nervous-system-terms
... Pick up messages from other cells and convey that information to the cell body. (Looks like branches around the cell) ...
... Pick up messages from other cells and convey that information to the cell body. (Looks like branches around the cell) ...
Neuron Structure
... – longest cytoplasmic extension from cell body – 100 axons could fit into typical human hair ...
... – longest cytoplasmic extension from cell body – 100 axons could fit into typical human hair ...
Nervous - Lamont High
... – longest cytoplasmic extension from cell body – 100 axons could fit into typical human hair ...
... – longest cytoplasmic extension from cell body – 100 axons could fit into typical human hair ...
The Nervous system
... another cell = synapse • The synapse is a small gap that separates the axon terminal from the dendrites of the next neuron or another cell • The terminals contain tiny sacs or vesicles filled with neurotransmitters = chemicals used by a neuron to transmit an impulse across a synapse • The impulse wi ...
... another cell = synapse • The synapse is a small gap that separates the axon terminal from the dendrites of the next neuron or another cell • The terminals contain tiny sacs or vesicles filled with neurotransmitters = chemicals used by a neuron to transmit an impulse across a synapse • The impulse wi ...
Synapse
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
... Interferes with homeostasis (temp.) Feel depressed until body makes enough of its own serotonin to feel ‘normal’ again Destroys serotonin neurons axons and terminals After exposure to MDMA for 4 days, it takes more than 7 years for your brain to recover. ...
Anatomy of the Basal Ganglia
... eye movements. Types of Neurons in the Striatum Medium spiny neurons—make up 95% of the total. Use GABA as a transmitter. Are the output neurons of the striatum. Large aspiny neurons—interneurons that use ACh as a transmitter. Medium aspiny cells—interneurons that use somatostatin as a neurotransmit ...
... eye movements. Types of Neurons in the Striatum Medium spiny neurons—make up 95% of the total. Use GABA as a transmitter. Are the output neurons of the striatum. Large aspiny neurons—interneurons that use ACh as a transmitter. Medium aspiny cells—interneurons that use somatostatin as a neurotransmit ...
Biopsychology
... Shows what behaviors(/cognitions) occur if we stimulate or damage (lesion) a particular area of the brain. Electroencephalogram (EEG) & Evoked Potentials The EEG measures the brain's electrical activity using electrodes placed on the scalp. Indicates a person’s state of arousal. The Evoked Pot ...
... Shows what behaviors(/cognitions) occur if we stimulate or damage (lesion) a particular area of the brain. Electroencephalogram (EEG) & Evoked Potentials The EEG measures the brain's electrical activity using electrodes placed on the scalp. Indicates a person’s state of arousal. The Evoked Pot ...
PPT
... to cut the corpus callosum, which is the main connection between the hemispheres, in order to limit the spreading of epileptic activity. These split-brain patients typically behaved and felt like healthy people in everyday life situations. In laboratory experiments, however, the consequences of the ...
... to cut the corpus callosum, which is the main connection between the hemispheres, in order to limit the spreading of epileptic activity. These split-brain patients typically behaved and felt like healthy people in everyday life situations. In laboratory experiments, however, the consequences of the ...
Nervous System Cells
... • Neurons can be classified according to the direction in which they conduct impulses • Afferent neurons – transmit to the spinal cord or brain • Efferent neurons – transmit away from the brain or spinal cord ...
... • Neurons can be classified according to the direction in which they conduct impulses • Afferent neurons – transmit to the spinal cord or brain • Efferent neurons – transmit away from the brain or spinal cord ...
Using the State-Space Paradigm to Analyze Information Representation in Neural Systems
... point process nature of neural encoding. The advent in the last 10 years of the capability to record with multiple electrode arrays the simultaneous spiking activity of many neurons (¿100) has made it possible to study information encoding by ensembles rather than by simply single neurons. Hence, an ...
... point process nature of neural encoding. The advent in the last 10 years of the capability to record with multiple electrode arrays the simultaneous spiking activity of many neurons (¿100) has made it possible to study information encoding by ensembles rather than by simply single neurons. Hence, an ...
