Standard EPS Shell Presentation
... A compass does NOT pt. directly to the geo. N pole, but near it. It will always be slightly E or W of the G N Pole. ( mag. S. P is about 600 miles( 1000 km) from GNP). Magnetic Declination. The difference between the direction the needle points, and True G North, is called You can measure the “angl ...
... A compass does NOT pt. directly to the geo. N pole, but near it. It will always be slightly E or W of the G N Pole. ( mag. S. P is about 600 miles( 1000 km) from GNP). Magnetic Declination. The difference between the direction the needle points, and True G North, is called You can measure the “angl ...
Document
... although certain isotopes of many other elements nuclei can also be observed. NMR studies a magnetic nucleus, like that of a hydrogen atom (protium being the most receptive isotope at natural abundance) by aligning it with a very powerful external magnetic field and perturbing this alignment using a ...
... although certain isotopes of many other elements nuclei can also be observed. NMR studies a magnetic nucleus, like that of a hydrogen atom (protium being the most receptive isotope at natural abundance) by aligning it with a very powerful external magnetic field and perturbing this alignment using a ...
chapter24a - Interactive Learning Toolkit
... domains of the material. A magnetic field can force the domains to line up, and the material itself can become magnetic. (Ex: iron, nickel, cobalt, steel) Paramagnetic materials are weakly attracted to magnets. The atoms of these substances contain electrons most of which spin in the same direction, ...
... domains of the material. A magnetic field can force the domains to line up, and the material itself can become magnetic. (Ex: iron, nickel, cobalt, steel) Paramagnetic materials are weakly attracted to magnets. The atoms of these substances contain electrons most of which spin in the same direction, ...
Electromagnetism is the interaction between electricity and
... An electromagnet is made up of a solenoid wrapped around an iron core. The magnetic field of a solenoid makes the domains inside the iron core line up. The magnetic field of the electromagnet is the field of the solenoid plus the field of the magnetized core. As a result, the magnetic field of an el ...
... An electromagnet is made up of a solenoid wrapped around an iron core. The magnetic field of a solenoid makes the domains inside the iron core line up. The magnetic field of the electromagnet is the field of the solenoid plus the field of the magnetized core. As a result, the magnetic field of an el ...
Chapter 27 Questions
... 10. A singly charged positive ion has a mass of 3.2 x10-26 kg. After being accelerated through a potential difference of 833 V, the ion enters a magnetic field of 0.92 T along a direction perpendicular to the direction of the field. Calculate the radius of the path of the ion in the field. 11. A co ...
... 10. A singly charged positive ion has a mass of 3.2 x10-26 kg. After being accelerated through a potential difference of 833 V, the ion enters a magnetic field of 0.92 T along a direction perpendicular to the direction of the field. Calculate the radius of the path of the ion in the field. 11. A co ...
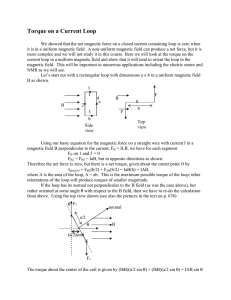
Torque on a Current Loop
... oriented in space. Quantum mechanics tells us that when placed in a magnetic field the nucleus will experience a torque due to the interaction of the magnetic dipole with the external magnetic field and this will result in two possible orientations of the nuclear magnetic dipole, said to be spin up ...
... oriented in space. Quantum mechanics tells us that when placed in a magnetic field the nucleus will experience a torque due to the interaction of the magnetic dipole with the external magnetic field and this will result in two possible orientations of the nuclear magnetic dipole, said to be spin up ...
SPH 3U(G) TEST
... Which statement about the magnetic north pole of Earth is true? a. Its location never changes. b. It corresponds to the N-pole of a bar magnet. c. It is at the same location as the geographic north pole of Earth. d. It corresponds to the S-pole of a bar magnet. e. both A and D ...
... Which statement about the magnetic north pole of Earth is true? a. Its location never changes. b. It corresponds to the N-pole of a bar magnet. c. It is at the same location as the geographic north pole of Earth. d. It corresponds to the S-pole of a bar magnet. e. both A and D ...
Chapter-36-four-square-questions_-answer
... Q4: What is a magnetic field? What are magnetic field lines? A magnetic field is the space around a magnet where a magnetic force is exerted. Magnetic field lines are lines that are drawn to represent the magnetic field. Q5: What is the direction of the magnetic field outside a magnet? How does how ...
... Q4: What is a magnetic field? What are magnetic field lines? A magnetic field is the space around a magnet where a magnetic force is exerted. Magnetic field lines are lines that are drawn to represent the magnetic field. Q5: What is the direction of the magnetic field outside a magnet? How does how ...
Section 17.1 - CPO Science
... 17.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
... 17.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
Magnetism 17.1 Properties of Magnets 17.2 Electromagnets 17.3
... 17.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
... 17.1 Declination and “true north” Because Earth’s geographic north pole (true north) and magnetic south pole are not located at the exact same place, a compass will not point directly to the geographic north pole. ...
Al-Balqa Applied University
... Evaluation of students’ performance (final grade) will be based on the following three categories: Exams. Two in-class exams will be given. Each will cover about 40% of lectures Final Exam: The final exam will cover all the class material. Allocation of Marks Exam I Exam II Participation and act ...
... Evaluation of students’ performance (final grade) will be based on the following three categories: Exams. Two in-class exams will be given. Each will cover about 40% of lectures Final Exam: The final exam will cover all the class material. Allocation of Marks Exam I Exam II Participation and act ...
Unpacking Outcomes - NESD Curriculum Corner
... plates separated by a distance. Examine how the electric field strength at a point varies according to the inverse square of the distance between two charges Solve problems related to Coulomb’s Law including electrostatic equilibrium in one-and two-dimensions. Represent magnetic fields using magneti ...
... plates separated by a distance. Examine how the electric field strength at a point varies according to the inverse square of the distance between two charges Solve problems related to Coulomb’s Law including electrostatic equilibrium in one-and two-dimensions. Represent magnetic fields using magneti ...
Earth's magnetic field

Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. Its magnitude at the Earth's surface ranges from 25 to 65 microteslas (0.25 to 0.65 gauss). Roughly speaking it is the field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 10 degrees with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the center of the Earth. Unlike a bar magnet, however, Earth's magnetic field changes over time because it is generated by a geodynamo (in Earth's case, the motion of molten iron alloys in its outer core).The North and South magnetic poles wander widely, but sufficiently slowly for ordinary compasses to remain useful for navigation. However, at irregular intervals averaging several hundred thousand years, the Earth's field reverses and the North and South Magnetic Poles relatively abruptly switch places. These reversals of the geomagnetic poles leave a record in rocks that are of value to paleomagnetists in calculating geomagnetic fields in the past. Such information in turn is helpful in studying the motions of continents and ocean floors in the process of plate tectonics.The magnetosphere is the region above the ionosphere and extends several tens of thousands of kilometers into space, protecting the Earth from the charged particles of the solar wind and cosmic rays that would otherwise strip away the upper atmosphere, including the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.