Electricity & Chemistry
... negative side of a battery to the positive side. This potential energy is in the form of electrons ...
... negative side of a battery to the positive side. This potential energy is in the form of electrons ...
CHAPTER 39 NEURONS AND NERVOUS SYSTEMS
... 4. A. L. Hodgkin and A. F. Huxley later confirmed this theory. a. They and other researchers inserted a tiny electrode into the giant axon of a squid. b. The electrode was attached to a voltmeter and an oscilloscope to trace a change in voltage over time. c. The voltage measured the difference in th ...
... 4. A. L. Hodgkin and A. F. Huxley later confirmed this theory. a. They and other researchers inserted a tiny electrode into the giant axon of a squid. b. The electrode was attached to a voltmeter and an oscilloscope to trace a change in voltage over time. c. The voltage measured the difference in th ...
Axons, but not cell bodies, are activated by electrical stimulation in
... Extracellular recordings of single units were obtained with tungsten-in-glass microelectrodes (Merrill and Ainsworth 1972) with 15to 25- m exposed tips and plated with platinum black (impedance less than 0.5 MW at 1000 Hz). The Neurolog recording system was used for amplification and filtering. Filt ...
... Extracellular recordings of single units were obtained with tungsten-in-glass microelectrodes (Merrill and Ainsworth 1972) with 15to 25- m exposed tips and plated with platinum black (impedance less than 0.5 MW at 1000 Hz). The Neurolog recording system was used for amplification and filtering. Filt ...
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
... toward”) consists of nerve fibers (axons) that convey impulses to the central nervous system from sensory receptors located throughout the body (see the blue fibers in Figure 11.2). Sensory fibers conveying impulses from the skin, skeletal muscles, and joints are called somatic afferent fibers (soma ...
... toward”) consists of nerve fibers (axons) that convey impulses to the central nervous system from sensory receptors located throughout the body (see the blue fibers in Figure 11.2). Sensory fibers conveying impulses from the skin, skeletal muscles, and joints are called somatic afferent fibers (soma ...
Nervous System - Intermediate School Biology
... It does not stop once it has started Impulse arrives at synaptic knobs Neurotransmitter vesicles are activated by ions and release neurotransmitter chemicals These neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft for a very short time. They transmit the impulse to the next neurone. After trans ...
... It does not stop once it has started Impulse arrives at synaptic knobs Neurotransmitter vesicles are activated by ions and release neurotransmitter chemicals These neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic cleft for a very short time. They transmit the impulse to the next neurone. After trans ...
Ch48(2) - ISpatula
... 26) Neural transmission across a mammalian synaptic gap is accomplished by A) the movement of sodium and potassium ions from the presynaptic into the postsynaptic neuron. B) impulses traveling as electrical currents across the gap. C) impulses causing the release of a chemical signal and its diffus ...
... 26) Neural transmission across a mammalian synaptic gap is accomplished by A) the movement of sodium and potassium ions from the presynaptic into the postsynaptic neuron. B) impulses traveling as electrical currents across the gap. C) impulses causing the release of a chemical signal and its diffus ...
Brainsignals, Synaptic Transmission and Short
... which is connected with thousands of other cells by synapses ...
... which is connected with thousands of other cells by synapses ...
Characterization of the Bed Nucleus of the Stria Terminalis
... The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) is part of the extended amygdala which receives heavy projections from the basolateral amygdala and other areas, and projects to hypothalamic and brainstem target areas that mediate autonomic and behavioral responses to aversive or threatening stimuli. ...
... The bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST) is part of the extended amygdala which receives heavy projections from the basolateral amygdala and other areas, and projects to hypothalamic and brainstem target areas that mediate autonomic and behavioral responses to aversive or threatening stimuli. ...
File: Chap011, Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
... The resting membrane potential is proportional to the tendency for K+ to diffuse out of the cell. D) Negatively charged Cl- ions are attracted by negative charges in the cell. E) The purpose of the sodium-potassium exchange pump is to create the resting membrane potential. Answer: c Level: 2 ...
