Flowers and weeds: cell-type specific pruning in the developing
... pruning is required for adapting the LGN excitatory circuitry to the properties of the natural environment, why is it absent in the inhibitory branch of the network, which is widely regarded as fundamental for sharpening neuronal selectivity and improving perceptual discrimination in almost every ot ...
... pruning is required for adapting the LGN excitatory circuitry to the properties of the natural environment, why is it absent in the inhibitory branch of the network, which is widely regarded as fundamental for sharpening neuronal selectivity and improving perceptual discrimination in almost every ot ...
Back propagation-step-by-step procedure
... • Step 4: Present the pattern as inputs to {I}. Linear activation function is used as the output of the input layer. {O}I={I}I • Step 5: Compute the inputs to the hidden layers by multiplying corresponding weights of synapses as {I}H=[V]T{O}I • Step 6: The hidden layer units,evaluates the output us ...
... • Step 4: Present the pattern as inputs to {I}. Linear activation function is used as the output of the input layer. {O}I={I}I • Step 5: Compute the inputs to the hidden layers by multiplying corresponding weights of synapses as {I}H=[V]T{O}I • Step 6: The hidden layer units,evaluates the output us ...
THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
... • Merocrine glands: release fluid by exocytosis • Eccrine – Most common – Secretion is mostly water with solutes – Cools body down ...
... • Merocrine glands: release fluid by exocytosis • Eccrine – Most common – Secretion is mostly water with solutes – Cools body down ...
The Nervous System - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 27-2 Describe the functions of the nervous system. 27-3 Describe the structure of a neuron. 27-4 Describe the function of a nerve impulse and how a nerve impulse is created. 27-5 Describe the structure and function of a synapse. 27-6 Describe the fun ...
... nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 27-2 Describe the functions of the nervous system. 27-3 Describe the structure of a neuron. 27-4 Describe the function of a nerve impulse and how a nerve impulse is created. 27-5 Describe the structure and function of a synapse. 27-6 Describe the fun ...
lecture 36
... The receptor must have specificity for the stimulus energy The receptor’s receptive field must be stimulated Stimulus energy must be converted into a graded potential A generator potential in the associated sensory neuron must reach threshold Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publish ...
... The receptor must have specificity for the stimulus energy The receptor’s receptive field must be stimulated Stimulus energy must be converted into a graded potential A generator potential in the associated sensory neuron must reach threshold Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publish ...
An Extended Model for Stimulus Onset Asynchrony (SOA) in Stroop
... Therefore, positive response time means slower than the control, and negative means faster than the control. The solid lines are the response times of the incongruent case, while the dashed lines are those of the congruent case. (a) Human data by Glaser and Glaser [11]. Note that for the incongruent ...
... Therefore, positive response time means slower than the control, and negative means faster than the control. The solid lines are the response times of the incongruent case, while the dashed lines are those of the congruent case. (a) Human data by Glaser and Glaser [11]. Note that for the incongruent ...
An octopaminergic system in the CNS of the snails, Lymnaea
... feeding network: electrical coupling was demonstrated between OC neurons and members of the B4 cluster motoneurons, moreover chemically transmitted synaptic responses were recorded both on feeding motoneurons (B1, B2 cells) and the SO modulatory interneuron after the stimulation of OC neurons. Howev ...
... feeding network: electrical coupling was demonstrated between OC neurons and members of the B4 cluster motoneurons, moreover chemically transmitted synaptic responses were recorded both on feeding motoneurons (B1, B2 cells) and the SO modulatory interneuron after the stimulation of OC neurons. Howev ...
Functional roles of melanocortin-4 receptor in hippocampal synapse
... E-mail:[email protected] Abstract: Objective Melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R), which belongs to the Gprotein coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily, is one of the five melanocortin receptors (MCRs) that is expressed abundantly in the central nervous system. MC4R ...
... E-mail:[email protected] Abstract: Objective Melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R), which belongs to the Gprotein coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily, is one of the five melanocortin receptors (MCRs) that is expressed abundantly in the central nervous system. MC4R ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... organs including the eye, the salivary glands, the sweat glands, the gut, the heart, smooth muscle of the blood vessels and the piloerector muscles of the skin hairs. Some preganglionic fibers pass through the paravertebral ganglia and join to form the splanchnic nerves, which pass to the celiac, hy ...
... organs including the eye, the salivary glands, the sweat glands, the gut, the heart, smooth muscle of the blood vessels and the piloerector muscles of the skin hairs. Some preganglionic fibers pass through the paravertebral ganglia and join to form the splanchnic nerves, which pass to the celiac, hy ...
12-4 Membrane Potential
... • All communication, information processing, and control functions of the nervous system ...
... • All communication, information processing, and control functions of the nervous system ...
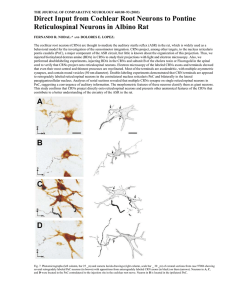
A Type of Basket Cell in Superficial Layers of the Cat Visual Cortex
... Thus, a high degree of selectivity with regard to the postsynaptic partners is apparent which could be compared to that shown by chandelier cells7, 25. If, as postulated, basket and chandelier cells exert an inhibitory action7,9,18,zz,24, 25, the selective distribution of their axon terminals would ...
... Thus, a high degree of selectivity with regard to the postsynaptic partners is apparent which could be compared to that shown by chandelier cells7, 25. If, as postulated, basket and chandelier cells exert an inhibitory action7,9,18,zz,24, 25, the selective distribution of their axon terminals would ...
glucocorticoids
... water is so slow that there is a danger of water intoxication and only glococorticoids can repair this deficit. ...
