Solenoids
... 3. Your thumb gives the direction of the magnetic field in the center of the loop, where it is straight. 4. Field lines curve around and make complete loops. ...
... 3. Your thumb gives the direction of the magnetic field in the center of the loop, where it is straight. 4. Field lines curve around and make complete loops. ...
angle of inclination
... Because of the relationship between the angle of inclination and the latitude on the Earth’s surface where an Fe-rich rock formed, we can use this information to determine the “paleolatitude” for an iron-rich rock. British geophysicists measured the angles of inclination of Ferich rocks of a wide r ...
... Because of the relationship between the angle of inclination and the latitude on the Earth’s surface where an Fe-rich rock formed, we can use this information to determine the “paleolatitude” for an iron-rich rock. British geophysicists measured the angles of inclination of Ferich rocks of a wide r ...
Problems for week 8
... k ) m/s through a region where both a uniform magnetic field and a uniform electric field exist. (a) Calculate the total force on the moving ...
... k ) m/s through a region where both a uniform magnetic field and a uniform electric field exist. (a) Calculate the total force on the moving ...
untitled text
... Department of Medicinal & Applied Chemistry, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung 80708, Taiwan ...
... Department of Medicinal & Applied Chemistry, Kaohsiung Medical University, Kaohsiung 80708, Taiwan ...
Metallic thin films possess unique magnetic properties, which is
... Metallic thin films possess unique magnetic properties, which is absent in their bulkier form. Through studying the hysteresis curves, which records the change of the magnetization of the sample with a changing external magnetic field, it is observed that the samples have different values of magneti ...
... Metallic thin films possess unique magnetic properties, which is absent in their bulkier form. Through studying the hysteresis curves, which records the change of the magnetization of the sample with a changing external magnetic field, it is observed that the samples have different values of magneti ...
magnetism electricity test review
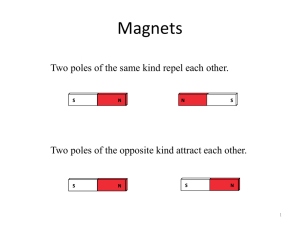
... Magnetism Poles, magnetic field lines, attraction, repulsion, geographic poles, magnetic poles, magnetic domains, electromagnet, magnetic force and distance, “soft” iron, ...
... Magnetism Poles, magnetic field lines, attraction, repulsion, geographic poles, magnetic poles, magnetic domains, electromagnet, magnetic force and distance, “soft” iron, ...
Sample Quizzes Physics 132
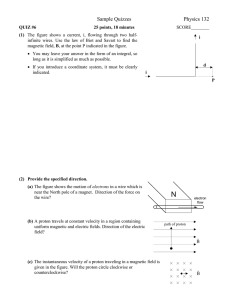
... (1) The figure shows a current, i, flowing through two halfinfinite wires. Use the law of Biot and Savart to find the magnetic field, B, at the point P indicated in the figure. ...
... (1) The figure shows a current, i, flowing through two halfinfinite wires. Use the law of Biot and Savart to find the magnetic field, B, at the point P indicated in the figure. ...
Magnetic Storms Video Note Skeleton
... Scientists found more and more reversals, On average 1 reversal every 200 thous years. Whenever the earth’s magnet field reversed direction, the magnetic intensity was very weak. Beneath the south atlantic, Jeremy has found clear evidence for a region of magnetic anomalies places where the field has ...
... Scientists found more and more reversals, On average 1 reversal every 200 thous years. Whenever the earth’s magnet field reversed direction, the magnetic intensity was very weak. Beneath the south atlantic, Jeremy has found clear evidence for a region of magnetic anomalies places where the field has ...
Magnetism Word List
... An object that attracts magnetic materials and attracts and repels other magnets Magnetic material A material that is attracted to a magnet Iron A magnetic element Cobalt A magnetic element Nickel A magnetic element Steel A material containing iron, which causes it to be a magnetic material Magnetis ...
... An object that attracts magnetic materials and attracts and repels other magnets Magnetic material A material that is attracted to a magnet Iron A magnetic element Cobalt A magnetic element Nickel A magnetic element Steel A material containing iron, which causes it to be a magnetic material Magnetis ...
Magnetic Forces
... that of a giant bar magnet. The solar wind warps this base field into a slightly different shape. However, in either case, Earth's magnetic field lines come together at the planet's poles... which is why compasses work, and is also why the aurora are most frequently seen near the North and South Pol ...
... that of a giant bar magnet. The solar wind warps this base field into a slightly different shape. However, in either case, Earth's magnetic field lines come together at the planet's poles... which is why compasses work, and is also why the aurora are most frequently seen near the North and South Pol ...
Earth's magnetic field

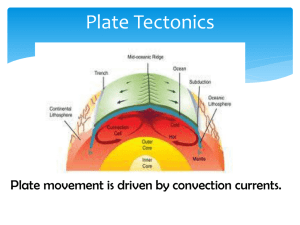
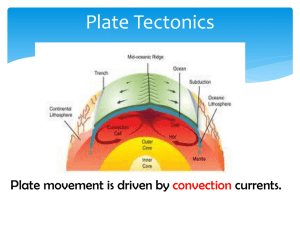
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. Its magnitude at the Earth's surface ranges from 25 to 65 microteslas (0.25 to 0.65 gauss). Roughly speaking it is the field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 10 degrees with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the center of the Earth. Unlike a bar magnet, however, Earth's magnetic field changes over time because it is generated by a geodynamo (in Earth's case, the motion of molten iron alloys in its outer core).The North and South magnetic poles wander widely, but sufficiently slowly for ordinary compasses to remain useful for navigation. However, at irregular intervals averaging several hundred thousand years, the Earth's field reverses and the North and South Magnetic Poles relatively abruptly switch places. These reversals of the geomagnetic poles leave a record in rocks that are of value to paleomagnetists in calculating geomagnetic fields in the past. Such information in turn is helpful in studying the motions of continents and ocean floors in the process of plate tectonics.The magnetosphere is the region above the ionosphere and extends several tens of thousands of kilometers into space, protecting the Earth from the charged particles of the solar wind and cosmic rays that would otherwise strip away the upper atmosphere, including the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.