Drug İnteractions
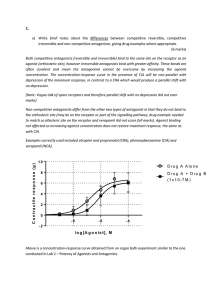
... Reversible antagonists readily dissociate from their receptor; Irreversible antagonists form a stable, permanent or nearly permanent chemical bond ...
... Reversible antagonists readily dissociate from their receptor; Irreversible antagonists form a stable, permanent or nearly permanent chemical bond ...
Benton Daly (Fall `10 file)
... the information from their studies of Avandia. They broke their responsibility to their consumers by downplaying vital information. The company should have been forthcoming when they first learned about the possible risks; instead, the information was only revealed when the FDA prompted them to reve ...
... the information from their studies of Avandia. They broke their responsibility to their consumers by downplaying vital information. The company should have been forthcoming when they first learned about the possible risks; instead, the information was only revealed when the FDA prompted them to reve ...
Spare Receptors
... How can an agonist be “partial”? The precise mechanism is not known. We can imagine that a receptor can take two shapes: the inactive form, and an active form, in the absence, as well as the presence of bound ligand; A full agonist binds to the active form more tightly than to inactive form; while ...
... How can an agonist be “partial”? The precise mechanism is not known. We can imagine that a receptor can take two shapes: the inactive form, and an active form, in the absence, as well as the presence of bound ligand; A full agonist binds to the active form more tightly than to inactive form; while ...
Aminoglycosides
... E. coli, proteus, Pseudomonas, Enterococci and Staph aureus *) Lack activity against most anaerobic or facultative bacteria and activity against G+ve# organisms is limited * in combination # Strept pyogenes is highly resistant ...
... E. coli, proteus, Pseudomonas, Enterococci and Staph aureus *) Lack activity against most anaerobic or facultative bacteria and activity against G+ve# organisms is limited * in combination # Strept pyogenes is highly resistant ...
PREMEDICATION DRUGS
... c) has a long duration of action d) may cause nausea and vomiting e) has inverse agonist action at benzodiazepine receptors ...
... c) has a long duration of action d) may cause nausea and vomiting e) has inverse agonist action at benzodiazepine receptors ...
No Slide Title
... children are at equal risk. Find the kids at highest risk for serious ADRs due to genetic factors ...
... children are at equal risk. Find the kids at highest risk for serious ADRs due to genetic factors ...
Alcohol & Marijuana: Impact on the Body
... Rx drugs are easy to obtain Street value is high, so those who have them are making $ U.S. consumes 80% of the worlds opiate supply ER’s: alcohol & Rx drug use in combination 50% most DUI related blood draws contain other substances in addition to alcohol 20% of people in the U.S. have u ...
... Rx drugs are easy to obtain Street value is high, so those who have them are making $ U.S. consumes 80% of the worlds opiate supply ER’s: alcohol & Rx drug use in combination 50% most DUI related blood draws contain other substances in addition to alcohol 20% of people in the U.S. have u ...
Instructions for Completing HUSC-RSC Form 1002
... address each of the designated minimum acceptance criteria on each batch of the radioactive drug. In such an event, compliance of the radioactive drug with the applicable minimum acceptance criterion should be addressed in the preclinical validation studies. For certain criteria (e.g., sterility, py ...
... address each of the designated minimum acceptance criteria on each batch of the radioactive drug. In such an event, compliance of the radioactive drug with the applicable minimum acceptance criterion should be addressed in the preclinical validation studies. For certain criteria (e.g., sterility, py ...
Comparison of Drug Approval Process in United States
... This topic aims at reviewing the drug filing and different aspects of obtaining United States Food & Drug Administration (USFDA) and European Medicines Agency (EMA) approval for a drug in order to get a Marketing Authorization in US & Europe and their effective role in improving the standards laid d ...
... This topic aims at reviewing the drug filing and different aspects of obtaining United States Food & Drug Administration (USFDA) and European Medicines Agency (EMA) approval for a drug in order to get a Marketing Authorization in US & Europe and their effective role in improving the standards laid d ...
