EP-307 Introduction to Quantum Mechanics
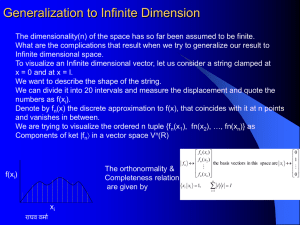
... Generalization to Infinite Dimension The dimensionality(n) of the space has so far been assumed to be finite. What are the complications that result when we try to generalize our result to Infinite dimensional space. To visualize an Infinite dimensional vector, let us consider a string clamped at x ...
... Generalization to Infinite Dimension The dimensionality(n) of the space has so far been assumed to be finite. What are the complications that result when we try to generalize our result to Infinite dimensional space. To visualize an Infinite dimensional vector, let us consider a string clamped at x ...
Functions and Algorithms
... 1.1. Functions “map” one object to another object. The objects can be anything, e.g. numbers, sets, or cities. We will concentrate on integers. 1.2. Algorithms are finite, step-by-step, lists of well defined steps to solve a problem. The problem can be from any subject, but again we will concentrate ...
... 1.1. Functions “map” one object to another object. The objects can be anything, e.g. numbers, sets, or cities. We will concentrate on integers. 1.2. Algorithms are finite, step-by-step, lists of well defined steps to solve a problem. The problem can be from any subject, but again we will concentrate ...
Keynote Presentation: Retrieve Form for Data-Capture (RFD): an Integration Profile to Enable EHR Capture of Clinical Trial Data
... agency to surface data-capture forms within an Electronic Health Record (EHR). When applied to the clinical research realm, RFD offers an elegant, straightforward solution to the problem of capturing clinical research data inside of an EHR. A handful of thought-leading pharmaceutical companies and t ...
... agency to surface data-capture forms within an Electronic Health Record (EHR). When applied to the clinical research realm, RFD offers an elegant, straightforward solution to the problem of capturing clinical research data inside of an EHR. A handful of thought-leading pharmaceutical companies and t ...
DFS_1_Introduction
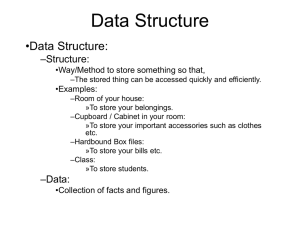
... •The advantages of, –Storing the same data in a computer than, –Storing in a physical file / physical world. ...
... •The advantages of, –Storing the same data in a computer than, –Storing in a physical file / physical world. ...
Recursion and Implementation of Functions
... • Allocated when function or compound statement is entered • Released when function or compound statement is exited • Values are not retained from one call to next (or among recursions) CS-2303, C-Term 2010 ...
... • Allocated when function or compound statement is entered • Released when function or compound statement is exited • Values are not retained from one call to next (or among recursions) CS-2303, C-Term 2010 ...
Coach - Computer Science and Engineering
... The program targets research equipment for multiinvestigator teams doing experimental computer science - typically fund 4-5 US universities each ...
... The program targets research equipment for multiinvestigator teams doing experimental computer science - typically fund 4-5 US universities each ...
Recursive Equation Solving with Excel
... Figure 5: The secant algorithm is implemented in Excel, taking advantage of the recursive calculation option. At left, we enter the formulas described in the text. At the middle, we create a circular reference by making the contents of cell B2 equal to “=B8” or “=x_new” (the cell B8 is labeled ...
... Figure 5: The secant algorithm is implemented in Excel, taking advantage of the recursive calculation option. At left, we enter the formulas described in the text. At the middle, we create a circular reference by making the contents of cell B2 equal to “=B8” or “=x_new” (the cell B8 is labeled ...
Document
... Enhanced apply-to-all • αf applies f to each element of a list • Called apply-to-all • apply-to-all1 applies a dyadic function (two arguments) to a fixed object and a list of objects • apply-to-all2 applies a dyadic function to a pair of equal length lists ...
... Enhanced apply-to-all • αf applies f to each element of a list • Called apply-to-all • apply-to-all1 applies a dyadic function (two arguments) to a fixed object and a list of objects • apply-to-all2 applies a dyadic function to a pair of equal length lists ...