... The resting membrane potential is proportional to the tendency for K+ to diffuse out of the cell. D) Negatively charged Cl- ions are attracted by negative charges in the cell. E) The purpose of the sodium-potassium exchange pump is to create the resting membrane potential. Answer: c Level: 2 ...
Chapter 11: Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue
... The resting membrane potential is proportional to the tendency for K+ to diffuse out of the cell. D) Negatively charged Cl- ions are attracted by negative charges in the cell. E) The purpose of the sodium-potassium exchange pump is to create the resting membrane potential. Answer: c Level: 2 ...
... The resting membrane potential is proportional to the tendency for K+ to diffuse out of the cell. D) Negatively charged Cl- ions are attracted by negative charges in the cell. E) The purpose of the sodium-potassium exchange pump is to create the resting membrane potential. Answer: c Level: 2 ...
Lecture-29-2012-Bi
... 1. Reconstituted, cell-free systems for ER exit and retrieval 2. Better real-time markers for compartmentalized receptors and transporters a. Imaging mass spectrometry b. Plasma membrane binding only? Possible with impermeant derivatives c. ER binding only? More challenging, especially for antagonis ...
... 1. Reconstituted, cell-free systems for ER exit and retrieval 2. Better real-time markers for compartmentalized receptors and transporters a. Imaging mass spectrometry b. Plasma membrane binding only? Possible with impermeant derivatives c. ER binding only? More challenging, especially for antagonis ...
Nerve Cells and Nervous Systems - ReadingSample - Beck-Shop
... the location of transmitter receptors. Direct injection of a dye into a neuron by means of very fine pipettes (or microelectrodes – see Box 1.2) has allowed the visualisation of neurons from which electrical recordings have b een made. The development of confocal microscopy together with fluorescent ...
... the location of transmitter receptors. Direct injection of a dye into a neuron by means of very fine pipettes (or microelectrodes – see Box 1.2) has allowed the visualisation of neurons from which electrical recordings have b een made. The development of confocal microscopy together with fluorescent ...
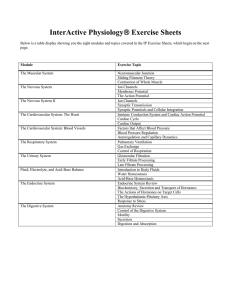
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... a. If the membrane reaches the trigger point, known as __________________, what electrical potential will be generated? __________________________________________ b. During the depolarization phase, voltage-gated __________ channels open and _______ enters the cell. ...
... a. If the membrane reaches the trigger point, known as __________________, what electrical potential will be generated? __________________________________________ b. During the depolarization phase, voltage-gated __________ channels open and _______ enters the cell. ...
Neuro Review for Quiz 1 (lectures organized according
... neurohormones travel further than neurotransmitters. Amine transmitters (Ach, adrenaline, noradrenaline, dopamine, serotonin) come from precursors in diet but active form must be produced in neuron (?) Serotonin – low levels associated with depression (?) Glial cells convert Glutamate to Lac ...
... neurohormones travel further than neurotransmitters. Amine transmitters (Ach, adrenaline, noradrenaline, dopamine, serotonin) come from precursors in diet but active form must be produced in neuron (?) Serotonin – low levels associated with depression (?) Glial cells convert Glutamate to Lac ...
BOX 31.2 DIFFERENCES BETWEEN THE VESTIBULAR AND
... flocculonodular lobe. These excitatory neurons receive mossy fiber input, like granule cells, but synapse locally onto granule cells. Golgi cells feed back to unipolar brush cells with mixed glycinergic and GABAergic synapses, in contrast to the purely GABAergic feedback to granule cells (Dugue, Dum ...
... flocculonodular lobe. These excitatory neurons receive mossy fiber input, like granule cells, but synapse locally onto granule cells. Golgi cells feed back to unipolar brush cells with mixed glycinergic and GABAergic synapses, in contrast to the purely GABAergic feedback to granule cells (Dugue, Dum ...
