* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Inscribed-Angles-Notes-12.3
Survey
Document related concepts
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Steinitz's theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Area of a circle wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
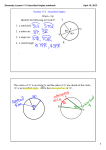
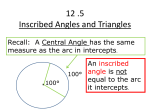
Geometry Inscribed Angle Activity Date: _________ In the next section, we are going to look at angles inscribed in circles. There are two kids of angles that can be inscribed in a circle: * An angle whose vertex is AT the center of the circle * An angle whose vertex is ON the circle. 1. a) AXB _____ 1 _____ 2 _____ 3 _____ m Arc AB _____ 2. a) 4 _____ 5 _____ 6 _____ b) Conjecture: b) Conjecture: c) Conjecture: In conclusion: Geometry Inscribed Angles Notes Date: _____________ Objective 1: I can find the measure of an inscribed angle. Let’s recap the activity: Below, the vertex of _____ is on ________, and the sides of ______ are _______ of the circle. ______ is an _________________. _____ is the ____________________ of _____. Theorem 4 describes the relationship between an inscribed angle and its intercepted arc. Theorem 4: Inscribed Angle Theorem The measure of an inscribed angle is _________________________ of its intercepted arc. There are three different ways that an angle can be inscribed inside of a circle. I. II. III. Regardless of where the center of the circle is located, you will still use Theorem 4 to find the measure of inscribed angles. Example 1: Use Theorem 4 to find the measure of inscribed angles. A) Find the values of a and b. B) Use the diagram above and find mPQR if m Arc RS = 60 . C) Find the values of x and y in the circle below. These corollaries below will help you find the measures of angles in circles. Corollaries to the Inscribed Angle Theorem (theorem 4): (1) Two inscribed angles that intercept (2) An angle inscribed in a semicircle the same arc are ________________. is a ___________________. Example 2: Use the above corollaries to find the measure of the numbered angles. A) B) C) Find the values of a and b. D) Find the value of x.