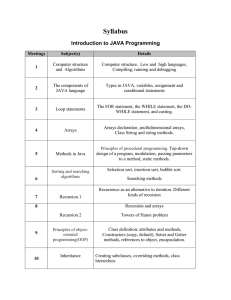
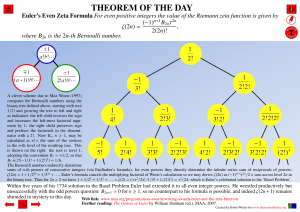
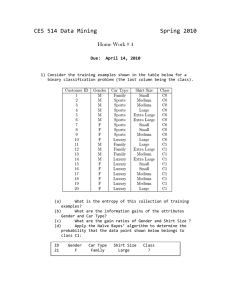
Linear Programming MSIS 651 Homework 4
... 2. AMPL project: Do problems 14.9 all parts. Then model it as an AMPL project and enter the data given at the beginning of the problem in the .dat file and solve. Report both primal and dual values in the output. 3. Does Dijkstra’s algorithm work if some arc costs are negative? Discuss your answer. ...
... 2. AMPL project: Do problems 14.9 all parts. Then model it as an AMPL project and enter the data given at the beginning of the problem in the .dat file and solve. Report both primal and dual values in the output. 3. Does Dijkstra’s algorithm work if some arc costs are negative? Discuss your answer. ...
Office of Emergency Management Mr. Andrew Mark
... • Floyd-Warshall’s Algorithm • Our Algorithm (MESA) ...
... • Floyd-Warshall’s Algorithm • Our Algorithm (MESA) ...
The Information Universe of the (Near) Future
... MaRVIN scales by: •distribution (over many nodes) •approximation (sound but incomplete) •anytime convergence (more complete over time) ...
... MaRVIN scales by: •distribution (over many nodes) •approximation (sound but incomplete) •anytime convergence (more complete over time) ...
Weekly Handout Number 1
... • Algorithm performance (The technical term is complexity) – A good algorithm implemented by a bad programmer will beat a bad algorithm implemented by a good programmer – A time function, f, of the dataset size is often used to measure effectiveness as the data set size grows. For example, f(n) <= c ...
... • Algorithm performance (The technical term is complexity) – A good algorithm implemented by a bad programmer will beat a bad algorithm implemented by a good programmer – A time function, f, of the dataset size is often used to measure effectiveness as the data set size grows. For example, f(n) <= c ...
ICDM04Stream
... Idea 1: using observable statistical traits from the model itself to guess the error on unlabeled streaming data. Idea 2: using very small number of specifically acquired examples to statistically estimate the error – similar to estimate poll to estimate Bush or Kerry will win the presidency. ...
... Idea 1: using observable statistical traits from the model itself to guess the error on unlabeled streaming data. Idea 2: using very small number of specifically acquired examples to statistically estimate the error – similar to estimate poll to estimate Bush or Kerry will win the presidency. ...
Sai-Bio
... The score can be binary, discrete or continuous Input format is flexible and allows genes to be in more than one group or cluster Thus does not exclude biclustering or ...
... The score can be binary, discrete or continuous Input format is flexible and allows genes to be in more than one group or cluster Thus does not exclude biclustering or ...
Deployment of Sensing Devices on Critical Infrastructure
... As we solve each general case in turn, we are able to solve the next-higher general case until we finally solve the most general case, the original problem. ...
... As we solve each general case in turn, we are able to solve the next-higher general case until we finally solve the most general case, the original problem. ...
Association Rule Mining in Peer-to
... For each node to maintain an assumption of the correct result Update the result whenever new data arrives Nodes compute the result through local negotiation with their immediate neighbor ...
... For each node to maintain an assumption of the correct result Update the result whenever new data arrives Nodes compute the result through local negotiation with their immediate neighbor ...