Course Outlines
... G.SRT.5 Use congruence and similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and prove relationships in geometric figures. *G.SRT.8 Use trigonometric ratios and the Pythagorean Theorem to solve right triangles in applied problems G.GPE.4 Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraic ...
... G.SRT.5 Use congruence and similarity criteria for triangles to solve problems and prove relationships in geometric figures. *G.SRT.8 Use trigonometric ratios and the Pythagorean Theorem to solve right triangles in applied problems G.GPE.4 Use coordinates to prove simple geometric theorems algebraic ...
Exponent
... a comparison of two numbers using division: can be written as a fraction, with a colon: or a to b ...
... a comparison of two numbers using division: can be written as a fraction, with a colon: or a to b ...
Coordinate Geometry
... Summary of Methods for Coordinate Geometry Proofs To prove that a figure is isosceles or equilateral, use: 1. The distance formula to show equal lengths. To prove that a triangle is a right triangle, use: 1. The distance formula to verify the Pythagorean Theorem; or 2. The slope formula to show that ...
... Summary of Methods for Coordinate Geometry Proofs To prove that a figure is isosceles or equilateral, use: 1. The distance formula to show equal lengths. To prove that a triangle is a right triangle, use: 1. The distance formula to verify the Pythagorean Theorem; or 2. The slope formula to show that ...
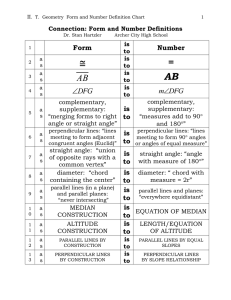
Geometry Form and Number Definition Chart
... Geometry lends itself strongly to study of both number and form. The proof aspect of a geometry course, for example, allows for use of both the number definition of an idea and the form definition of the same idea to justify steps in the same two-column proof. An example follows. Theorem: Vertical a ...
... Geometry lends itself strongly to study of both number and form. The proof aspect of a geometry course, for example, allows for use of both the number definition of an idea and the form definition of the same idea to justify steps in the same two-column proof. An example follows. Theorem: Vertical a ...
Math 8 - Singapore American School
... Understand that a function is a rule that assigns to each input exactly one output. The graph of a function is the set of ordered pairs consisting of an input and the corresponding output. G8.F.2 ...
... Understand that a function is a rule that assigns to each input exactly one output. The graph of a function is the set of ordered pairs consisting of an input and the corresponding output. G8.F.2 ...
Geometry Fall 2016 Topics
... f. Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse [solving quadratic equations by factoring, completing the square, or using the Quadratic Formula (OPTIONAL)] g. Pythagorean Theorem (proof using areas of squares and triangles) (Ch. 8-2) h. Determining whether a triangle is obtuse, right, or acute (Ch. 8-3) i. ...
... f. Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse [solving quadratic equations by factoring, completing the square, or using the Quadratic Formula (OPTIONAL)] g. Pythagorean Theorem (proof using areas of squares and triangles) (Ch. 8-2) h. Determining whether a triangle is obtuse, right, or acute (Ch. 8-3) i. ...
h = Width of the Median class
... called the standard form, is : ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a ≠ 0, a, b, c are real numbers. Roots (or Solutions) of a Quadratic Equation : Those values of x, which satisfy a quadratic equation, are called roots (or solutions) of the equation. Thus, a real number α is called a root of the quadratic equ ...
... called the standard form, is : ax2 + bx + c = 0, where a ≠ 0, a, b, c are real numbers. Roots (or Solutions) of a Quadratic Equation : Those values of x, which satisfy a quadratic equation, are called roots (or solutions) of the equation. Thus, a real number α is called a root of the quadratic equ ...
Analytic geometry
In classical mathematics, analytic geometry, also known as coordinate geometry, or Cartesian geometry, is the study of geometry using a coordinate system. This contrasts with synthetic geometry.Analytic geometry is widely used in physics and engineering, and is the foundation of most modern fields of geometry, including algebraic, differential, discrete and computational geometry.Usually the Cartesian coordinate system is applied to manipulate equations for planes, straight lines, and squares, often in two and sometimes in three dimensions. Geometrically, one studies the Euclidean plane (two dimensions) and Euclidean space (three dimensions). As taught in school books, analytic geometry can be explained more simply: it is concerned with defining and representing geometrical shapes in a numerical way and extracting numerical information from shapes' numerical definitions and representations. The numerical output, however, might also be a vector or a shape. That the algebra of the real numbers can be employed to yield results about the linear continuum of geometry relies on the Cantor–Dedekind axiom.