (CNS) are often devastating and irreversible. In the cricket (Gryllus bimaculatus), unilateral deafferentation of the auditory neurons of the prothoracic ganglia induces these cells to send dendrites across the mi ...
Chapter 14
... Muscle tissues convert chemical signals into mechanical force • Key Concepts (1): – Muscles are effectors targeted by the nervous system and composed primarily of muscle tissue. – Muscle tissues are classified into three types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Collectively, muscle and bone tis ...
... Muscle tissues convert chemical signals into mechanical force • Key Concepts (1): – Muscles are effectors targeted by the nervous system and composed primarily of muscle tissue. – Muscle tissues are classified into three types: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Collectively, muscle and bone tis ...
An Introduction to the ANS and Higher
... • Swollen segment packed with neurotransmitter vesicles • Pass along or near surface of effector cells • No specialized postsynaptic membranes • Membrane receptors on surfaces of target cells ...
... • Swollen segment packed with neurotransmitter vesicles • Pass along or near surface of effector cells • No specialized postsynaptic membranes • Membrane receptors on surfaces of target cells ...
Parts of the nervous system
... 7 B. The nerve impulse travels from one neuron to another until it reaches the spinal cord. 6 C. The brain interprets the message as ”a rag is burning”. 8 D. The motor neurons send a message to the leg and arm muscles. 1/2 E. The sensory receptors in the boy’s eyes are stimulated by light from the b ...
... 7 B. The nerve impulse travels from one neuron to another until it reaches the spinal cord. 6 C. The brain interprets the message as ”a rag is burning”. 8 D. The motor neurons send a message to the leg and arm muscles. 1/2 E. The sensory receptors in the boy’s eyes are stimulated by light from the b ...
Instrumental Conditioning Driven by Apparently Neutral Stimuli: A
... (a) phasic DA responses have been recorded following stimuli with no apparent rewarding value, if these stimuli have not been previously shown to the organism: novelty causes phasic DA independently of the appetitive value of the stimulus; (b) while the time required to establish an association vari ...
... (a) phasic DA responses have been recorded following stimuli with no apparent rewarding value, if these stimuli have not been previously shown to the organism: novelty causes phasic DA independently of the appetitive value of the stimulus; (b) while the time required to establish an association vari ...
Lecture 22
... phonotaxis using his too-long sound wave? We determine direction to sound sources by comparing IIDs: interaural intensity differences. These differences arise in a right and left ear because of different path lengths (one ear is closer to the sound than the other) and they arise because of sound dif ...
... phonotaxis using his too-long sound wave? We determine direction to sound sources by comparing IIDs: interaural intensity differences. These differences arise in a right and left ear because of different path lengths (one ear is closer to the sound than the other) and they arise because of sound dif ...
At the crossroads of metabolism and reproduction in the brain
... to this: the body cannot commit to pregnancy without resources sufficient to carry it to full term. Clinically, this relationship is illustrated by the well-established infertility associated with anorexia and starvation, wherein the neuroendocrine gonadotrophic axis shuts down. Curiously, infertili ...
... to this: the body cannot commit to pregnancy without resources sufficient to carry it to full term. Clinically, this relationship is illustrated by the well-established infertility associated with anorexia and starvation, wherein the neuroendocrine gonadotrophic axis shuts down. Curiously, infertili ...
Chapter 7 Body Systems
... membrane is repolarized and is restoring the resting membrane potential; the few milliseconds after the absolute refractory period; membrane will respond only to a very strong stimulus Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. ...
... membrane is repolarized and is restoring the resting membrane potential; the few milliseconds after the absolute refractory period; membrane will respond only to a very strong stimulus Mosby items and derived items © 2007, 2003 by Mosby, Inc. ...
Document
... Early visual system: Retina • 5 types of cells: – Rods and cones: phototransduction into electrical signal – Lateral interaction of Bipolar cells through Horizontal cells. No action potentials for local computation – Action potentials in retinal ganglion cells coupled by Amacrine cells. Note • G_1 ...
