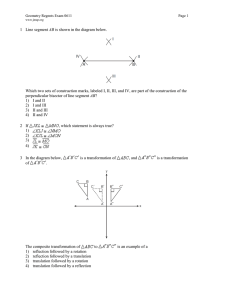
Class Notes Regents Review
... Ex: If a full circle has 360, then a straight angle has 180. T then T is TRUE Ex: If the sum of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360, then the sum of the interior angles of an octagon is 720. T then F is FALSE Ex: If the sum of the interior angles of an octagon is 720, then the sum of ...
... Ex: If a full circle has 360, then a straight angle has 180. T then T is TRUE Ex: If the sum of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is 360, then the sum of the interior angles of an octagon is 720. T then F is FALSE Ex: If the sum of the interior angles of an octagon is 720, then the sum of ...
2-1
... Check It Out! Example 3 Make a conjecture about the lengths of male and female whales based on the data. Average Whale Lengths Length of Female (ft) ...
... Check It Out! Example 3 Make a conjecture about the lengths of male and female whales based on the data. Average Whale Lengths Length of Female (ft) ...
Unit 1 Review
... ____ 26. given three points A, B, and C, B is between A and C if and only if all three of the points lie on the same line, and AB + BC = AC ____ 27. a plane that is divided into four regions by a horizontal line called the x-axis and a vertical line called the y-axis. ____ 28. a number used to ident ...
... ____ 26. given three points A, B, and C, B is between A and C if and only if all three of the points lie on the same line, and AB + BC = AC ____ 27. a plane that is divided into four regions by a horizontal line called the x-axis and a vertical line called the y-axis. ____ 28. a number used to ident ...
Congruent Triangles
... A. COORDINATE GEOMETRY The vertices of are R(─3, 0), S(0, 5), and T(1, 1). The vertices of ST are R(3, 0), S(0, ─5), and T(─1, ─1). Use the Distance Formula to find the length of each side of the triangles. ...
... A. COORDINATE GEOMETRY The vertices of are R(─3, 0), S(0, 5), and T(1, 1). The vertices of ST are R(3, 0), S(0, ─5), and T(─1, ─1). Use the Distance Formula to find the length of each side of the triangles. ...
Analytic geometry
In classical mathematics, analytic geometry, also known as coordinate geometry, or Cartesian geometry, is the study of geometry using a coordinate system. This contrasts with synthetic geometry.Analytic geometry is widely used in physics and engineering, and is the foundation of most modern fields of geometry, including algebraic, differential, discrete and computational geometry.Usually the Cartesian coordinate system is applied to manipulate equations for planes, straight lines, and squares, often in two and sometimes in three dimensions. Geometrically, one studies the Euclidean plane (two dimensions) and Euclidean space (three dimensions). As taught in school books, analytic geometry can be explained more simply: it is concerned with defining and representing geometrical shapes in a numerical way and extracting numerical information from shapes' numerical definitions and representations. The numerical output, however, might also be a vector or a shape. That the algebra of the real numbers can be employed to yield results about the linear continuum of geometry relies on the Cantor–Dedekind axiom.