Peripheral Nerve Repair
... •crucial for human movement and function • Highway for information processing and response •Sensory Neurons- send stimulation information from senses to the brain. • Motor Neurons- send commands from the brain to muscles or other organs ...
... •crucial for human movement and function • Highway for information processing and response •Sensory Neurons- send stimulation information from senses to the brain. • Motor Neurons- send commands from the brain to muscles or other organs ...
biological persp
... All that is psychological is first physiologicalreductionist! All behavior has a cause – deterministic! Psychology should investigate the brain, neurochemistry and genetics ...
... All that is psychological is first physiologicalreductionist! All behavior has a cause – deterministic! Psychology should investigate the brain, neurochemistry and genetics ...
Neuron Summary - MsHughesPsychology
... 1. Dendrite – a specialised, short, thin and widely branching fibre that is specialised to detect and receive incoming neural information (neural impulses) 2. Soma – cell body, the section that determines whether the neuron will be activated and thus transmit (pass on) the neural stimulation to othe ...
... 1. Dendrite – a specialised, short, thin and widely branching fibre that is specialised to detect and receive incoming neural information (neural impulses) 2. Soma – cell body, the section that determines whether the neuron will be activated and thus transmit (pass on) the neural stimulation to othe ...
The Nervous System: Overview The nervous system Divisions of the
... The somatic nervous system is associated with conscious processes, and contains two types of neuron: Motor neurons Sensory neurons ...
... The somatic nervous system is associated with conscious processes, and contains two types of neuron: Motor neurons Sensory neurons ...
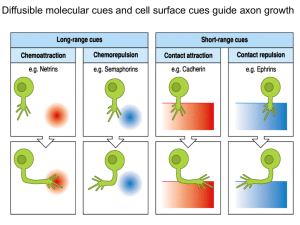
Option A Neural Development Study Guide A1 A2
... State when neural tube development begins in a human embryo: How do immature neurons reach their final location? ...
... State when neural tube development begins in a human embryo: How do immature neurons reach their final location? ...
Chapter 2 quiz level - easy topic: neurons
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) There are approximately ________ neurons in the brain of an average human being. A) 100 million B) 100 trillion C) 100 billion D) 100 thousand ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) There are approximately ________ neurons in the brain of an average human being. A) 100 million B) 100 trillion C) 100 billion D) 100 thousand ...
ppt - UTK-EECS
... One argument: Instead of understanding the human brain, we understand the computer. Therefore, NN dies out in 70s. 1980s, Japan started “the fifth generation computer research project”, namely, “knowledge information processing computer system”. The project aims to improve logical reasoning to reach ...
... One argument: Instead of understanding the human brain, we understand the computer. Therefore, NN dies out in 70s. 1980s, Japan started “the fifth generation computer research project”, namely, “knowledge information processing computer system”. The project aims to improve logical reasoning to reach ...
Action potential - Solon City Schools
... – Neurotransmitters cross synapse: different ones send different impulses and need to find receptors – It can either excite (fire) or inhibit (prevent firing) ...
... – Neurotransmitters cross synapse: different ones send different impulses and need to find receptors – It can either excite (fire) or inhibit (prevent firing) ...
Optical Stimulation of Engram-bearing Cells
... Here we have shown that optical activation of hippocampal cells that were active during fear conditioning is sufficient to elicit freezing behavior. Our results argue that defined cell populations can form a cellular basis for fear memory engrams. The memory engram that we selectively labeled and ma ...
... Here we have shown that optical activation of hippocampal cells that were active during fear conditioning is sufficient to elicit freezing behavior. Our results argue that defined cell populations can form a cellular basis for fear memory engrams. The memory engram that we selectively labeled and ma ...
Q1 (from chapter 1)
... A. Lobotomy causes drastic changes in personality and comportment B. Major motor and sensory pathways cross sides C. Bilateral hippocampectomy causes global aphasia D. In most people the left hemisphere is dominant for language abilities E. Orbitofrontal cortex is responsible for social behavior Q2 ...
... A. Lobotomy causes drastic changes in personality and comportment B. Major motor and sensory pathways cross sides C. Bilateral hippocampectomy causes global aphasia D. In most people the left hemisphere is dominant for language abilities E. Orbitofrontal cortex is responsible for social behavior Q2 ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.