Unit Map 2012-2013 - The North Slope Borough School District
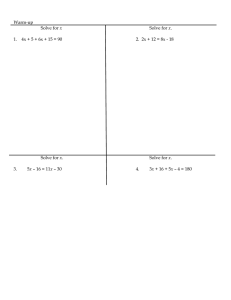
... G - SRT Define trigonometric ratios and solve problems involving right triangles. G-SRT.6. Understand that by similarity, side ratios in right triangles are properties of the angles in the triangle, leading to definitions of trigonometric ratios for acute angles. G-SRT.7. Explain and use the relatio ...
... G - SRT Define trigonometric ratios and solve problems involving right triangles. G-SRT.6. Understand that by similarity, side ratios in right triangles are properties of the angles in the triangle, leading to definitions of trigonometric ratios for acute angles. G-SRT.7. Explain and use the relatio ...
Chapter 7: Hyperbolic Geometry
... 2. A finite straight line may be produced to any length. 3. A circle may be described with any center and any radius. 4. All right angles are equal. 5. If a straight line meet two other straight lines so that as to make the interior angles on one side less than two right angles, the other straight l ...
... 2. A finite straight line may be produced to any length. 3. A circle may be described with any center and any radius. 4. All right angles are equal. 5. If a straight line meet two other straight lines so that as to make the interior angles on one side less than two right angles, the other straight l ...
Exponent
... a comparison of two numbers using division: can be written as a fraction, with a colon: or a to b ...
... a comparison of two numbers using division: can be written as a fraction, with a colon: or a to b ...
Analytic geometry
In classical mathematics, analytic geometry, also known as coordinate geometry, or Cartesian geometry, is the study of geometry using a coordinate system. This contrasts with synthetic geometry.Analytic geometry is widely used in physics and engineering, and is the foundation of most modern fields of geometry, including algebraic, differential, discrete and computational geometry.Usually the Cartesian coordinate system is applied to manipulate equations for planes, straight lines, and squares, often in two and sometimes in three dimensions. Geometrically, one studies the Euclidean plane (two dimensions) and Euclidean space (three dimensions). As taught in school books, analytic geometry can be explained more simply: it is concerned with defining and representing geometrical shapes in a numerical way and extracting numerical information from shapes' numerical definitions and representations. The numerical output, however, might also be a vector or a shape. That the algebra of the real numbers can be employed to yield results about the linear continuum of geometry relies on the Cantor–Dedekind axiom.