Biology and Behavior
... 1.The 4 major parts of the neuron are ____, ____, ____, _____. (list in order that the neuron receives the message) 2. Inside the neuron is a _____ charge, until an action potential occurs, making the charge _____. 3. Neurons can have excitatory and _____ effects on each other causing an action pote ...
... 1.The 4 major parts of the neuron are ____, ____, ____, _____. (list in order that the neuron receives the message) 2. Inside the neuron is a _____ charge, until an action potential occurs, making the charge _____. 3. Neurons can have excitatory and _____ effects on each other causing an action pote ...
overview
... Activities: The students begin this lesson by reviewing the steps of synaptic transmission with a partner. The lesson continues with the students modeling the pain pathway. This model is designed to reinforce the connection between the action potential and synaptic transmission. Once the class has r ...
... Activities: The students begin this lesson by reviewing the steps of synaptic transmission with a partner. The lesson continues with the students modeling the pain pathway. This model is designed to reinforce the connection between the action potential and synaptic transmission. Once the class has r ...
Peripheral Nervous System
... All-or-None Response • If a neuron responds at all, it responds completely • A nerve impulse is conducted whenever a stimulus of threshold intensity or above is applied to an axon • All impulses carried on an axon are the same strength ...
... All-or-None Response • If a neuron responds at all, it responds completely • A nerve impulse is conducted whenever a stimulus of threshold intensity or above is applied to an axon • All impulses carried on an axon are the same strength ...
BUILDING AN ARTIFICIAL BRAIN
... • Create a complex functionality without any a priori knowledge of how to achieve it… • Requires the desired Input/Output function! ...
... • Create a complex functionality without any a priori knowledge of how to achieve it… • Requires the desired Input/Output function! ...
Lecture 5
... epileptic seizures: wavelike electrical activity of a large number of neurons, often associated with loss of consciousness and involuntary body ...
... epileptic seizures: wavelike electrical activity of a large number of neurons, often associated with loss of consciousness and involuntary body ...
Document
... • Biosynthetic center of a neuron • Spherical nucleus with nucleolus • Well-developed Golgi apparatus • Rough ER called Nissl bodies (chromatophilic substance) Cell Body (Perikaryon or Soma) • Network of neurofibrils (neurofilaments) • Axon hillock—cone-shaped area from which axon arises • Clusters ...
... • Biosynthetic center of a neuron • Spherical nucleus with nucleolus • Well-developed Golgi apparatus • Rough ER called Nissl bodies (chromatophilic substance) Cell Body (Perikaryon or Soma) • Network of neurofibrils (neurofilaments) • Axon hillock—cone-shaped area from which axon arises • Clusters ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... 2) Name the three stages in the processing of information by nervous systems. 3) Distinguish between sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons. 4) List and describe the major parts of a neuron and explain the function of each. 5) Describe the function of astrocytes, radial glia, oligodendrocy ...
... 2) Name the three stages in the processing of information by nervous systems. 3) Distinguish between sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons. 4) List and describe the major parts of a neuron and explain the function of each. 5) Describe the function of astrocytes, radial glia, oligodendrocy ...
(580.422) Lecture 7, Synaptic Transmission
... terminals, but have diffusely localized cell bodies. These include GABA acting at GABAB receptors, often a transmitter at presynaptic inhibitory terminals that acts by decreasing presynaptic Ca currents; glutamate; adenosine; and peptides. Among the peptides, opioids (enkephalins) are important in p ...
... terminals, but have diffusely localized cell bodies. These include GABA acting at GABAB receptors, often a transmitter at presynaptic inhibitory terminals that acts by decreasing presynaptic Ca currents; glutamate; adenosine; and peptides. Among the peptides, opioids (enkephalins) are important in p ...
Chapter 48 – Nervous Systems
... 2) Name the three stages in the processing of information by nervous systems. 3) Distinguish between sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons. 4) List and describe the major parts of a neuron and explain the function of each. 5) Describe the function of astrocytes, radial glia, oligodendrocy ...
... 2) Name the three stages in the processing of information by nervous systems. 3) Distinguish between sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons. 4) List and describe the major parts of a neuron and explain the function of each. 5) Describe the function of astrocytes, radial glia, oligodendrocy ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue: Part A
... • Biosynthetic center of a neuron • Spherical nucleus with nucleolus • Well-developed Golgi apparatus • Rough ER called Nissl bodies (chromatophilic substance) Cell Body (Perikaryon or Soma) • Network of neurofibrils (neurofilaments) • Axon hillock—cone-shaped area from which axon arises • Clusters ...
... • Biosynthetic center of a neuron • Spherical nucleus with nucleolus • Well-developed Golgi apparatus • Rough ER called Nissl bodies (chromatophilic substance) Cell Body (Perikaryon or Soma) • Network of neurofibrils (neurofilaments) • Axon hillock—cone-shaped area from which axon arises • Clusters ...
The Nervous System
... A. definition: _________________________________________________________________ B. involves a simple nerve pathway called a _____________________ Example – touching a hot pan i. sensory receptors in fingers respond to the hot metal ii. an impulse relaying this information is sent via sensory neuron ...