Chapter 12 *Lecture PowerPoint Nervous Tissue
... • About 1 trillion (1012) neurons in the nervous system • Neuroglia outnumber the neurons by as much as 50 to 1 • Neuroglia or glial cells – Support and protect the neurons – Bind neurons together and form framework for nervous tissue – In fetus, guide migrating neurons to their destination – If mat ...
... • About 1 trillion (1012) neurons in the nervous system • Neuroglia outnumber the neurons by as much as 50 to 1 • Neuroglia or glial cells – Support and protect the neurons – Bind neurons together and form framework for nervous tissue – In fetus, guide migrating neurons to their destination – If mat ...
CHAPTER 46 NEURONS AND NERVOUS SYSTEM
... 4. The 1963 Nobel Prize went to the British researchers A. L. Hodgkin and A. F. Huxley who confirmed this theory. a. They and other researchers inserted a tiny electrode into giant axon of a squid. b. The electrode was attached to a voltmeter and oscilloscope to trace a change in voltage over time. ...
... 4. The 1963 Nobel Prize went to the British researchers A. L. Hodgkin and A. F. Huxley who confirmed this theory. a. They and other researchers inserted a tiny electrode into giant axon of a squid. b. The electrode was attached to a voltmeter and oscilloscope to trace a change in voltage over time. ...
Nervous System Basics: Neurons
... b. This change in charge is called depolarization. c. As depolarization occurs, the Na+/K+ pump works to return the axon to its resting state 1) This is called repolarization 2) See website ...
... b. This change in charge is called depolarization. c. As depolarization occurs, the Na+/K+ pump works to return the axon to its resting state 1) This is called repolarization 2) See website ...
Neurobiology
... • The lipid-rich, water-poor, nature of compact myelin gives the latter good electrical insulating properties. • Action potentials are transmitted much faster along the axons (by saltatory conduction) due to the ion channel clustering and the insulating properties of the myelin sheath. ...
... • The lipid-rich, water-poor, nature of compact myelin gives the latter good electrical insulating properties. • Action potentials are transmitted much faster along the axons (by saltatory conduction) due to the ion channel clustering and the insulating properties of the myelin sheath. ...
Lecture 3 NS_2015
... The transmitter molecules once released bind and influence the membrane potential of the postsynaptic membrane, determining excitation or inhibition The postsynaptic membrane has receptor proteins with 2 components: • A binding component/sites for ligands/neurotransmitters • An ionophore component t ...
... The transmitter molecules once released bind and influence the membrane potential of the postsynaptic membrane, determining excitation or inhibition The postsynaptic membrane has receptor proteins with 2 components: • A binding component/sites for ligands/neurotransmitters • An ionophore component t ...
EPH-ective control of cytokinesis
... Incomplete cytokinesis also occurs in animals, giving rise to polyploid cells (hepatocytes) or syncitia (germ cells). Until recently cytokinesis was viewed as a mechanism orchestrated only by cell intrinsic factors,2 yet in Salpingoeca Rosetta the switch from unicellular to multicellular state can b ...
... Incomplete cytokinesis also occurs in animals, giving rise to polyploid cells (hepatocytes) or syncitia (germ cells). Until recently cytokinesis was viewed as a mechanism orchestrated only by cell intrinsic factors,2 yet in Salpingoeca Rosetta the switch from unicellular to multicellular state can b ...
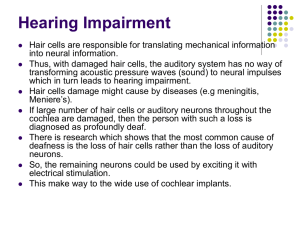
Cochlear Implant 1
... Thus, with damaged hair cells, the auditory system has no way of transforming acoustic pressure waves (sound) to neural impulses which in turn leads to hearing impairment. Hair cells damage might cause by diseases (e.g meningitis, Meniere’s). If large number of hair cells or auditory neurons through ...
... Thus, with damaged hair cells, the auditory system has no way of transforming acoustic pressure waves (sound) to neural impulses which in turn leads to hearing impairment. Hair cells damage might cause by diseases (e.g meningitis, Meniere’s). If large number of hair cells or auditory neurons through ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.