Dr. Carl Davis presentation
... substrates is regulated in animals and humans by clearance, either by direct elimination (biliary and/or renal) or by enzyme-mediated metabolism – Generally this is a detoxication process that prevents accumulation of bioactive compounds in the body • can also produce reactive metabolites and toxici ...
... substrates is regulated in animals and humans by clearance, either by direct elimination (biliary and/or renal) or by enzyme-mediated metabolism – Generally this is a detoxication process that prevents accumulation of bioactive compounds in the body • can also produce reactive metabolites and toxici ...
F1-Single Domain Antibody Service.ai
... (see below). The antigen-binding site of these unusual heavy chain antibodies is formed only by a single heavy chain variable domain, designated as single domain antibodies (sdAbs). sdAbs combine the advantages of conventional antibodies with important features of smaller molecule sdAb drugs. The un ...
... (see below). The antigen-binding site of these unusual heavy chain antibodies is formed only by a single heavy chain variable domain, designated as single domain antibodies (sdAbs). sdAbs combine the advantages of conventional antibodies with important features of smaller molecule sdAb drugs. The un ...
History
... • Biologic: A blood product or an active drug ingredient which is generally a protein isolated from a biomass produced by a natural or recombinant organism. ...
... • Biologic: A blood product or an active drug ingredient which is generally a protein isolated from a biomass produced by a natural or recombinant organism. ...
Drug Nomenclature
... observe for adverse effects. • Notify nurse manager and physician. • Write description of error on medical record and remedial steps taken. • Complete special form for reporting errors. ...
... observe for adverse effects. • Notify nurse manager and physician. • Write description of error on medical record and remedial steps taken. • Complete special form for reporting errors. ...
THE UNIVERSITY OF AUCKLAND
... b) Based on the data, what type of drug (i.e. type of agonist or antagonist) does Drug B appear most likely to be? Explain your answer and provide an example of this type of drug. (3 marks) Full marks could be achieved with either CRA or NCA, depending on how data was interpreted – either was fine, ...
... b) Based on the data, what type of drug (i.e. type of agonist or antagonist) does Drug B appear most likely to be? Explain your answer and provide an example of this type of drug. (3 marks) Full marks could be achieved with either CRA or NCA, depending on how data was interpreted – either was fine, ...
Sustained Release Dosage Forms The Sustained
... does not permit the prompt termination of therapy. ...
... does not permit the prompt termination of therapy. ...
seminar on self emulsifying drug delivery system
... of mixing), N is the number of droplets of radius, r, and Ợ represents the interfacial energy. With time, the two phases of the emulsion will tend to separate, in order to reduce the interfacial area, and subsequently, the free energy of the systems. ...
... of mixing), N is the number of droplets of radius, r, and Ợ represents the interfacial energy. With time, the two phases of the emulsion will tend to separate, in order to reduce the interfacial area, and subsequently, the free energy of the systems. ...
The Why and How of Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion
... candidates.6,7 Lack of efficacy, in addition to insufficient response of the target, may of course be caused by poor absorption, inadequate distribution and/or rapid metabolism, leading to too low drug concentrations at the target site.8 And since toxicity is also a major factor of attrition, the de ...
... candidates.6,7 Lack of efficacy, in addition to insufficient response of the target, may of course be caused by poor absorption, inadequate distribution and/or rapid metabolism, leading to too low drug concentrations at the target site.8 And since toxicity is also a major factor of attrition, the de ...
MS Powerpoint | 1794.87 KB - Understanding Animal Research
... Computers can be programmed with information about a disease and a treatment to try and predict what will happen when the treatment is given. Computer model of artery ...
... Computers can be programmed with information about a disease and a treatment to try and predict what will happen when the treatment is given. Computer model of artery ...
Logistic Regression Part 2
... In a study evaluating the potential adverse side effects of statin use on mobility problems (may or may not be the case) • Muscle weakness is in the pathway (= mediator) • Prior muscle weakness before statin use may also be a confounder ...
... In a study evaluating the potential adverse side effects of statin use on mobility problems (may or may not be the case) • Muscle weakness is in the pathway (= mediator) • Prior muscle weakness before statin use may also be a confounder ...