... water is so slow that there is a danger of water intoxication and only glococorticoids can repair this deficit. ...
BRAIN FOUNDATION RESEARCH REPORTS Author: Dr Tim
... Background. In rodents we had shown that the number of tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactive (TH+) or dopaminergic neurones is altered up or down by ±10-15% following 1-2 weeks exposure to environmental or behavioural stimuli, including length of light:dark cycle (photoperiod), sex pairing, or environ ...
... Background. In rodents we had shown that the number of tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactive (TH+) or dopaminergic neurones is altered up or down by ±10-15% following 1-2 weeks exposure to environmental or behavioural stimuli, including length of light:dark cycle (photoperiod), sex pairing, or environ ...
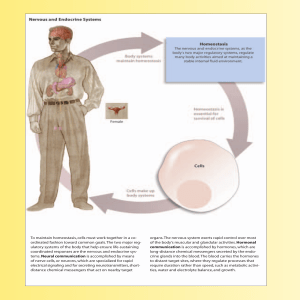
To maintain homeostasis, cells must work together in a co
... event might be (1) a change in the electrical field in the vicinity of an excitable membrane; (2) an interaction of a chemical messenger with a surface receptor on a nerve or muscle cell membrane; (3) a stimulus, such as sound waves stimulating specialized nerve cells in your ear; or (4) a spontaneo ...
... event might be (1) a change in the electrical field in the vicinity of an excitable membrane; (2) an interaction of a chemical messenger with a surface receptor on a nerve or muscle cell membrane; (3) a stimulus, such as sound waves stimulating specialized nerve cells in your ear; or (4) a spontaneo ...
Document
... potentials occur in several types of animal cells, called excitable cells, which include neurons, muscle cells, and endocrine cells, • is generated by special types of voltage-gated ion channels embedded in a cell's plasma membrane. ...
... potentials occur in several types of animal cells, called excitable cells, which include neurons, muscle cells, and endocrine cells, • is generated by special types of voltage-gated ion channels embedded in a cell's plasma membrane. ...
atterning the nervous system through development and evolution: a
... neurons providing a signal for control would result in helpless behavior. Their results suggest that the habenula is involved in the computation of control over stress. Such an "everything-under-control" circuit may underlie a very satisfactory state of mind, and could indeed be involved in, or part ...
... neurons providing a signal for control would result in helpless behavior. Their results suggest that the habenula is involved in the computation of control over stress. Such an "everything-under-control" circuit may underlie a very satisfactory state of mind, and could indeed be involved in, or part ...
Science - Princeton University
... Inferotemporal Cortex of the Monkey Abstract. Neurons in iizferotemporal cortex (area T E ) o f the monkey had visual receptive fielcls which were very large (greclter than 10 by 10 degrees) and alnzost alwciys iizcluded the fovea. Some extended well into both halves o f the visual fielcl, while oth ...
... Inferotemporal Cortex of the Monkey Abstract. Neurons in iizferotemporal cortex (area T E ) o f the monkey had visual receptive fielcls which were very large (greclter than 10 by 10 degrees) and alnzost alwciys iizcluded the fovea. Some extended well into both halves o f the visual fielcl, while oth ...
Neurobiology
... Myelin and action potential transmission speed The speed with which the action potentials are propagated along the axons depends on: The diameter of the axon (determines the number and surface density of voltage-gated ion channels) The presence, or absence of a myelin sheath around the axon (sa ...
... Myelin and action potential transmission speed The speed with which the action potentials are propagated along the axons depends on: The diameter of the axon (determines the number and surface density of voltage-gated ion channels) The presence, or absence of a myelin sheath around the axon (sa ...
Investigating neural correlates of conscious perception by frequency
... recent psychophysical studies have demonstrated that perceptual rivalry can occur even when both stimuli are presented through the same eye or when they are alternated between the eyes (2). Furthermore, single-unit recordings during binocular rivalry in monkeys indicate that, while the firing of mos ...
... recent psychophysical studies have demonstrated that perceptual rivalry can occur even when both stimuli are presented through the same eye or when they are alternated between the eyes (2). Furthermore, single-unit recordings during binocular rivalry in monkeys indicate that, while the firing of mos ...
the summary and précis of the conference
... Despite the sparseness of the cortical connection matrix, the potential bandwidth of all of the neurons in the human cortex is around a Terabit/sec (assuming a maximum rate of 100 bit/sec over each axon in the white matter), comparable to the total world backbone capacity of the Internet in 2002. H ...
... Despite the sparseness of the cortical connection matrix, the potential bandwidth of all of the neurons in the human cortex is around a Terabit/sec (assuming a maximum rate of 100 bit/sec over each axon in the white matter), comparable to the total world backbone capacity of the Internet in 2002. H ...
Multimodal Virtual Environments: Response Times, Attention, and
... trimodal signals Faster processing at the perceptual stage allow users more time in consequent cognitive stages Contributing to the great sense of presence ...
... trimodal signals Faster processing at the perceptual stage allow users more time in consequent cognitive stages Contributing to the great sense of presence ...
Long-term depression
... excitatory 2 postsynaptic receptor subtypes AMPA ---> Na+ NMDA ---> Ca++ Glu ligand for both ~ ...
... excitatory 2 postsynaptic receptor subtypes AMPA ---> Na+ NMDA ---> Ca++ Glu ligand for both ~ ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.