... Early visual system: Retina • 5 types of cells: – Rods and cones: phototransduction into electrical signal – Lateral interaction of Bipolar cells through Horizontal cells. No action potentials for local computation – Action potentials in retinal ganglion cells coupled by Amacrine cells. Note • G_1 ...
spinal cord - Dr Magrann
... SIMPLE REFLEX ARC. They process information without the brain. So if you touch a hot stove, the sensory input comes into the spinal cord, the association neurons send the information to the lower motor neurons, the muscle contracts, and you take your hand off the stove before your brain even knows i ...
... SIMPLE REFLEX ARC. They process information without the brain. So if you touch a hot stove, the sensory input comes into the spinal cord, the association neurons send the information to the lower motor neurons, the muscle contracts, and you take your hand off the stove before your brain even knows i ...
The nerve A nerve is an enclosed, cable
... system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs. ...
... system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs. ...
CHAP 17c - Dr. Gerry Cronin
... shown impacting different parts of membranous labyrinth. This is a representation of sounds waves of different frequencies being transduced at the segment of the basilar membrane that is “tuned” for a particular pitch ...
... shown impacting different parts of membranous labyrinth. This is a representation of sounds waves of different frequencies being transduced at the segment of the basilar membrane that is “tuned” for a particular pitch ...
Pontine Respiratory Center
... the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve then inhibits the apneustic centre thus switching off the inspiration . • This is a protective mechanism preventing excess inflation of the lungs. The threshold for this reflex is ...
... the vagus nerve. The vagus nerve then inhibits the apneustic centre thus switching off the inspiration . • This is a protective mechanism preventing excess inflation of the lungs. The threshold for this reflex is ...
The Auditory System
... But the sound waves coming into the ears are just the sum of all these different acoustic signals. The auditory system then separates these acoustic inputs to generate the “sounds” we hearthe “auditory scene”. This takes extensive learning early in life but the mechanisms are not ...
... But the sound waves coming into the ears are just the sum of all these different acoustic signals. The auditory system then separates these acoustic inputs to generate the “sounds” we hearthe “auditory scene”. This takes extensive learning early in life but the mechanisms are not ...
Marieb_ch3c
... Adult body cells are not all the same. There are many kinds of cells, all specialized for particular functions ...
... Adult body cells are not all the same. There are many kinds of cells, all specialized for particular functions ...
A quick summary: The skeletal system is made up of
... ability to oversee and regulate our vital organs such as the heart, kidneys, lungs, etc. All of these functions are controlled by special areas in the brain. The peripheral nerves send messages to the brain about our external and internal environment. In response, these special areas of the brains s ...
... ability to oversee and regulate our vital organs such as the heart, kidneys, lungs, etc. All of these functions are controlled by special areas in the brain. The peripheral nerves send messages to the brain about our external and internal environment. In response, these special areas of the brains s ...
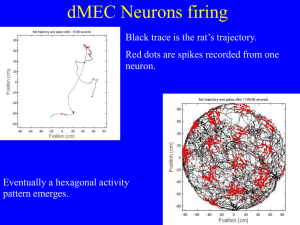
How grid cells neurons encode rat position
... • Ultimately not useful: the blood oxygen level changes slowly in response to activity The bold signal changes over the course of several seconds ...
... • Ultimately not useful: the blood oxygen level changes slowly in response to activity The bold signal changes over the course of several seconds ...
neuroloc
... The LSO calculates IID by subtracting the response of the contralateral ear from the response of the ipsilateral ear using inhibition. By adjusting the amount of inhibition delivered by MNTB, can make different LSO neurons respond over different ranges of IIDs. ...
... The LSO calculates IID by subtracting the response of the contralateral ear from the response of the ipsilateral ear using inhibition. By adjusting the amount of inhibition delivered by MNTB, can make different LSO neurons respond over different ranges of IIDs. ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.