... A. definition: _________________________________________________________________ B. involves a simple nerve pathway called a _____________________ Example – touching a hot pan i. sensory receptors in fingers respond to the hot metal ii. an impulse relaying this information is sent via sensory neuron ...
Unit 3D Worksheet 1) In the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS
... 3)Effectors of the Somatic Nervous System (SNS) innervate skeletal ___________via ______ heavily ________________axon. This would be an afferent/efferent sensory/motor neuron. 4) Effectors of the ANS innervate ___________muscle, __________muscle and ________via a ______neuron __________made up of __ ...
... 3)Effectors of the Somatic Nervous System (SNS) innervate skeletal ___________via ______ heavily ________________axon. This would be an afferent/efferent sensory/motor neuron. 4) Effectors of the ANS innervate ___________muscle, __________muscle and ________via a ______neuron __________made up of __ ...
Anatomy of the Nervous System
... – “efferent neurons” – Relay info to effectors: muscles, organs, and glands (can produce a response) ...
... – “efferent neurons” – Relay info to effectors: muscles, organs, and glands (can produce a response) ...
Introduction
... been no published models where gaze and retinal signals are combined to code for movement kinematics. In Rosenbaum, et al (1999), the authors present a computational model for solving the inverse kinematics problem for reaching and grasping movements. The essence of their idea is that movements are ...
... been no published models where gaze and retinal signals are combined to code for movement kinematics. In Rosenbaum, et al (1999), the authors present a computational model for solving the inverse kinematics problem for reaching and grasping movements. The essence of their idea is that movements are ...
The Resting Potential II
... o permeability describes the ease with which an ion can move through the membrane o conductance describes the ability of a given ion species to carry electrical current across the membrane conductance depends on permeability, but it also depends on concentration permeability of the membrane coul ...
... o permeability describes the ease with which an ion can move through the membrane o conductance describes the ability of a given ion species to carry electrical current across the membrane conductance depends on permeability, but it also depends on concentration permeability of the membrane coul ...
Biology 218 – Human Anatomy - RIDDELL
... i. central nervous system (CNS), which consists of the brain and spinal cord ii. peripheral nervous system (PNS), which consists of [1] cranial nerves that emerge from the brain, and [2] spinal nerves that emerge from the spinal cord; the PNS contains [a] sensory or afferent neurons which transmit n ...
... i. central nervous system (CNS), which consists of the brain and spinal cord ii. peripheral nervous system (PNS), which consists of [1] cranial nerves that emerge from the brain, and [2] spinal nerves that emerge from the spinal cord; the PNS contains [a] sensory or afferent neurons which transmit n ...
Ch 7 - Nervous system
... its activity. • It signals the body through electrical impulses that communicate with the body cells. • Its signaling and responding abilities are highly specific and rapid. ...
... its activity. • It signals the body through electrical impulses that communicate with the body cells. • Its signaling and responding abilities are highly specific and rapid. ...
Central Nervous system - UPM EduTrain Interactive Learning
... Unit 1: Introduction to the Brain and Human Behaviour AIM: Explain the brain as a source of control and behaviour ...
... Unit 1: Introduction to the Brain and Human Behaviour AIM: Explain the brain as a source of control and behaviour ...
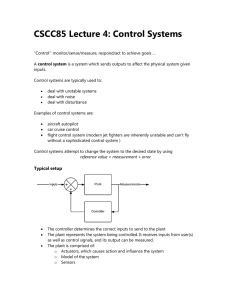
CSCC85 Lecture 4: Control Systems
... The plant represents the system being controlled. It receives inputs from user(s) as well as control signals, and its output can be measured. The plant is comprised of: o Actuators, which causes action and influence the system o Model of the system o Sensors ...
... The plant represents the system being controlled. It receives inputs from user(s) as well as control signals, and its output can be measured. The plant is comprised of: o Actuators, which causes action and influence the system o Model of the system o Sensors ...
The Nervous System
... Nervous System: Two Main Parts Part II: Peripheral Nervous System – Consist of all parts of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord – Function handles the central nervous system’s ...
... Nervous System: Two Main Parts Part II: Peripheral Nervous System – Consist of all parts of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord – Function handles the central nervous system’s ...
Ch 2 neurotrans and nervous sys
... – Involved in muscle movement and memory (undersupply - ALZ) Serotonin – Involved in mood and sleep (Undersupply - Depression) Dopamine – Involved in movement and reward systems (Excess - Schizophrenia, undersupply - Parkinson‘s ) GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) – Inhibitory NT (undersupply – seizure ...
... – Involved in muscle movement and memory (undersupply - ALZ) Serotonin – Involved in mood and sleep (Undersupply - Depression) Dopamine – Involved in movement and reward systems (Excess - Schizophrenia, undersupply - Parkinson‘s ) GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) – Inhibitory NT (undersupply – seizure ...
Biology Option Review Section E
... birth and successful survival until reproduction can occur, able to instinctively remember the beach they were born on, known as natal beaches, and travel immense distances when the time comes to lay their eggs, back to the beaches where they were born as they were able to survive themselves, thus t ...
... birth and successful survival until reproduction can occur, able to instinctively remember the beach they were born on, known as natal beaches, and travel immense distances when the time comes to lay their eggs, back to the beaches where they were born as they were able to survive themselves, thus t ...