Answer - Imagine School at Lakewood Ranch
... Explore online information about the information introduced in this chapter. Click on the Connect button to launch your browser and go to the Mathematics: Applications and Concepts, Course 2 Web site. At this site, you will find extra examples for each lesson in the Student Edition of your textboo ...
... Explore online information about the information introduced in this chapter. Click on the Connect button to launch your browser and go to the Mathematics: Applications and Concepts, Course 2 Web site. At this site, you will find extra examples for each lesson in the Student Edition of your textboo ...
MA 3330 Practice Final Answers in red Name April 24, 2009 1. True
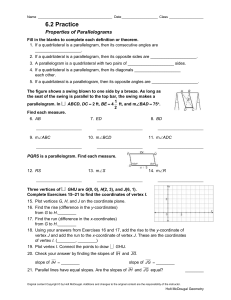
... In the Figure for Problem 7, show how you would construct two triangles which have the same angle sum as 4ABC and at least one of the triangles has an angle that is less than or equal to one-fourth of ∠A. Draw two separate pictures below, clearly indicating how the construction was done. In other wo ...
... In the Figure for Problem 7, show how you would construct two triangles which have the same angle sum as 4ABC and at least one of the triangles has an angle that is less than or equal to one-fourth of ∠A. Draw two separate pictures below, clearly indicating how the construction was done. In other wo ...
Warm-Up Exercises
... The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°. THEOREM 4.2: Exterior Angle Theorem The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two nonadjacent interior angles. ...
... The sum of the measures of the interior angles of a triangle is 180°. THEOREM 4.2: Exterior Angle Theorem The measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two nonadjacent interior angles. ...
Achievement Standard 2.2
... Trig graphs with up to two transformations (eg: y = Asin Bx, or y = A sin (x - C) or y = sin(Bx – C) ) using either degrees or radians Write the equation of a function (from the achieved section) if given the graph (problems may be in context) ...
... Trig graphs with up to two transformations (eg: y = Asin Bx, or y = A sin (x - C) or y = sin(Bx – C) ) using either degrees or radians Write the equation of a function (from the achieved section) if given the graph (problems may be in context) ...
Honors Geometry Unit #3 Lesson #1 Parallel Lines – are coplanar
... same-side interior angles are supplementary. (Theorem) same-side exterior angles are supplementary. (Theorem) How do we know that lines are parallel (when we don’t know their slopes?)? If any of the above angle relationships are true, then the lines are parallel! This means that lines are parall ...
... same-side interior angles are supplementary. (Theorem) same-side exterior angles are supplementary. (Theorem) How do we know that lines are parallel (when we don’t know their slopes?)? If any of the above angle relationships are true, then the lines are parallel! This means that lines are parall ...
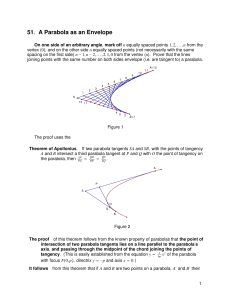
51. A Parabola as an Envelope
... SB at A and B. (The reader can use analytic geometry, for instance, to show that a unique such parabola exists.) The tangent line joining the point P numbered 7 on SA SP BQ meets the other side in a point Q so that PA by Apollonius’ Theorem. But QS SP v n"v , and it follows that Q is the point o ...
... SB at A and B. (The reader can use analytic geometry, for instance, to show that a unique such parabola exists.) The tangent line joining the point P numbered 7 on SA SP BQ meets the other side in a point Q so that PA by Apollonius’ Theorem. But QS SP v n"v , and it follows that Q is the point o ...
Steinitz's theorem

In polyhedral combinatorics, a branch of mathematics, Steinitz's theorem is a characterization of the undirected graphs formed by the edges and vertices of three-dimensional convex polyhedra: they are exactly the (simple) 3-vertex-connected planar graphs (with at least four vertices). That is, every convex polyhedron forms a 3-connected planar graph, and every 3-connected planar graph can be represented as the graph of a convex polyhedron. For this reason, the 3-connected planar graphs are also known as polyhedral graphs. Steinitz's theorem is named after Ernst Steinitz, who submitted its first proof for publication in 1916. Branko Grünbaum has called this theorem “the most important and deepest known result on 3-polytopes.”The name ""Steinitz's theorem"" has also been applied to other results of Steinitz: the Steinitz exchange lemma implying that each basis of a vector space has the same number of vectors, the theorem that if the convex hull of a point set contains a unit sphere, then the convex hull of a finite subset of the point contains a smaller concentric sphere, and Steinitz's vectorial generalization of the Riemann series theorem on the rearrangements of conditionally convergent series.↑ ↑ 2.0 2.1 ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