Self Modifying Cartesian Genetic Programming: Finding algorithms
... that indicate the location in the graph where the node takes its inputs from. However SMCGP also has three real-valued genes which encode parameters that may be required for the function (primarily self modification (SM) functions use these and in many cases they are truncated to integers when neces ...
... that indicate the location in the graph where the node takes its inputs from. However SMCGP also has three real-valued genes which encode parameters that may be required for the function (primarily self modification (SM) functions use these and in many cases they are truncated to integers when neces ...
C++ Classes and Data Structures
... – A problem solution is a program consisting of a system of interacting classes of objects • Each object has characteristics and behaviors related to the solution • A class is a set of objects having the same type ...
... – A problem solution is a program consisting of a system of interacting classes of objects • Each object has characteristics and behaviors related to the solution • A class is a set of objects having the same type ...
solutions - MathsGeeks
... b) This is asking for a comment on skewness. Carry out and and as the data is positively skewed. This can clearly be seen by the the box plot i.e. the line is left of centre. c) The data is positively skewed so most delays are small and there are infrequent longer delays. Most passengers would be re ...
... b) This is asking for a comment on skewness. Carry out and and as the data is positively skewed. This can clearly be seen by the the box plot i.e. the line is left of centre. c) The data is positively skewed so most delays are small and there are infrequent longer delays. Most passengers would be re ...
Domain Knowledge and its Impact on Analytics
... was built and delivered great gains where cost per new customer in the top decile was one fifth of the cost per new customer in the bottom decile. These type of results can be expected in models that are developed for existing customers where we have much more and richer type data. But with acquisit ...
... was built and delivered great gains where cost per new customer in the top decile was one fifth of the cost per new customer in the bottom decile. These type of results can be expected in models that are developed for existing customers where we have much more and richer type data. But with acquisit ...
Some “facts” about software…
... • Significantly cheaper than RAM since it lacks versatility • How does the data get in there? – Mask programming – data is programmed in at the time of silicon fabrication – PROM – special programming devices allow the user to write data one time – EPROM – data is erased under ultra-violet light or ...
... • Significantly cheaper than RAM since it lacks versatility • How does the data get in there? – Mask programming – data is programmed in at the time of silicon fabrication – PROM – special programming devices allow the user to write data one time – EPROM – data is erased under ultra-violet light or ...
trick-or-treat.pdf
... set error always go to zero? If a neural net with 2^N hidden units is trained on the same training set, will the training set error always go to zero? Explain your reasoning? (4) Derive backprop for just the output unit of a neural net trained with −1*[target*log(output) + (1−target)*log(1−output)] ...
... set error always go to zero? If a neural net with 2^N hidden units is trained on the same training set, will the training set error always go to zero? Explain your reasoning? (4) Derive backprop for just the output unit of a neural net trained with −1*[target*log(output) + (1−target)*log(1−output)] ...
Metody Inteligencji Obliczeniowej
... Conclusion: separability in the hidden space is perhaps too much to desire ... inspection of clusters is sufficient for perfect classification; add second Gaussian layer to capture this activity; train second RBF on the data (stacking), reducing number of clusters. ...
... Conclusion: separability in the hidden space is perhaps too much to desire ... inspection of clusters is sufficient for perfect classification; add second Gaussian layer to capture this activity; train second RBF on the data (stacking), reducing number of clusters. ...
Document
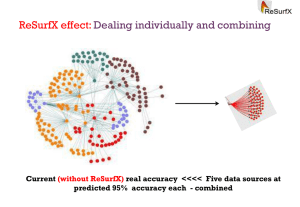
... indicates that most Rosetta specific genes are false positives. These are either what is estimated to be below the sensitivity of the technology with this number of replicates by ReSurfX, or errored due to other limitations. ...
... indicates that most Rosetta specific genes are false positives. These are either what is estimated to be below the sensitivity of the technology with this number of replicates by ReSurfX, or errored due to other limitations. ...
python-example
... list of mixed integers and strings. The integers are to be sorted in order The strings are to be sorted in order With the constraint that integers appear where integers were in the original list, and strings appear where strings appeared in the original list. ...
... list of mixed integers and strings. The integers are to be sorted in order The strings are to be sorted in order With the constraint that integers appear where integers were in the original list, and strings appear where strings appeared in the original list. ...
review1
... double max = _________; for (int i = 0; i < __________; ++i) if (________________) max = a[i]; 6. A recursive binary search algorithm always reduces the problem size by how much at each recursive call? For example, how many searches are needed if the array size is 128? How likely is it that we will ...
... double max = _________; for (int i = 0; i < __________; ++i) if (________________) max = a[i]; 6. A recursive binary search algorithm always reduces the problem size by how much at each recursive call? For example, how many searches are needed if the array size is 128? How likely is it that we will ...
Database Security
... important. • Basic techniques – using “atomic operation” > Read-then-(if OK)Write: A Write query to a field is conditioned on its current contents being as specified (in case it was modified recently by someone else) ...
... important. • Basic techniques – using “atomic operation” > Read-then-(if OK)Write: A Write query to a field is conditioned on its current contents being as specified (in case it was modified recently by someone else) ...