Locandina Slater.cdr - univr dsnm - Università degli Studi di Verona
... (AChRs) located on the post-synaptic muscle fibre, to operate the transmission of the nerve impulse (action potential) from the motor neuron to the muscle fibre, where it finally evokes the contraction. One of the many interesting questions to be asked about cells is how nearly their performance rea ...
... (AChRs) located on the post-synaptic muscle fibre, to operate the transmission of the nerve impulse (action potential) from the motor neuron to the muscle fibre, where it finally evokes the contraction. One of the many interesting questions to be asked about cells is how nearly their performance rea ...
It takes all kinds to make a brain
... mitral cells8. There is some evidence that every ORN projects to each and every principal neuron in its target glomerulus9,10. Moreover, each mitral cell is postsynaptic to a single glomerulus. Thus, all of the sister mitral cells postsynaptic to the same glomerulus carry approximately the same sign ...
... mitral cells8. There is some evidence that every ORN projects to each and every principal neuron in its target glomerulus9,10. Moreover, each mitral cell is postsynaptic to a single glomerulus. Thus, all of the sister mitral cells postsynaptic to the same glomerulus carry approximately the same sign ...
LO #1
... Why This Topic? Action potentials are the basic unit of signaling in the central nervous system (CNS). Neurons are complex organs (computers?) that receive signals from many other neurons; summation of excitation and inhibition by postsynaptic neurons permits a neuron to integrate the electrical in ...
... Why This Topic? Action potentials are the basic unit of signaling in the central nervous system (CNS). Neurons are complex organs (computers?) that receive signals from many other neurons; summation of excitation and inhibition by postsynaptic neurons permits a neuron to integrate the electrical in ...
ASCENDING TRACTS
... At the end of lecture, students should be able to know: Sensory pathways and receptors. Spinothalamic pathway. Spinothalamic damage. Dorsal column pathway. Dorsal column damage. Spinocerebellar pathway. Spinocerebellar tract damage. ...
... At the end of lecture, students should be able to know: Sensory pathways and receptors. Spinothalamic pathway. Spinothalamic damage. Dorsal column pathway. Dorsal column damage. Spinocerebellar pathway. Spinocerebellar tract damage. ...
PSYB1 Revision sheet Biopsychology JM09
... The function of a motor neuron is to carry information from the central nervous system to the muscles/glands/effectors, whereas the function of a sensory neuron is to carry information from the sense organs to the central nervous system. Synaptic Transmission ...
... The function of a motor neuron is to carry information from the central nervous system to the muscles/glands/effectors, whereas the function of a sensory neuron is to carry information from the sense organs to the central nervous system. Synaptic Transmission ...
Nervous system
... • K+ gates close and Na+ gates open • Na+ rushes into the cell making the interior more positive. This change in charge is called the action potential. • The opening of one gate causes the gate next to it to open (hence - the all-or-none) ...
... • K+ gates close and Na+ gates open • Na+ rushes into the cell making the interior more positive. This change in charge is called the action potential. • The opening of one gate causes the gate next to it to open (hence - the all-or-none) ...
Chapter 48 PowerPoint 2016 - Spring
... • When a stimulus depolarizes the membrane, Na+ channels open, allowing Na+ to diffuse into the cell • The movement of Na+ into the cell increases the depolarization and causes even more Na+ channels to open • A strong stimulus results in a massive change in membrane voltage called an action potenti ...
... • When a stimulus depolarizes the membrane, Na+ channels open, allowing Na+ to diffuse into the cell • The movement of Na+ into the cell increases the depolarization and causes even more Na+ channels to open • A strong stimulus results in a massive change in membrane voltage called an action potenti ...
document
... cell? Allow students to discuss different scenarios. List their suggestions on the board. (You may want to group their suggestions into two broad ...
... cell? Allow students to discuss different scenarios. List their suggestions on the board. (You may want to group their suggestions into two broad ...
Document
... dendrite: i. receives messages and sends them to the cell body ii. many branched extensions ...
... dendrite: i. receives messages and sends them to the cell body ii. many branched extensions ...
Gated Channels
... (a) In a bare plasma membrane (without voltage-gated channels), as on a dendrite, voltage decays because current leaks across the membrane. Voltage-gated Stimulus ion channel ...
... (a) In a bare plasma membrane (without voltage-gated channels), as on a dendrite, voltage decays because current leaks across the membrane. Voltage-gated Stimulus ion channel ...
Nerve Cross Section
... The functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron, a cell that is capable of generating and propagating electrical signals in the form of action potentials. Neurons can be found in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and in the nerves of the peripheral nervous system. All neuron ...
... The functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron, a cell that is capable of generating and propagating electrical signals in the form of action potentials. Neurons can be found in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and in the nerves of the peripheral nervous system. All neuron ...
Memory notes Explaining memory Learning required memorisation
... One change – the way the neuron functions as there is an increase in the amt of the neurotransmitter being produced and released by the neurons; that is the specific chemical substance used by neurons to communicate. Second change – to the structure of the slug’ neuron where the number of branches ...
... One change – the way the neuron functions as there is an increase in the amt of the neurotransmitter being produced and released by the neurons; that is the specific chemical substance used by neurons to communicate. Second change – to the structure of the slug’ neuron where the number of branches ...
Nervous System I
... A greater intensity stimulus produces a higher frequency of action potentials, not a stronger action potential. ...
