Records, Stacks and Queues
... then look for the right one, eliminate all characters in between. Cry fowl when a left parenthesis occurs again without a right one. ...
... then look for the right one, eliminate all characters in between. Cry fowl when a left parenthesis occurs again without a right one. ...
(add1 (sum 2 2))
... Just knowing the value of a purple number, like 56, doesn't tell you how it was constructed as (+ n1 n2) . There are many choices of n1 and n2 that would build 56. ...
... Just knowing the value of a purple number, like 56, doesn't tell you how it was constructed as (+ n1 n2) . There are many choices of n1 and n2 that would build 56. ...
Slide 1
... • Other data structures are: arrays, records, lists, trees, stacks, queues, etc.. • Data structures are organized similarly in all the programming languages. • The latter means that data structures can be studied independently of a particular programming language. • Knowing data structures, it is ea ...
... • Other data structures are: arrays, records, lists, trees, stacks, queues, etc.. • Data structures are organized similarly in all the programming languages. • The latter means that data structures can be studied independently of a particular programming language. • Knowing data structures, it is ea ...
Recursion
... number, the solution to the problem can be found by adding (a) the solution to the smaller subproblem of summing the squares in the range m+1:n and (b) the solution to the subproblem of finding the square of m. (a) is then solved in the same way (recursion). • We stop when we reach the base case tha ...
... number, the solution to the problem can be found by adding (a) the solution to the smaller subproblem of summing the squares in the range m+1:n and (b) the solution to the subproblem of finding the square of m. (a) is then solved in the same way (recursion). • We stop when we reach the base case tha ...
Paradigms
... • A logic program defines a set of relations. • This “knowledge” can be used in various ways by the interpreter to solve different “queries”. • In contrast, the programs in other languages • Make explicit HOW the “declarative knowledge” is used to solve the query. ...
... • A logic program defines a set of relations. • This “knowledge” can be used in various ways by the interpreter to solve different “queries”. • In contrast, the programs in other languages • Make explicit HOW the “declarative knowledge” is used to solve the query. ...
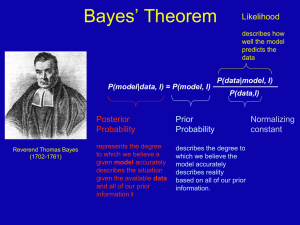
Uncertainty Exercise
... read during the past three months (including books for school). The results from those 20 students are shown below. Find the mean, median, and mode for this data. I. 2, 4, 5, 1, 3, 2, 5, 6, 1, 2, 4, 3, 6, 10, 12, 10, 2, 8, 6, 7 First, add all the numbers. Put the result here:____________ Second, div ...
... read during the past three months (including books for school). The results from those 20 students are shown below. Find the mean, median, and mode for this data. I. 2, 4, 5, 1, 3, 2, 5, 6, 1, 2, 4, 3, 6, 10, 12, 10, 2, 8, 6, 7 First, add all the numbers. Put the result here:____________ Second, div ...
Section CS1.1-Types_Identifiers handout
... a single-precision 32-bit IEEE 754 floating point (-3.4x1038 to 3.4x1038 approximately) a double-precision 64-bit IEEE 754 floating point (-1.8x10308 to 1.8x10308 approximately) true or false Unicode character set (includes ASCII) ...
... a single-precision 32-bit IEEE 754 floating point (-3.4x1038 to 3.4x1038 approximately) a double-precision 64-bit IEEE 754 floating point (-1.8x10308 to 1.8x10308 approximately) true or false Unicode character set (includes ASCII) ...
Structure & Interpretation of Computer Programs
... Unlike C++ and Java, scheme does not worry about types! Don't ...
... Unlike C++ and Java, scheme does not worry about types! Don't ...
Abstract Data Type
... When realized in a computer program, the ADT is represented by an interface, which shields a corresponding implementation. ...
... When realized in a computer program, the ADT is represented by an interface, which shields a corresponding implementation. ...
Abstract Data Type
... When realized in a computer program, the ADT is represented by an interface, which shields a corresponding implementation. ...
... When realized in a computer program, the ADT is represented by an interface, which shields a corresponding implementation. ...
CRR and American Options1
... Implement in Python the Binomial model (CoxRoss-Rubenstein) and calculate the price as function of time to maturity and strike and show in a graph how the solution converge to the ...
... Implement in Python the Binomial model (CoxRoss-Rubenstein) and calculate the price as function of time to maturity and strike and show in a graph how the solution converge to the ...
COS_470-Practice-Week_05YanaAleksieva
... 1. Create a recursive LISP function named insert1 that will insert a number num into a sorted in increasing order list of numbers nums (defun insert1 (num nums) ;; num is a number ;; nums is a list of numbers (sorted in increasing order) (if (or (null nums) (<= num(car nums))) (cons num nums) ...
... 1. Create a recursive LISP function named insert1 that will insert a number num into a sorted in increasing order list of numbers nums (defun insert1 (num nums) ;; num is a number ;; nums is a list of numbers (sorted in increasing order) (if (or (null nums) (<= num(car nums))) (cons num nums) ...