Rational Use of Drugs - International Journal of Biomedicine
... The features of drug usage in individual diseases. To implement the rational choice of drugs, certain aspects must be considered. Therefore, certain classes of diseases necessitate the use of drugs with extremely high sensitivity in patients, and some diseases necessitate the use of drugs with a nar ...
... The features of drug usage in individual diseases. To implement the rational choice of drugs, certain aspects must be considered. Therefore, certain classes of diseases necessitate the use of drugs with extremely high sensitivity in patients, and some diseases necessitate the use of drugs with a nar ...
Human Research Involving Drugs and Biologics 1.0 Purpose:
... 4.2 Investigational new drug: a new drug or biological drug that is used in a clinical investigation. The term also includes a biological product that is used in vitro for diagnostic purposes. The terms "investigational drug" and "investigational new drug" are synonymous. 4.3 Biologics License Appli ...
... 4.2 Investigational new drug: a new drug or biological drug that is used in a clinical investigation. The term also includes a biological product that is used in vitro for diagnostic purposes. The terms "investigational drug" and "investigational new drug" are synonymous. 4.3 Biologics License Appli ...
Dr. Kunwar Shailubhai
... Drug candidates - Custom Synthesis - SAR studies - Combinatorial Synthesis - Biopharmaceuticals ...
... Drug candidates - Custom Synthesis - SAR studies - Combinatorial Synthesis - Biopharmaceuticals ...
Drug İnteractions
... Reversible antagonists readily dissociate from their receptor; Irreversible antagonists form a stable, permanent or nearly permanent chemical bond ...
... Reversible antagonists readily dissociate from their receptor; Irreversible antagonists form a stable, permanent or nearly permanent chemical bond ...
shands - UF Health Professionals
... have tried to address the effect that hoarding has on shortages. The FDA encourages the establishment of limited access programs that only release drugs based on specified criteria. These criteria may be based on the amount that can be obtained at 1 time or based on the reason that the patient needs ...
... have tried to address the effect that hoarding has on shortages. The FDA encourages the establishment of limited access programs that only release drugs based on specified criteria. These criteria may be based on the amount that can be obtained at 1 time or based on the reason that the patient needs ...
loading dose
... What will be the result of administering a highly protein-bound drug to a patient with liver failure? – A. There will be no significant difference in the distribution of the drug. – B. The drug will reach the target cells more quickly and therefore will not be as effective. – C. The drug will reach ...
... What will be the result of administering a highly protein-bound drug to a patient with liver failure? – A. There will be no significant difference in the distribution of the drug. – B. The drug will reach the target cells more quickly and therefore will not be as effective. – C. The drug will reach ...
Drug design
Drug design, sometimes referred to as rational drug design or simply rational design, is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. The drug is most commonly an organic small molecule that activates or inhibits the function of a biomolecule such as a protein, which in turn results in a therapeutic benefit to the patient. In the most basic sense, drug design involves the design of molecules that are complementary in shape and charge to the biomolecular target with which they interact and therefore will bind to it. Drug design frequently but not necessarily relies on computer modeling techniques. This type of modeling is often referred to as computer-aided drug design. Finally, drug design that relies on the knowledge of the three-dimensional structure of the biomolecular target is known as structure-based drug design. In addition to small molecules, biopharmaceuticals and especially therapeutic antibodies are an increasingly important class of drugs and computational methods for improving the affinity, selectivity, and stability of these protein-based therapeutics have also been developed.The phrase ""drug design"" is to some extent a misnomer. A more accurate term is ligand design (i.e., design of a molecule that will bind tightly to its target). Although design techniques for prediction of binding affinity are reasonably successful, there are many other properties, such as bioavailability, metabolic half-life, side effects, etc., that first must be optimized before a ligand can become a safe and efficacious drug. These other characteristics are often difficult to predict with rational design techniques. Nevertheless, due to high attrition rates, especially during clinical phases of drug development, more attention is being focused early in the drug design process on selecting candidate drugs whose physicochemical properties are predicted to result in fewer complications during development and hence more likely to lead to an approved, marketed drug. Furthermore, in vitro experiments complemented with computation methods are increasingly used in early drug discovery to select compounds with more favorable ADME (absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion) and toxicological profiles.