... A greater intensity stimulus produces a higher frequency of action potentials, not a stronger action potential. ...
Ch 31: Urinary System
... - Either by the number of times a single neuron “fires” or the total number of neurons “firing” at once ...
... - Either by the number of times a single neuron “fires” or the total number of neurons “firing” at once ...
ppt
... Synaptic Potentials •Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP) •triggered by excitatory neurotransmitters •open ligand-gated Na+ channels •allows Na+ to flow inside the cell •causing a slight depolarization of the postsynaptic cell •moves the postsynaptic cell closer to firing an action potential ...
... Synaptic Potentials •Excitatory Postsynaptic Potential (EPSP) •triggered by excitatory neurotransmitters •open ligand-gated Na+ channels •allows Na+ to flow inside the cell •causing a slight depolarization of the postsynaptic cell •moves the postsynaptic cell closer to firing an action potential ...
Nerve tissue
... membrane covered by the terminal bud has clefts and ridges called junctional folds. The axon loses its myelin sheath and dilates, establishing close, irregular contact with the muscle fiber. Muscle contraction begins with the release of acetylcholine from the synaptic vesicles. This neurotransmitter ...
... membrane covered by the terminal bud has clefts and ridges called junctional folds. The axon loses its myelin sheath and dilates, establishing close, irregular contact with the muscle fiber. Muscle contraction begins with the release of acetylcholine from the synaptic vesicles. This neurotransmitter ...
Sussillo, David Recurrent Neural Network Dynamics Mar
... say, have a task... and have rodent or monkey...= system get the neurobio data (firing rates from a pop. of neurons) guess mechanism then make a model and have the model generate simulated data and see if there is a match... but what should the solutions look like... eg consider a generic router wit ...
... say, have a task... and have rodent or monkey...= system get the neurobio data (firing rates from a pop. of neurons) guess mechanism then make a model and have the model generate simulated data and see if there is a match... but what should the solutions look like... eg consider a generic router wit ...
The Nervous System
... the myelin sheaths around the axons of many vertebrate neurons ● neurons are myelinated during development in which Schwann cells or oligodendrocytes grow around the axons, creating many layers of lipid membrane o provides electrical insulation for the axon as a poor conductor of ...
... the myelin sheaths around the axons of many vertebrate neurons ● neurons are myelinated during development in which Schwann cells or oligodendrocytes grow around the axons, creating many layers of lipid membrane o provides electrical insulation for the axon as a poor conductor of ...
Lecture_30_2014
... A. Both the voltage-gated Na+ channels and voltage gated K+ channels are open. B. All of the K+ channels (both leak and voltage gated) are open. C. The voltage gated Na+ channels are open, but the voltage gated K+ channels have not opened yet. D. The voltage gated Na+ channels are open, but the K+ c ...
... A. Both the voltage-gated Na+ channels and voltage gated K+ channels are open. B. All of the K+ channels (both leak and voltage gated) are open. C. The voltage gated Na+ channels are open, but the voltage gated K+ channels have not opened yet. D. The voltage gated Na+ channels are open, but the K+ c ...
CLASS #1: 9 Jan 2001
... world are produced by activity in different neurons. In other words, matter how the neurons are activated the perception produced is the same D. Relationship between stimulus and perception: Sensations and perceptions are NOT copies of physical stimuli. The CNS constructs our perceptions, using its ...
... world are produced by activity in different neurons. In other words, matter how the neurons are activated the perception produced is the same D. Relationship between stimulus and perception: Sensations and perceptions are NOT copies of physical stimuli. The CNS constructs our perceptions, using its ...
spinal cord
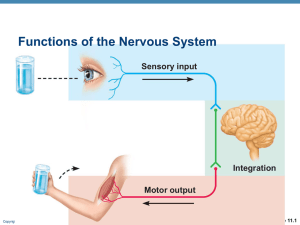
... control and coordination of life functions and activities 2 systems involved: 1. nervous- electrical system, brain,spine and nerves found in multicellular organisms 2. endocrine- chemical system, hormones found in all organisms Nervous System: definitions: a. stimulus- change in the internal or ex ...
... control and coordination of life functions and activities 2 systems involved: 1. nervous- electrical system, brain,spine and nerves found in multicellular organisms 2. endocrine- chemical system, hormones found in all organisms Nervous System: definitions: a. stimulus- change in the internal or ex ...
IN SEARCH OF PRINCIPLES IN INTEGRATIVE BIOLOGY
... average over a second or more is not relevant because it is mainly a function of electric organ discharge rate. We may call this case a number code (Fig. 7). Another type of receptor which does not code by altering spike interval is found in species that discharge the electric organ steadily at mode ...
... average over a second or more is not relevant because it is mainly a function of electric organ discharge rate. We may call this case a number code (Fig. 7). Another type of receptor which does not code by altering spike interval is found in species that discharge the electric organ steadily at mode ...
The Autonomic Nervous System The Sympathetic Division
... • Preganglionic fibers are short, connect to the sympathetic chain, and synapse with long postganglionic fibers • Preganglionic fibers produce ACh, postganglionic fibers produce NE or Ach ...
... • Preganglionic fibers are short, connect to the sympathetic chain, and synapse with long postganglionic fibers • Preganglionic fibers produce ACh, postganglionic fibers produce NE or Ach ...